Question: Create the arrays and assign randomized values for each element in the array. The randomized values should range from 1 to twice the size of
- Create the arrays and assign randomized values for each element in the array.
- The randomized values should range from 1 to twice the size of the array. For example, for an array of 200, assign random values between 1 and 400.
- Use a constant for the size of the array. Edit the value of the constant in different runs of the program to account for the various array sizes.
- Print your array to the screen to display your work. .
- Perform a step count test for linear search. You will be finding the total and an average number of steps after looping through your array 1000 times.
- Get a random number between 1 to twice the size of the array (eg... for an array of size 400, your values should be between 1 and 800)
- Search for the number in your array (it may or may not exist in your array).
- Count the number of steps it takes to find your target value, or confirm it is not in your array.
- If your target number is found, print out the number and the index where it was found
- Example: 1125 is the target number. If found in the array at index 412 then print "Target 1125 was found at index 412"
- If not found, print " Target 1125 was not found"
- Once you have confirmed your code is finding the target value correctly, you may comment out this code to speed things up
- I should be able to uncomment your code and confirm that it works.
- Example: 1125 is the target number. If found in the array at index 412 then print "Target 1125 was found at index 412"
- After each search, get a new random number to use for the next search.
- Do this 1000 times (you will loop through the array 1000 times using a different random target number each time.
- Display both the total step count of the 1000 linear searches and the average step count for linear search.
- Add up the steps to find the target for each iteration and sum these up for all 1000 runs to get TotalStepCount for that array size.
- Divide the total step count by 1000 to get the average
- For each array size, print to screen the total number of steps over 1000 iterations and the average number of steps
- Once complete, increase your array size to the next increment (eg.. if the array size is 600, increase to 800 and do all steps for that size array)
- You will do this for each array size. Search 1000 times in an array of size 200, then search 1000 times in an array of 400, etc...
- Get a random number between 1 to twice the size of the array (eg... for an array of size 400, your values should be between 1 and 800)
- Do the same thing using a binary search instead of a linear search
- The binary search requires a sorted list, so sort the list. You can use any sort you choose. We will discuss several (bubble, selection, insertion) and sample code is provided for a sort in the project directory on Canvas. On Canvas, look under Files - Class Resources for various coding examples.
- Similarly, as you did for linear search, perform and display the step count totals and the average for binary search after 1000 searches for each array size tested.
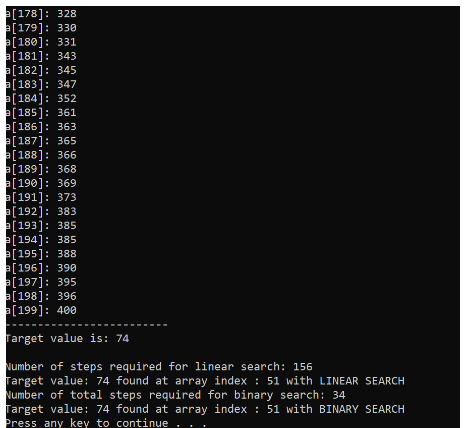
[178]: 328 [179]: 338 [180]: 331 [181]: 343 [182]: 345 [183]: 347 [184]: 352 [185]: 361 [186]: 363 [187]: 365 [188]: 366 [189]: 368 [190]: 369 [191]: 373 [192]: 383 [193]: 385 [194]: 385 [195]: 388 [196]: 390 [197]: 395 [198]: 396 [199]: 400 Target value is: 74 Number of steps required for linear search: 156 Target value: 74 found at array index : 51 with LINEAR SEARCH Number of total steps required for binary search: 34 Target value: 74 found at array index : 51 with BINARY SEARCH Press any key to continue
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


