Question: Using the Graph.java methods, and assuming the variable called graph has been assigned an instance of a Graph, write statements to add EDGES/vertices which represent
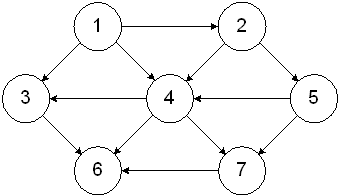
Using the Graph.java methods, and assuming the variable called graph has been assigned an instance of a Graph, write statements to add EDGES/vertices which represent the following graph (use 0 for the weight when adding). See GraphTester.java in the Graph Code Files folder in Catalyst for examples.
Graph.java:
import java.util.*; import java.util.Map.Entry; interface Visitor
// --- assumes definition of simple class Pair
// --- Vertex class ------------------------------------------------------ class Vertex
public Vertex( E x ) { data = x; dist = INFINITY; nextInPath = null; } public Vertex() { this(null); }
public void addToAdjList(Vertex
return (data.equals(other.data));
} public int hashCode() { return (data.hashCode()); }
public void showAdjList() { Iterator
System.out.print( "Adj List for " + data + ": "); iter = adjList.entrySet().iterator(); while( iter.hasNext() ) { entry = iter.next(); pair = entry.getValue(); System.out.print( pair.first.data + "(" + String.format("%3.1f", pair.second) + ") " ); } System.out.println(); }
}
public class Graph
// public graph methods -------------------------------- public Graph () { vertexSet = new HashMap
for (k = 0; k src, dst;
// put both source and dest into vertex list(s) if not already there src = addToVertexSet(source); dst = addToVertexSet(dest);
// add dest to source's adjacency list src.addToAdjList(dst, cost); //dst.addToAdjList(src, cost); // ADD THIS IF UNDIRECTED GRAPH } public void addEdge(E source, E dest, int cost) { addEdge(source, dest, (double)cost); } // adds vertex with x in it, and always returns ref to it public Vertex
// find if Vertex already in the list: foundVertex = vertexSet.get(x); if ( foundVertex != null ) // found it, so return it { return foundVertex; }
// the vertex not there, so create one retVal = new Vertex
return retVal; // should never happen } public boolean remove(E start, E end) { Vertex
return removedOK; } public void showAdjTable() { Iterator
System.out.println( "------------------------ "); iter = vertexSet.entrySet().iterator(); while( iter.hasNext() ) { (iter.next().getValue()).showAdjList(); } System.out.println(); }
public void clear() { vertexSet.clear(); } /** Breadth-first traversal from the parameter startElement*/ public void breadthFirstTraversal(E startElement, Visitor
/** Postorder traversal from the parameter startElement */ public void depthFirstTraversal(E startElement, Visitor
}
GraphTester.java:
import java.util.*; import java.text.*;
//------------------------------------------------------ public class GraphTester { // ------- main -------------- public static void main(String[] args) { // build graph Graph
myGraph1.showAdjTable();
}
}
5 2 7 6 3
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


