Question: Critically analyze and answer. Banking during the Great Recession. During the Great Recession of 2008-2009, US commercial banks grew nervous about the economic outlook, in




Critically analyze and answer.
Banking during the Great Recession. During the Great Recession of 2008-2009, US commercial banks grew nervous about the economic outlook, in particular borrowers' ability to repay loans. As a consequence, commercial banks increased the ratio of reserves to deposits (i.e. they lent out a smaller fraction of their deposits).
a. within the AS/AD model, what are the short-run effects on inflation, real GDP and unemployment of this change in banks' behavior? Please illustrate using graphs, assuming that the economy starts at the long-run equilibrium.
b. Suppose, to start with, that policy makers do not respond to this change in commercial banks' behavior and that the classical dichotomy holds. What would be the long run effect on the price level and output? Please make sure to carefully explain how and why this happens.
c. Next, suppose that you sit on the Board of Governors of the Fed. Given the mandate of the Fed, what would you do in response to the change in commercial banks' behavior? Please carefully describe how your preferred policy would be implemented, including its (potential) ef- fect on money supply, the Fed's balance sheet and the interest rate. Please also illustrate its impact on the economy in the AS/AD framework....



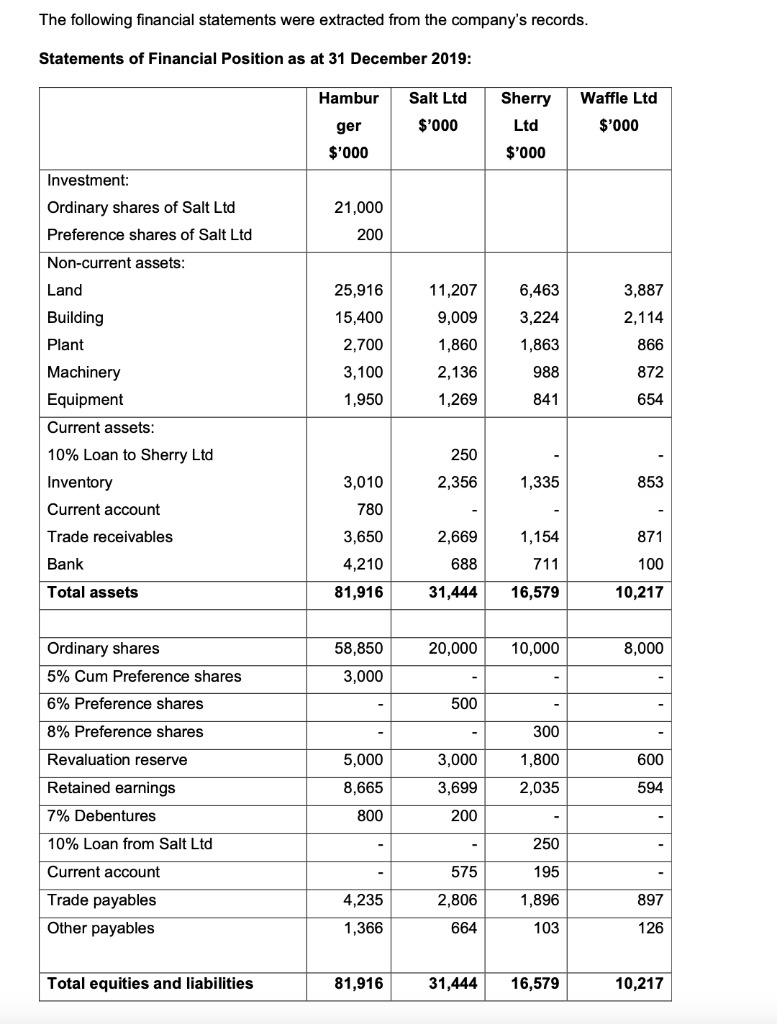
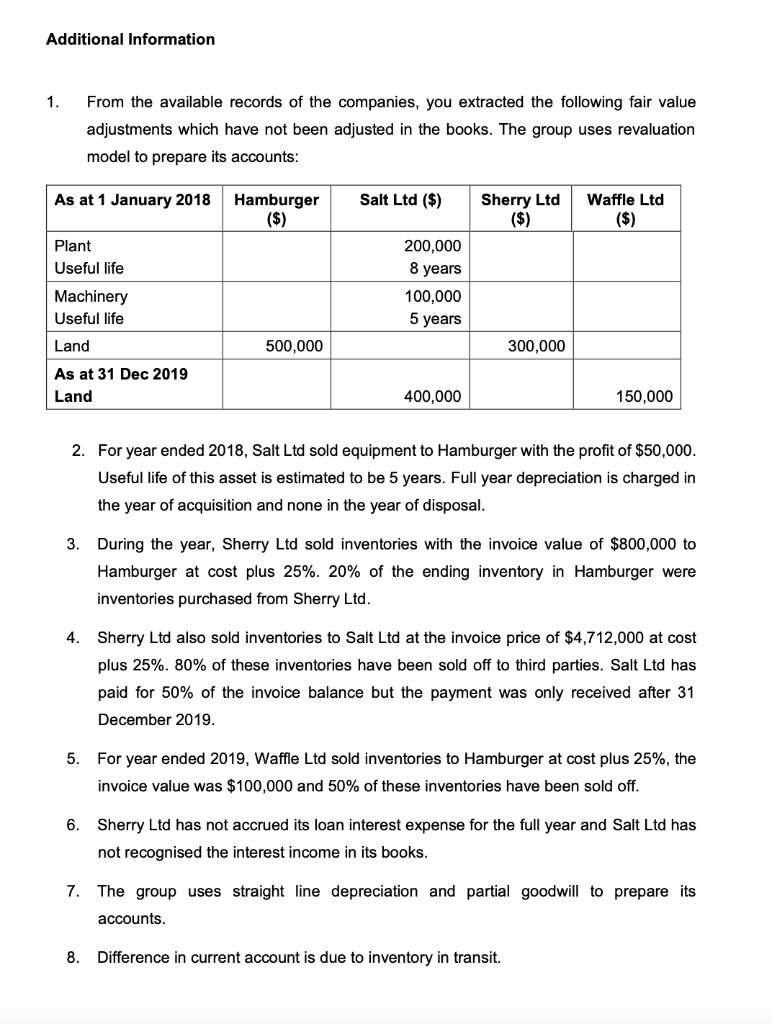

You are given the following information about the term structure of interest rates: The 1-year spot rate is 4.1% pa. The 2-year spot rate is 4.0% pa. The 4-year spot rate is 4.4% pa. The 5-year spot rate is 4.5% pa. (i) Calculate the theoretical price of a 3-year zero-coupon bond that is issued at time 2 and is redeemable at par. [2] (ii) A 1-year zero-coupon bond is issued at time 3 and has a theoretical price of f95.50 per f100 nominal. Given that the bond is redeemable at par, calculate: (a) the 3-year spot rate, and (b) the 1-year forward rate starting at time 2. [3] (iii) Calculate the gross redemption yield on a bond that pays annual coupons of 6% pa (at times 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5) and is redeemable