Question: Create two classes with Java to satisfy each requirement. 11 11 Song -title: String -artist: String -time: int[] -INFO DELIMITER: String = -TIME DELIMITER: String
Create two classes with Java to satisfy each requirement.
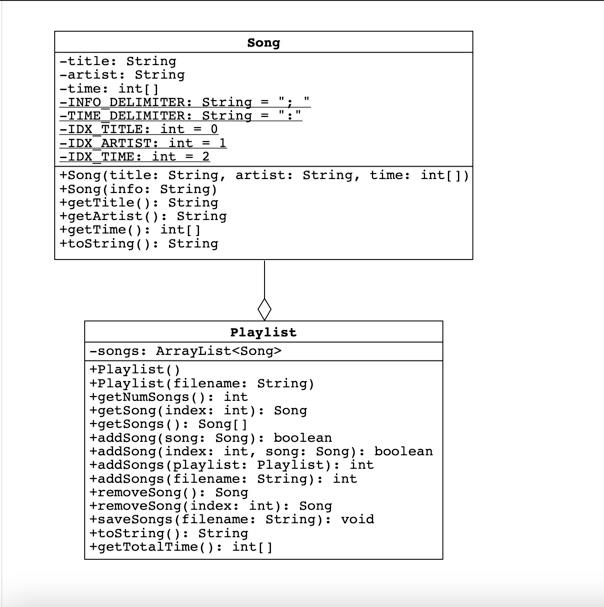
![-title: String -artist: String -time: int[] -INFO DELIMITER: String = -TIME DELIMITER:](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2024/09/66f53215780d9_17366f53215144dd.jpg)

11 11 Song -title: String -artist: String -time: int[] -INFO DELIMITER: String = -TIME DELIMITER: String -IDX TITLE: int = 0 -IDX ARTIST: int = 1 -IDX TIME: int = 2 +Song(title: String, artist: String, time: int[) +Song(info: String) +getTitle(): String +getArtist(): String +getTime(): int[] +toString(): String Playlist -songs: ArrayList +Playlist +Playlist (filename: String) +get NumSongs(): int +get Song(index: int): Song +get Songs(): Song[] +addSong (song: Song): boolean +addSong(index: int, song: Song): boolean +addSongs (playlist: Playlist): int +addSongs (filename: String): int +remove Song(): Song +remove Song Index: int): Song +save Songs (filename: String): void +toString(): String +get TotalTime(): int[] Song Class Song has been expanded with a second constructor and a toString method. The constructor initializes Song objects by parsing information stored in Strings. The toString method returns String representations of Songs in the format parsed by the constructor. Song (String info) : Initialize a Song by parsing a String that contains the title, artist, and time with a semicolon and a space used as the delimiter. For example, the info String for the song "Where the Streets Have No Name" by U2 is "Where the Streets Have No Name; u2; 5:36" The time is given as a number of hours, minutes, and seconds separated by colons. The minutes and seconds are numbers between 0 and 59. If the song is less than an hour, only the minutes and seconds are given. Similarly, if the song is less than a minute, only the seconds are given. .toString(): Return a String representation of the song in the same format as the info Strings parsed by the new constructor. For example, suppose a Song is instantiated with the following code: Song song = new Song("Where the Streets Have No Name", "U2", new int[] { Calling song.toString() returns the info String shown above. If the song is longer than a minute, pad the number of seconds with a leading O if it is less than 10. Similarly, if the song is longer than an hour, ensure that the number of minutes also has two digits. Song Hints Break an info String into pieces using the String class split method. Remove magic numbers from your code by replacing them with the static constants shown in the UML diagram. For instance, pass INFO_DELIMITER to the split method, rather than "; ". This will make your code more readable, A String of digits can be converted to an int with the Integer class parseint method. The easiest way to pad an int with zeros is to use the String class format method. Pass the method the format String "902d", which indicates that the int should be formatted as a String of at least two digits. Playlist Class Playlist has been refactored to use an ArrayList, which allows it to encapsulate an arbitrary number of Songs. The starter code includes updated versions of most of the methods from Lab 3, but you need to update the methods described below. Playlist(): Initialize an empty Playlist addSong(int index, Song song) : Add the given Song to the Playlist at the given index. If the Song reference is null or the index is out of bounds (less than 0 or greater than the index of the last Song plus 1), leave the Playlist unchanged. If the song is added, return true; otherwise, return false. .addSongs (Playlist playlist) : Add the given Songs to the end of the Playlist in the given order. Return the number of added Songs. If the Playlist reference is null return O. removeSong(int index): Remove and return the song with the given index. If the index is out of bounds (less than 0 or greater than the index of the last Song), return null. Playlist has been expanded with methods that read and write song information to text files. A method has also been added that returns the total time Playlist(String filename) : Initialize a Playlist by parsing a text file of info Strings with the given name. The resulting Playlist contains a Song for each line of the file, and the Song order matches the order of the info Strings. .addSongs(String filename): Read a file of info Strings with the given name. For each line of the file, create a Song and add it to the end of the Playlist. .toString(): Return the String representations of the Songs joined by line separators. For example, suppose a Playlist contains the songs "Resistance" and "Madness" by Muse. Calling toString returns "Resistance; Muse; 5:46" + System.Line Separator() + "Madness; Muse; 4:39 The line Separator method returns the correct newline character sequence for your operating system (" " for Windows and " " for macos and Linux). saveSongs (String filename) : Save the output of toString to a file with the given name. Overwrite the contents of the file if it already exists. getTotalTime(): Return the total time of all the Songs as an array of integers. Use the same format as the time field in the Song class. Playlist Hints The new constructor can be implemented in just two lines. First, use this to call the other constructor. Next, call addSongs to read the file. Implement addSongs by reading each line of the file and passing it to the new Song constructor Use a String Joiner to implement toString, Implement getTotalTime in two steps: 1. Calculate the total number of seconds, minutes, and hours. Hi. Use integer division and modular arithmetic to convert the excess seconds to minutes and the excess minutes to hours Reading and Writing Files In your first programming course, you may have used the Scanner and PrintWriter classes to read and write files. You're welcome to use those classes here, but it's worth learning to use Buffered Reader and Buffered Writer as well. Objects of these classes can be created with the following statements: BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(filename)); BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(filename)); Call readLine on a BufferedReader to read the next line of a text file. The method returns null after it reads the last line. Call write on a Buffered Writer to write a given String to a text file. After you are done reading or writing, call close. Any method that uses a BufferedReader or Buffered Writer must be able to throw an input- output exception. To do this, import java.io.IOException and add "throws IOException" after the method's parameter list. (For an example, see the helper method checkFile at the end of the Playlist Test class. We'll learn much more about exceptions later in the semester

![-title: String -artist: String -time: int[] -INFO DELIMITER: String = -TIME DELIMITER:](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2024/09/66f53215780d9_17366f53215144dd.jpg)





