Question: Depreciation Analysis: Straight-Line Method versus Double Declining Balance Method Completing this activity will help you learn to: 1. analyze long-term asset depreciation by the straight-line

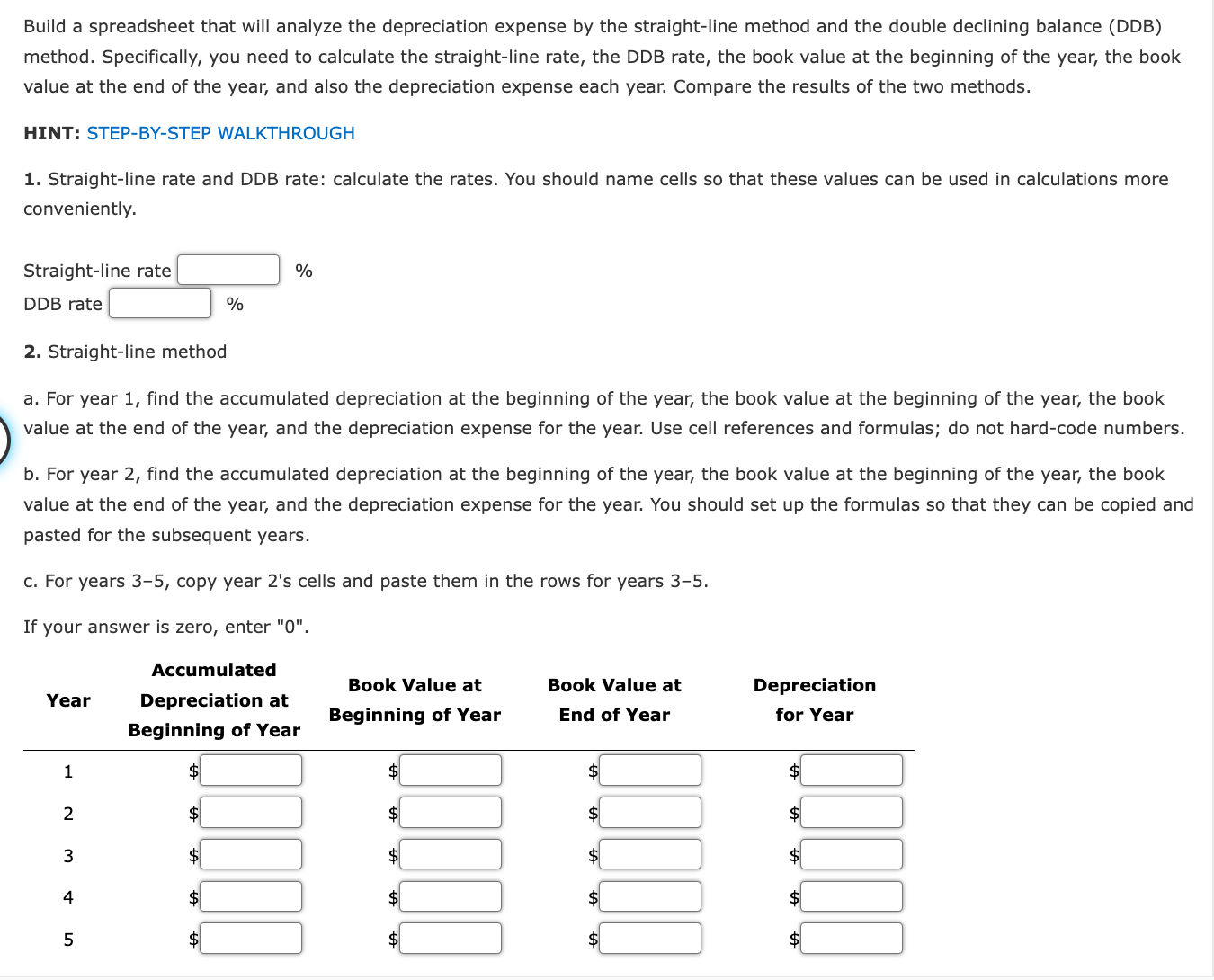
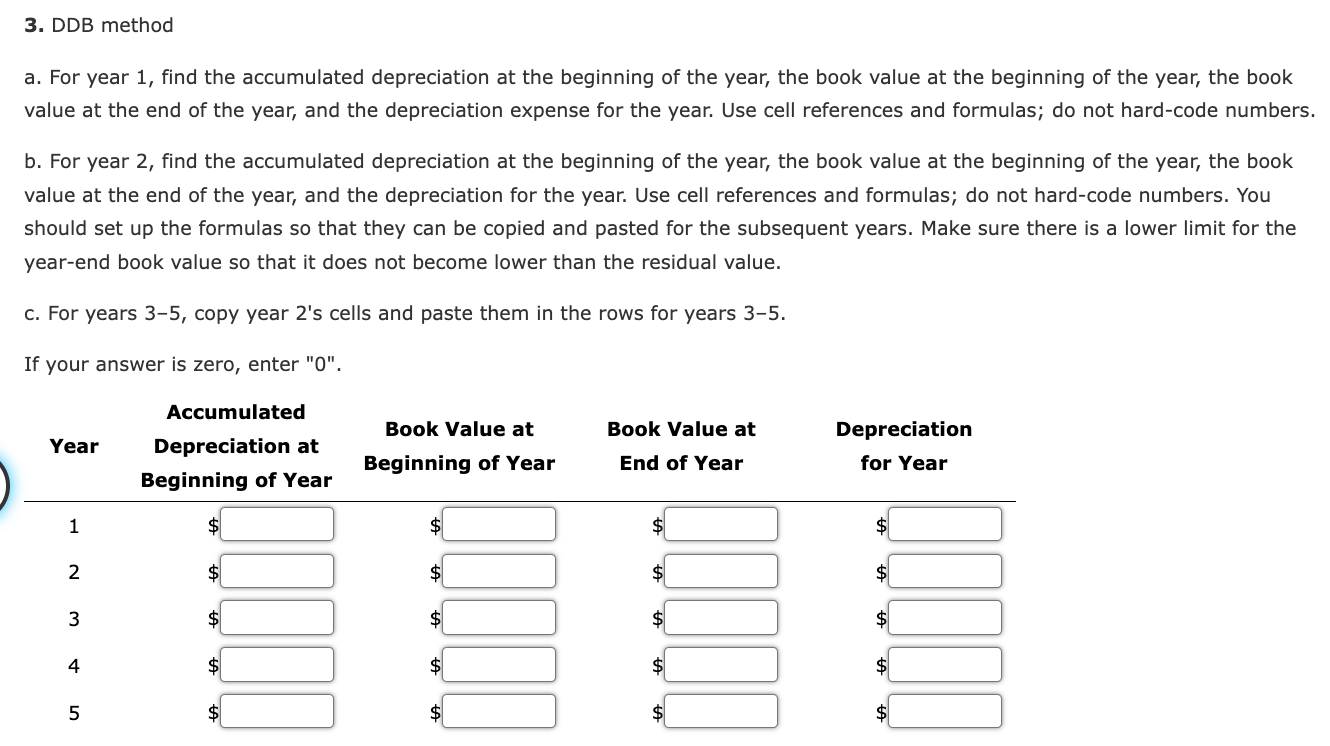
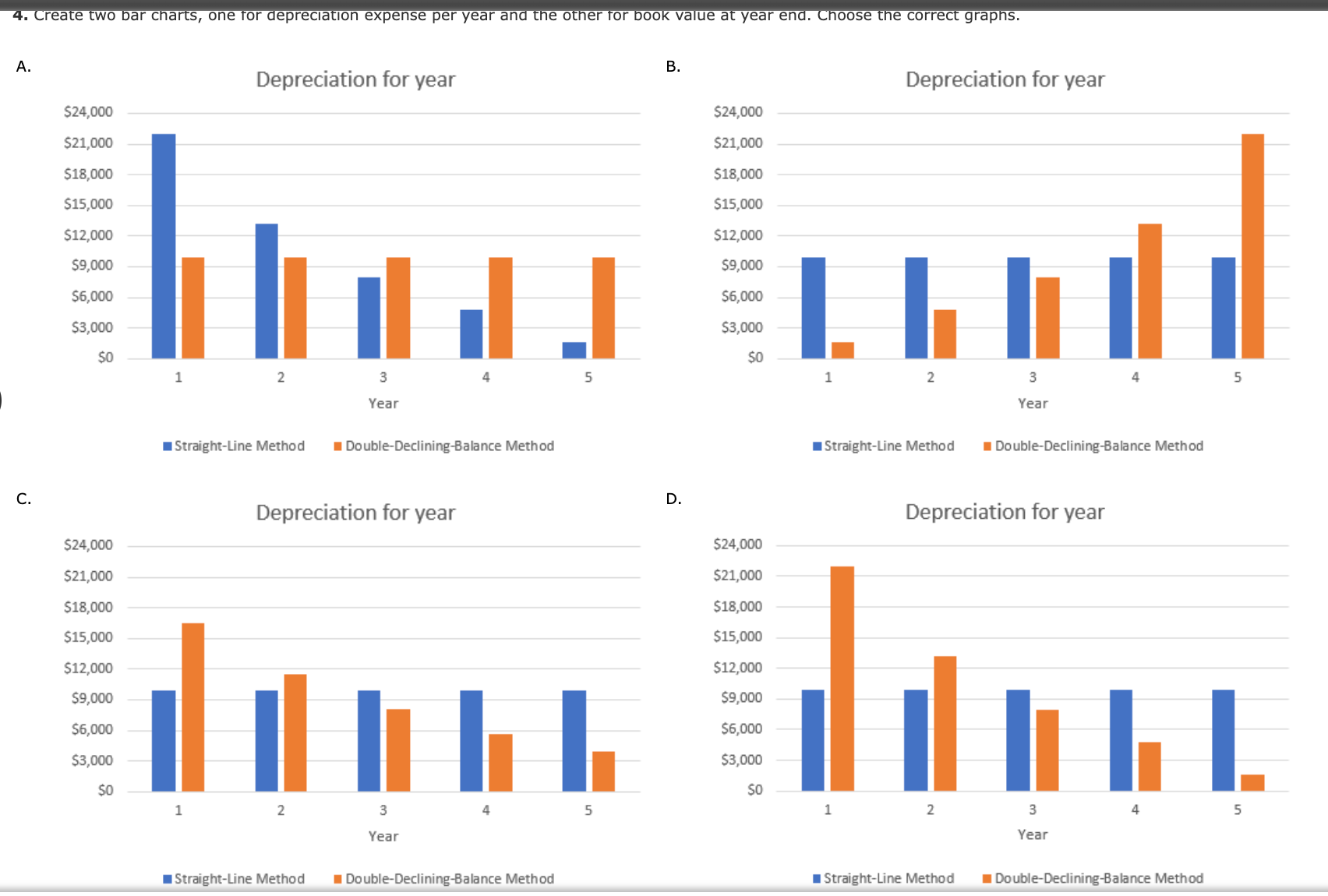
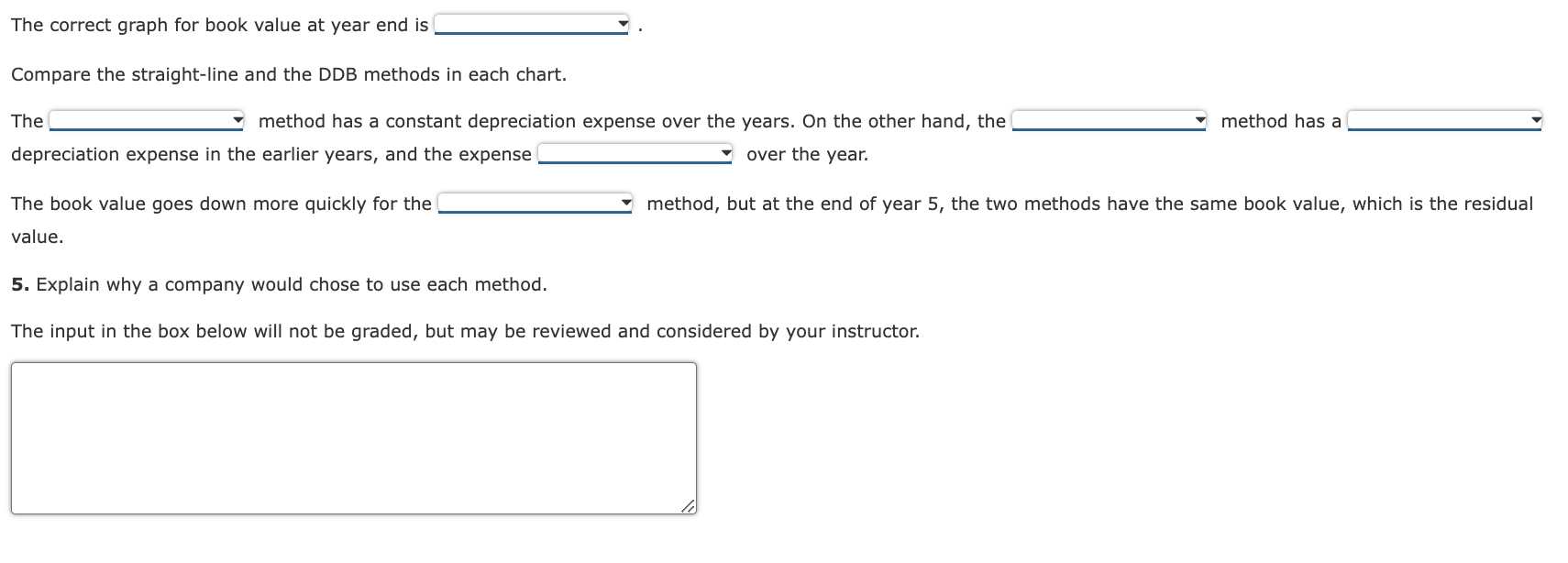
Depreciation Analysis: Straight-Line Method versus Double Declining Balance Method Completing this activity will help you learn to: 1. analyze long-term asset depreciation by the straight-line method and the double declining balance method. 2. create Excel calculations using cell references. 3. create Excel calculations using cell names. 4. create a limit for a cell value. 5. create Excel bar charts. Case scenario: You are working at an industrial supplier, Great Gadgets. You are planning to purchase a truck for work purposes. The truck costs $55,000 to purchase. You plan to use it for five years. After five years, you can sell it for $5,500. You want to find the depreciation expense per year. You also want to find the book value at the end of each year for the next five