Question: D, E, & F, please? Bond energy value: CH 3 OH 427 KJ/mol H 2 CO - C-O 782 KJ/mol -C-H364 KJ/mol H2 436 KJ/mol

D, E, & F, please? 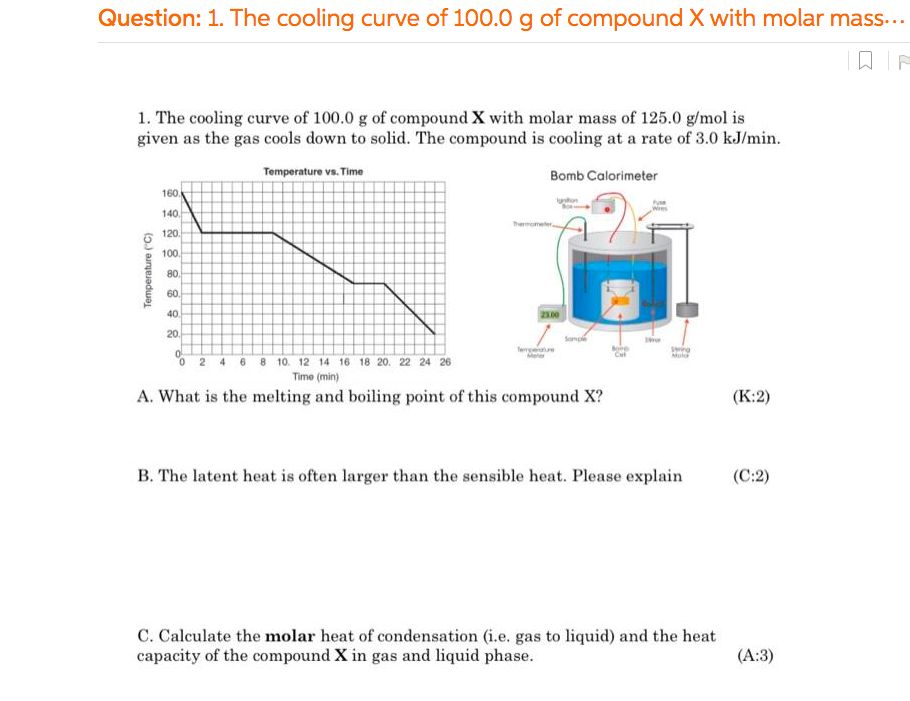
Bond energy value:
CH3OH 427 KJ/mol
H2CO
- C-O 782 KJ/mol
-C-H364 KJ/mol
H2 436 KJ/mol
D. Methanol was allowed to react according in a bomb calorimeter as shown above to the reaction below, calculate the heat of reaction of using the bond energy method. Note: You need to sketch the correct Lewis dot for this method. Is this an endo-or exo-thermic reaction? (K-2, A:1, C:2) CH3OH(9) H2CO(g) + H2(9) + E. Recalculate the heat of reaction in part D using Hess's Law with the mechanism shown below. (A:2, C:2) 2 CH3OH(g) + 3 029) 2CO2() + 4H2O(g) AH--1353 kJ H2CO(g) + O2(9) H2O(g) + CO2(9) AH-520 kJ 2 H2(9) + O2(9)- 2 H20() AH-484 kJ F. From part D, if the liquid used in the bomb calorimeter is the liquid phase of 450.0 g of compound X, calculate the final temperature of the compound X if the initial temperature of the compound X was at 90.0C when 15.0 gram of methanol is reacted in the bomb calorimeter. (A:2, 1:2) Question: 1. The cooling curve of 100.0 g of compound X with molar mass... 1. The cooling curve of 100.0 g of compound X with molar mass of 125.0 g/mol is given as the gas cools down to solid. The compound is cooling at a rate of 3.0 kJ/min. Temperature vs. Time Bomb Calorimeter 160 140 Wees 120 100 Temperature (C) 80 60 40 20 20 le so 0 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 26 Time (min) A. What is the melting and boiling point of this compound X? (K:2) B. The latent heat is often larger than the sensible heat. Please explain (C:2) C. Calculate the molar heat of condensation (i.e. gas to liquid) and the heat capacity of the compound X in gas and liquid phase. (A:3)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


