Question: Create an adjacency list to represent the following graph in Java. Note: Find a file called Graph.java in assignment 6 folder. Complete the getAdjlist (
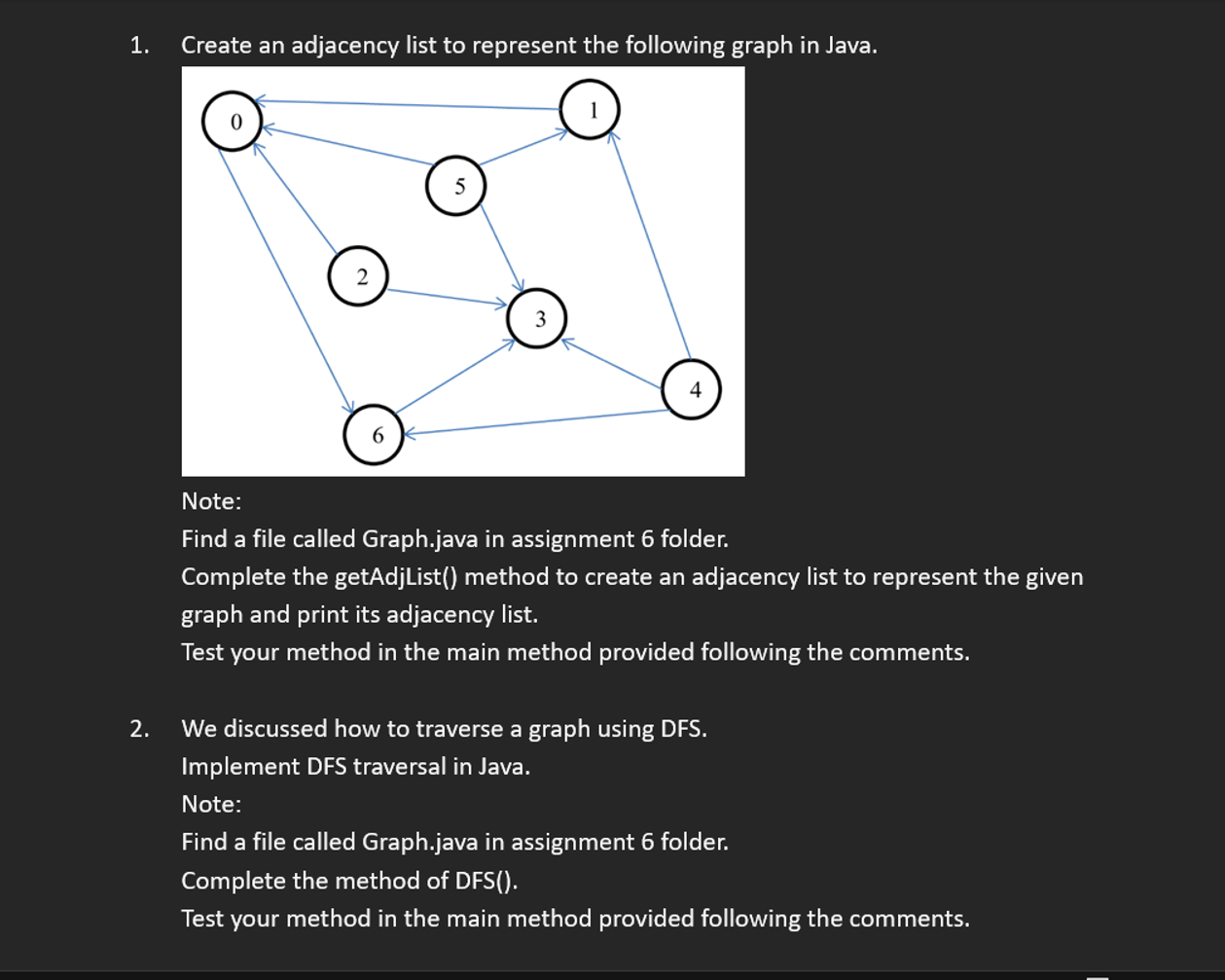
Create an adjacency list to represent the following graph in Java.
Note:
Find a file called Graph.java in assignment folder.
Complete the getAdjlist method to create an adjacency list to represent the given
graph and print its adjacency list.
Test your method in the main method provided following the comments.
We discussed how to traverse a graph using DFS
Implement DFS traversal in Java.
Note:
Find a file called Graph.java in assignment folder.
Complete the method of DFS
Test your method in the main method provided following the comments.import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.Stack;
public class Graph
private int edges; adjacency matrix
private LinkedList adjlist; adjacency list
private Object labels; vertex label, ie vertex its label A vertex its label B
public Graphint n
n: size of nodes
weighted graph
edges new intnn;
edgesij saves the weight of edge ij assume weight
for unweighted graph
set edgesij to if there exists an edge ij
set edgesij to otherwise
adjlist new LinkedListn;
adjlist saves the adjacency list of the graph
adjlisti saves a list of neighboring vertices of vertex i
labels new Objectn;
public void setLabelint vertex, Object label
vertex: vertex index, label: vertex name
labelsvertex label;
public Object getLabelint vertex
return labelsvertex;
public int size
return edges.length;
public void addEdgeint source, int target, int w
add an edge from vertex source to vertex target with w as weight
In an unweighted graph, w if there exists an edge from source to target
edgessourcetarget w;
edgestargetsource w;
In an undirected graph, set the symmetry element in the matrix with the same
weight
public boolean isEdgeint source, int target
if edgesij there exists an edge from vertex i to vertex j
return edgessourcetarget;
public void removeEdgeint source, int target
edgessourcetarget;
edgestargetsource;
In an undirected graph, set the symmetry element in the matrix to
public int getWeightint source, int target
return edgessourcetarget;
public int neighborsint vertex
find neighbors of a given vertex
int count ;
for int i ; i edgesvertexlength; i
if edgesvertexi
count;
final int answer new intcount;
count ;
for int i ; i edgesvertexlength; i
if edgesvertexi
answercount i;
return answer;
public int getUnvisitedNeighborint vertex, boolean visited
find an unvisited neighbor of a given vertex
if there exist multiple unvisited neighbors, return the first one found
if all neighbors are visited, return
for int i ; i edgesvertexlength; i
if edgesvertexi && visitedi false
return i;
return ;
public void getAdjList
Complete the method to create an adjacency list for the graph
Feel free to change the return type
public void print
Print adjacency list
int n edges.length;
for int i ; i n; i
System.out.printlnVertex i : adjlistitoString;
public void dfs DFS
Complete this method to traverse a graph using DFS
Start DFS from a randomly selected node in the graph
Print nodes in order as visited by DFS
Note: Follow the pseudocode of DFS in slides.
public static void mainString args
An example to create a graph using the Graph class
You should create a new graph to represent the one given in Assignment
Then test the function dfs and getAdjList on the graph you create
final Graph t new Graph;
tsetLabelA;
tsetLabelB;
tsetLabelC;
tsetLabelD;
tsetLabelE;
tsetLabelF;
taddEdge;
taddEdge;
taddEdge;
taddEdge;
taddEdge;
taddEdge;
taddEdge;
taddEdge;
taddEdge;
Test adjacency list
tgetAdjList;
tprint;
Test DFS
tdfs;
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