at 1 10% in 5 years' time. [4] [Total 9]2. Suppose that Romeo bumps into Juliet at Toscanini's and after talking about life over ice cream, they decide to enter into a trading agreement. Draw an Edgeworth box and show clearly all feasible allocations of chocolates and roses for Romeo and Juliet. Draw Romeo and Juliet's indifference curves within the box you can assume a = 3 = : for this part if you would like, but the indifference curves need not be completely accurate] and mark the endowment allocation. Shade in the allocations which would be Pareto improvements over the endowment allocation. [5 points]Question Hamburger Ltd. acquired 70% of the ordinary shares of Salt Ltd on 1 January 2013 with consideration transferred of $21 million. On the same date. Hamburger also acquired 40% of the preference shares issued by Salt Ltd by cash consideration of $200,000. Upon checking the previous year's statements. the retained earnings of Salt Ltd as at 1 January 2013 was $034,000. There were no issuance of new shares since acquisition date. Salt Ltd's partial goodwill has boon impaired by $462,000 for the year 2019. There was no Impai$ent recorded in the previous year. On 1 January 2019. Hamburger acquired 80% of the ordinary shares of Sherry Ltd with the following consideration: Cash payment on 1 January 2019 $2 million Horus ordinary shares valued at $5 million Additional cash payment payable on 1 January 2020 $3.3 million (Cost of capital is given as 10% per annum.) Hamburger also acquired 50% of the preference shares issued by Sherry Ltd on 1 January 2019 with cash consideration of $150.000. 0n 1 April 2019. Hamburger acquired 20% of Waffle Ltd ordinary shares with cash payment of $1 .5 million. There were no issuance of new shares for all the companies since 1 January 2018. The following financial statements were extracted from the company's records. Statements of Financial Position as at 31 December 2019: Hambur Salt Ltd Sherry Waffle Ltd ger $'000 Ltd $'000 $'000 $'000 Investment: Ordinary shares of Salt Ltd 21,000 Preference shares of Salt Ltd 200 Non-current assets: Land 25,916 11,207 6,463 3,887 Building 15,400 9,009 3,224 2,114 Plant 2,700 1,860 1,863 366 Machinery 3,100 2,136 988 872 Equipment 1,950 1,269 841 654 Current assets: 10% Loan to Sherry Ltd 