Question: Culver Inc. is a retailer using a perpetual inventory system. All sales returns from customers result in the goods being returned to inventory. (Assume
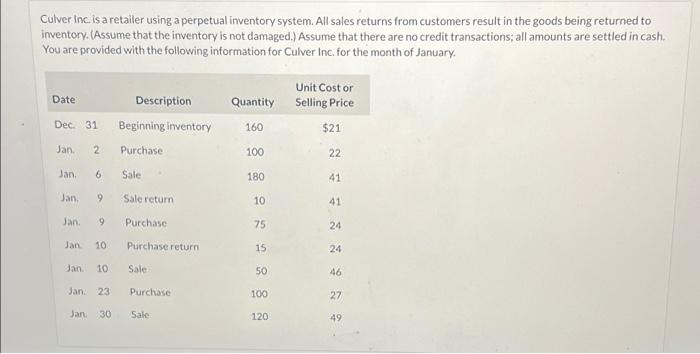


Culver Inc. is a retailer using a perpetual inventory system. All sales returns from customers result in the goods being returned to inventory. (Assume that the inventory is not damaged.) Assume that there are no credit transactions; all amounts are settled in cash. You are provided with the following information for Culver Inc. for the month of January. Unit Cost or Date Description Quantity Selling Price Dec. 31 Beginning inventory 160 $21 Jan. Purchase 100 22 Jan. 6. Sale 180 41 Jan, 9 Sale return 10 41 Jan. 6. Purchase 75 24 Jan 10 Purchase return 15 24 Jan. 10 Sale 50 46 Jan. 23 Purchase 100 27 Jan. 30 Sale 120 49 Using FIFO method, calculate (i) cost of goods sold, (i) ending inventory, and (i) gross profit. (Assume sales returns had a cost of $21 and purchase returns had a cost of $24.) Cost of goods sold %24 7540 Ending Inventory 24 2160 Gross Profit %24 7610 %24 Using Average method, calculate (i) cost of goods sold, (i) ending inventory, and (i) gross profit. (Round average cost to 3 decimal places, eg. 5.252 and final answers to 2 decimal places, eg 5.25) Cost of goods sold Ending Inventory %24 Gross Profit Culver Inc. is a retailer using a perpetual inventory system. All sales returns from customers result in the goods being returned to inventory. (Assume that the inventory is not damaged.) Assume that there are no credit transactions; all amounts are settled in cash. You are provided with the following information for Culver Inc. for the month of January. Unit Cost or Date Description Quantity Selling Price Dec. 31 Beginning inventory 160 $21 Jan. Purchase 100 22 Jan. 6. Sale 180 41 Jan, 9 Sale return 10 41 Jan. 6. Purchase 75 24 Jan 10 Purchase return 15 24 Jan. 10 Sale 50 46 Jan. 23 Purchase 100 27 Jan. 30 Sale 120 49 Using FIFO method, calculate (i) cost of goods sold, (i) ending inventory, and (i) gross profit. (Assume sales returns had a cost of $21 and purchase returns had a cost of $24.) Cost of goods sold %24 7540 Ending Inventory 24 2160 Gross Profit %24 7610 %24 Using Average method, calculate (i) cost of goods sold, (i) ending inventory, and (i) gross profit. (Round average cost to 3 decimal places, eg. 5.252 and final answers to 2 decimal places, eg 5.25) Cost of goods sold Ending Inventory %24 Gross Profit
Step by Step Solution
3.47 Rating (160 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Computation of cost of goods sold closing inventory and gross profit using average ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