years. You want to perform your analysis of two different depreciation methods: the straight-line method and the double declining balance method. Compare your results from the two methods. Create a reusable Excel spreadsheet to perform this analysis. Required: Download spreadsheet DepreciationCaseData-010766.xlsx Build a spreadsheet that will analyze the depreciation expense by the straight-line method and the double declining balance (DDB) method. Specifically, you need to calculate the straight-line rate, the DDB rate, the book value at the beginning of the year, the book value at the end of the year, and also the depreciation expense each year. Compare the results of the two methods. Build a spreadsheet that will analyze the depreciation expense by the straight-line method and the double declining balance (DDB) method. Specifically, you need to calculate the straight-line rate, the DDB rate, the book value at the beginning of the year, the book value at the end of the year, and also the depreciation expense each year. Compare the results of the two methods. HINT: STEP-BY-STEP WALKTHROUGH 1. Straight-line rate and DDB rate: calculate the rates. You should name cells so that these values can be used in calculations more conveniently. Straight-line rate % DDB rate % 2. Straight-line method a. For year 1, find the accumulated depreciation at the beginning of the year, the book value at the beginning of the year, the book value at the end of the year, and the depreciation expense for the year. Use cell references and formulas; do not hard-code numbers. b. For year 2, find the accumulated depreciation at the beginning of the year, the book value at the beginning of the year, the book value at the end of the year, and the depreciation expense for the year. You should set up the formulas so that they can be copied and pasted for the subsequent years. c. For years 3-5, copy year 2's cells and paste them in the rows for years 3-5. a. For year 1 , find the accumulated depreciation at the beginning of the year, the book value at the beginning of the year, the book value at the end of the year, and the depreciation expense for the year. Use cell references and formulas; do not hard-code numbers. b. For year 2, find the accumulated depreciation at the beginning of the year, the book value at the beginning of the year, the book value at the end of the year, and the depreciation for the year. Use cell references and formulas; do not hard-code numbers. You should set up the formulas so that they can be copied and pasted for the subsequent years. Make sure there is a lower limit for the year-end book value so that it does not become lower than the residual value. c. For years 3-5, copy year 2's cells and paste them in the rows for years 3-5. If your answer is zero, enter "0". The correct graph for book value at year end is Compare the straight-line and the DDB methods in each chart. The method has a constant depreciation expense over the years. On the other hand, the method has a depreciation expense in the earlier years, and the expense over the year. The book value goes down more quickly for the method, but at the end of year 5 , the two methods have the same book value, which is the residual value. 5. Explain why a company would chose to use each method. The input in the box below will not be graded, but may be reviewed and considered by your instructor
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


