Question: CS 2521 - LAB 03 FUNCTIONS AND PROCEDURES LAB GOALS: Learn about implementing functions and procedures, using address referencing, in MIPS We've learned how to


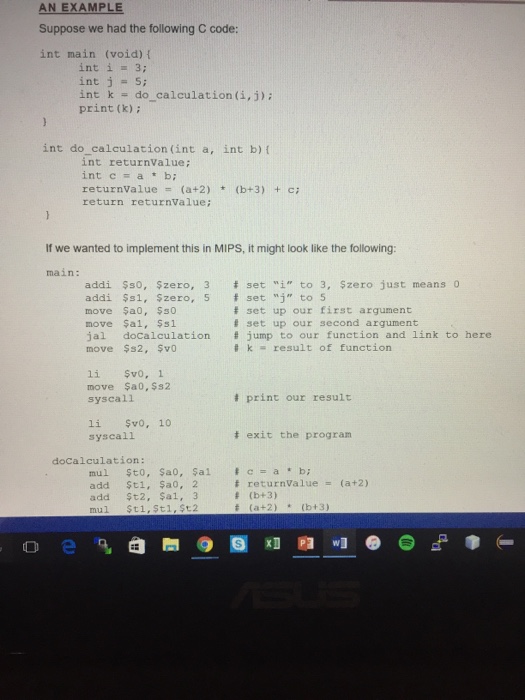
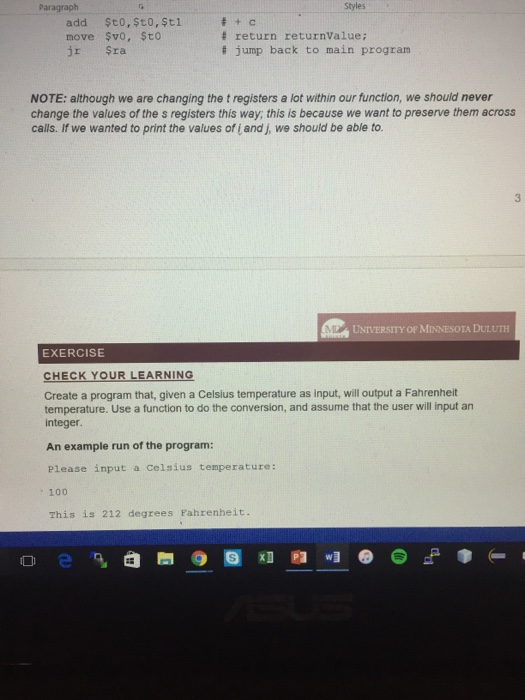
CS 2521 - LAB 03 FUNCTIONS AND PROCEDURES LAB GOALS: Learn about implementing functions and procedures, using address referencing, in MIPS We've learned how to implement branching and conditionals in MIPS, but what about functions? Recall that functions are a way to perform a specific task without having to rewrite all of the code each time, instead just (perhaps) passing in a few important values to the function and getting back the result. They are a way to avoid having to think about solving specific problems within a bigger problem, and are thus very useful. But how do we implement this functionality in MIPS? To understand how we can implement functions in MIPS, we have to understand what happens before and after a function is called. Let's look at an example of a function call (called calculate. value) within a program: //earlier program code int myInt = 2; int newint = calculate-value (my1nt); //program continues There are several things we should note about this call: 1. We give the function a value (which it presumably does something with) 2. The function has a return value, which we are setting a new integer to 3. The call to the function jumps (branches) to a different location in memory where the function resides After this we jump back to our program at the line just after the function call (llprogram continues) 4
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


