Question: Cu+ (aq) + 2 e Cu(s) Power Supply An external direct-current power supply is connected to two platinum electrodes immersed in a beaker containing
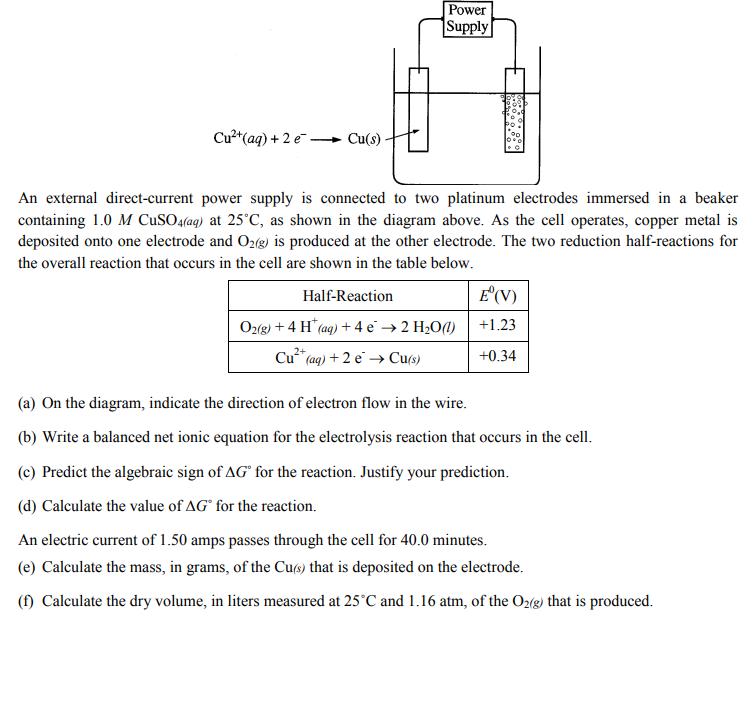
Cu+ (aq) + 2 e Cu(s) Power Supply An external direct-current power supply is connected to two platinum electrodes immersed in a beaker containing 1.0 M CuSO4(aq) at 25C, as shown in the diagram above. As the cell operates, copper metal is deposited onto one electrode and O2(g) is produced at the other electrode. The two reduction half-reactions for the overall reaction that occurs in the cell are shown in the table below. Half-Reaction O2(g) + 4 H (aq) + 4 e 2 HO(l) 2+ Cu+ (aq) + 2e Cu(s) E' (V) +1.23 +0.34 (a) On the diagram, indicate the direction of electron flow in the wire. (b) Write a balanced net ionic equation for the electrolysis reaction that occurs in the cell. (c) Predict the algebraic sign of AG for the reaction. Justify your prediction. (d) Calculate the value of AG for the reaction. An electric current of 1.50 amps passes through the cell for 40.0 minutes. (e) Calculate the mass, in grams, of the Cu(s) that is deposited on the electrode. (f) Calculate the dry volume, in liters measured at 25C and 1.16 atm, of the O2(g) that is produced.
Step by Step Solution
3.49 Rating (159 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
The detailed ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


