Question: // #define MAXWIDTH 100 - // #define MAXHEIGHT 100 //typedef struct //int width; - //int height; 1Board; // This function should run a sinlge tick
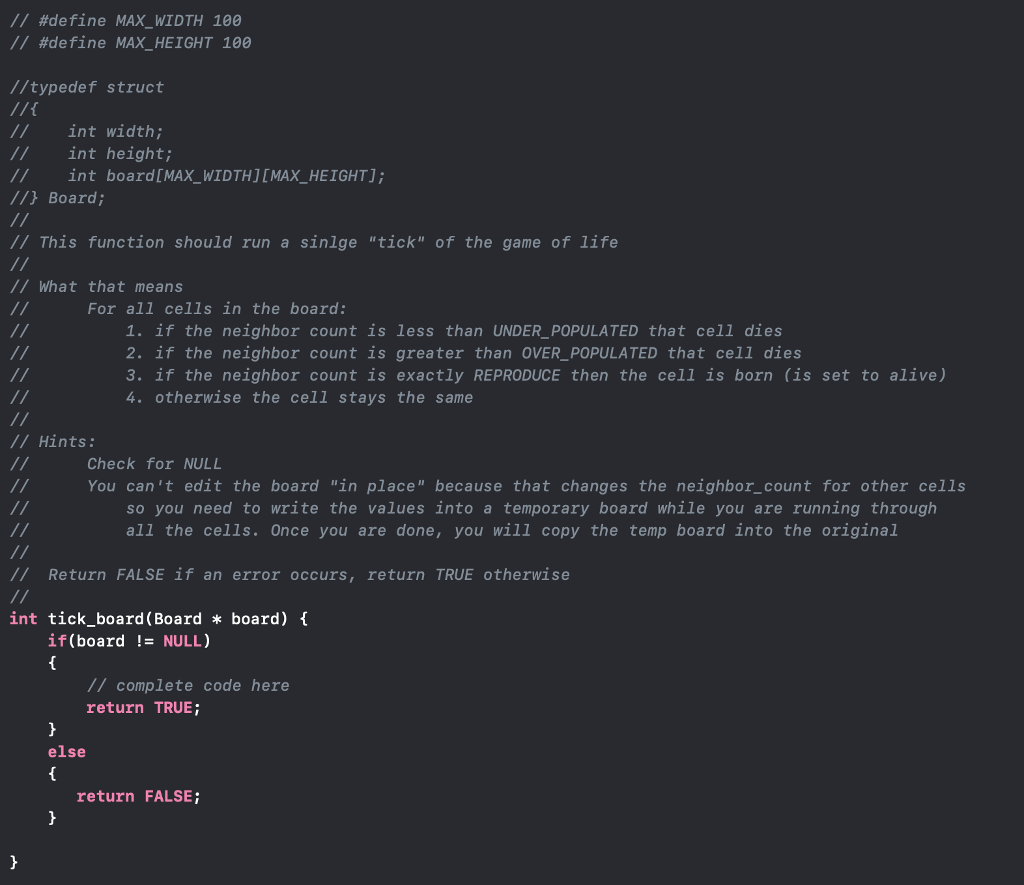
// #define MAXWIDTH 100 - // #define MAXHEIGHT 100 //typedef struct //int width; - //int height; 1Board; // This function should run a sinlge "tick" of the game of life // What that means nt board [MAX WIDTH] [MAX HEIGHT); For all cells in the board 1. if the neighbor count is less than UNDER_ POPULATED that cell dies 2. if the neighbor count is greater than OVER_POPULATED that cell dies 3. if the neighbor count is exactly REPRODUCE then the cell is born (is set to alive) 4. otherwise the cell stays the same // Hints: Check for NULL You can 't edit the board "in place" because that changes the neighbor_count for other cells so you need to write the values into a temporary board while you are running through all the cells. Once you are done, you will copy the temp board into the original // Return FALSE if an error occurs, return TRUE otherwise int tick_ board (Board board) f if(board ! NULL) /7complete code here return TRUE; else return FALSE // #define MAXWIDTH 100 - // #define MAXHEIGHT 100 //typedef struct //int width; - //int height; 1Board; // This function should run a sinlge "tick" of the game of life // What that means nt board [MAX WIDTH] [MAX HEIGHT); For all cells in the board 1. if the neighbor count is less than UNDER_ POPULATED that cell dies 2. if the neighbor count is greater than OVER_POPULATED that cell dies 3. if the neighbor count is exactly REPRODUCE then the cell is born (is set to alive) 4. otherwise the cell stays the same // Hints: Check for NULL You can 't edit the board "in place" because that changes the neighbor_count for other cells so you need to write the values into a temporary board while you are running through all the cells. Once you are done, you will copy the temp board into the original // Return FALSE if an error occurs, return TRUE otherwise int tick_ board (Board board) f if(board ! NULL) /7complete code here return TRUE; else return FALSE
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


