Question: Current Attempt in Progress table [ [ E , , S 5 It , , 0 5 , 8 ] , [ 0 ,
Current Attempt in Progress tableESItSSIT,,sSdeg Itau SESE,,deg ZITAAepsi IEZItau tableStatepkPaTdeg ChkJkgskJkgKx
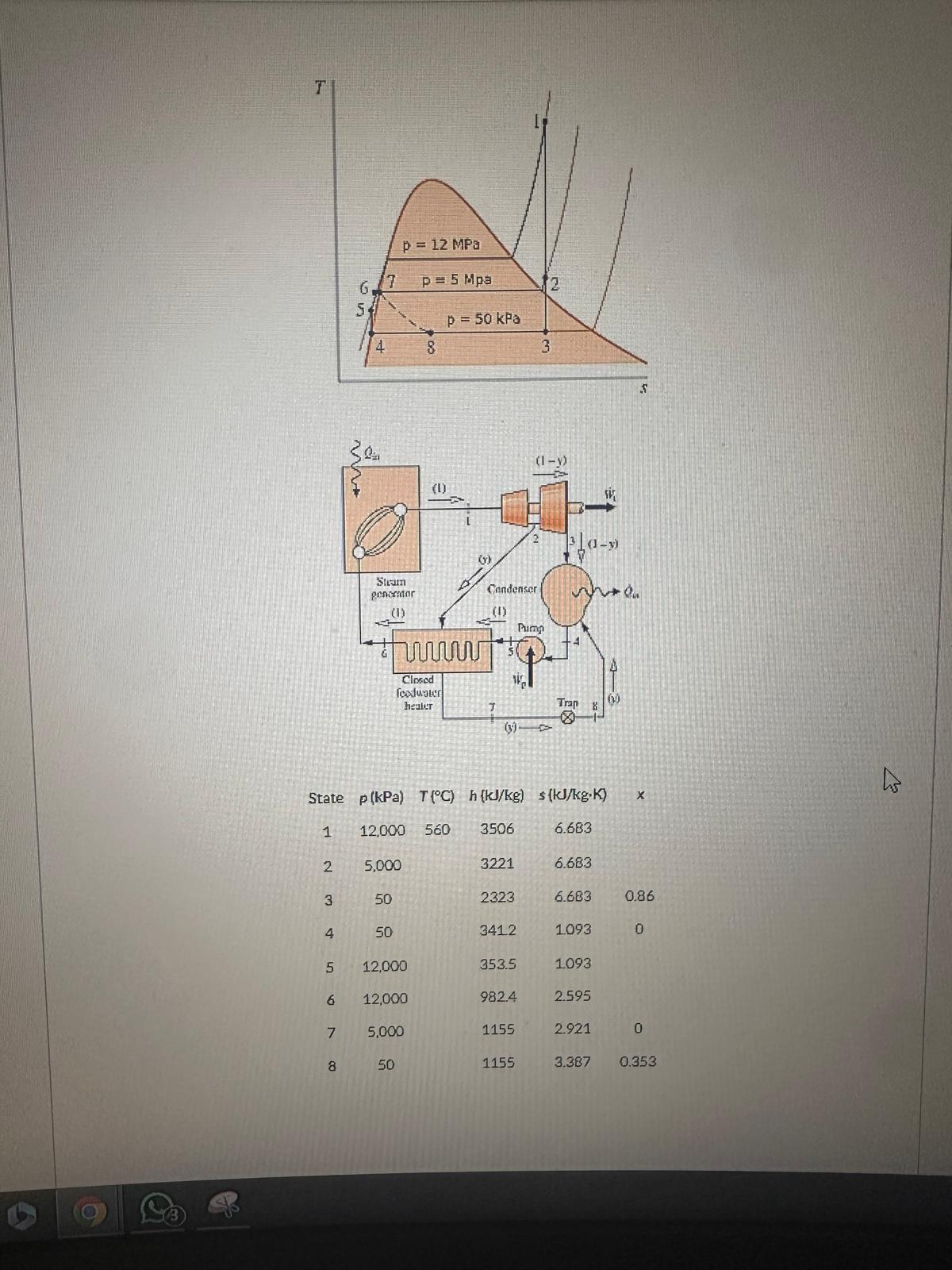
As indicated in the figure below, a power plant operates on a regenerative vapor power cycle with one closed
feedwater heater. Steam enters the first turbine stage at state where pressure is p MPa and temperature is
deg C Steam expands to state where pressure is p MPa and some of the steam is extracted and diverted to the closed feedwater heater. Condensate exits the feedwater heater at state as saturated liquid at a pressure of
p MPa, undergoes a throttling process through a trap to a pressure of pg kPa at state and then enters
the condenser. The remaining steam expands through the second turbine stage to a pressure of p kPa at state
and then enters the coldenser. Saturated liquid feedwater exiting the condenser at state at a pressure of pa
kPa enters a pump and exits the pump at a pressure of p MPa. The feedwater then flows through the
closed feedwater heater, exiting at state with a pressure of p MPa. The net power output for the cycle is
MW
For isentropic processes in each turbine stage and the pump, determine:
a the percent cycle thermal efficiency.
b the mass flow rate into the first turbine stage, in kgs
c the rate of entropy production in the closed feedwater heater, in kWK
d the rate of entropy production in the steam trap, in kWK
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