250 Inventory 3,010 2,356 1,335 853 Current account 780 Trade receivables 3,650 2,669 1,154 871 Bank 4,210 688 711 100 Total assets 81,916 31,444 16,579 10,217 Ordinary shares 58,850 20,000 10,000 8,000 5% Cum Preference shares 3,000 6% Preference shares 500 8% Preference shares 300 Revaluation reserve 5,000 3,000 1,800 600 Retained earnings 8,665 3,699 2,035 594 7% Debentures 800 200 10% Loan from Salt Ltd 250 Current account 575 195 Trade payables 4,235 2,806 1,896 897 Other payables 1,366 564 103 126 Total equities and liabilities 81,916 31,444 16,579 10,217Additional lnfonnation 1. From the available records of the companies. you extracted the following fair value adjustments which have not been adjusted in the books. The group uses revaluation model to prepare its accounts: (5] {Si {$1 Fiant 200.000 Useful life 0 years Machinery 100.000 Useful life 5 years 5mm he at 31 Dec 2019 Land 400.000 150.000 2. For year ended 2010. Salt Ltd sold equipment to Hamburger with the prot of $50,000. Useful life of this asset is estimated to be 5 years. Full year depreciation is charged in the year of acquisition and none in the year of disposal. 3. During the year. Sherry Ltd sold inventories with the invoice value of 5800.000 to Hamburger at cost plus 25%. 20% of the ending inventory in Hamburger were inventories purchased from Sherry Ltd. 4. Sherry Ltd also sold Inventories to Salt Ltd at the Invoice price of $4.?12.000 at cost plus 25%. 00% of these inventories have been sold off to third parties. Salt Ltd has paid for 50% of the invoice balance but the payment was only received after 31 December 2010. S. For year ended 2010. Wafe Ltd sold Inventories to Hamburger at cost plus 25%. the invoice value was $100.000 and 50% of these inventories have been sold off. 6. Sherry Ltd has not seemed its loan interest expense for the full year and Satt Ltd has not recognised the interest income in its books. i". The group uses straight line depreciation and partial goodwill to prepare its accounts. El. Difference in current account is due to inventory in transit. 9. All depreciation expenses and goodwill impairment are to be adjusted in administration expenses. Required: (a) Determine the GOODWILL of all the investments
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


