Question: Data structure 1 Queue Application Print Queue is where all received jobs and tasks are handled. The jobs are received from all connected devices on
Data structure
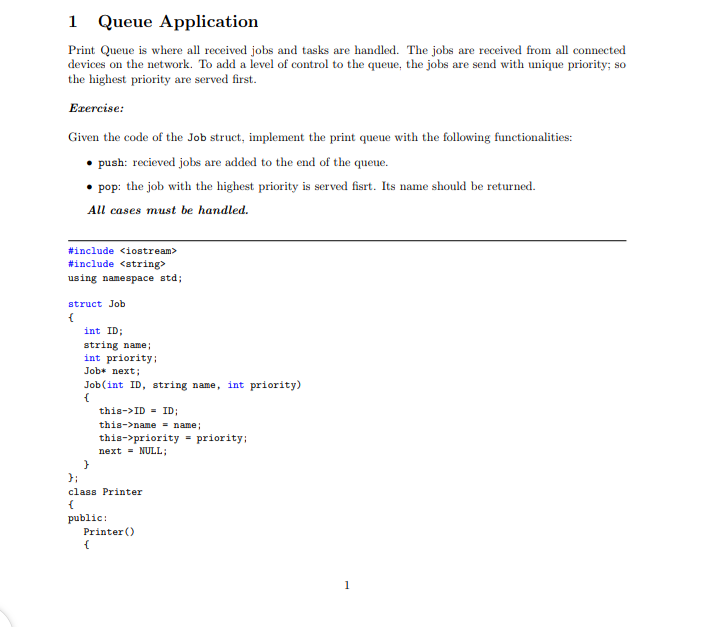

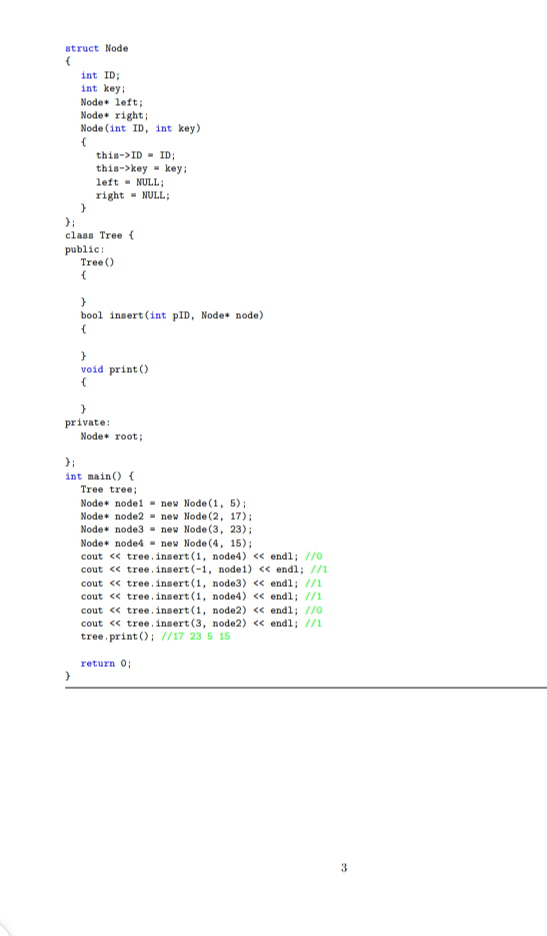
1 Queue Application Print Queue is where all received jobs and tasks are handled. The jobs are received from all connected devices on the network. To add a level of control to the queue, the jobs are send with unique priority; so the highest priority are served first. Exercise: Given the code of the Job struct, implement the print queue with the following functionalities: push: recieved jobs are added to the end of the queue. pop: the job with the highest priority is served fisrt. Its name should be returned. All cases must be handled. #include
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


