Question: Destination Hardware Address 6 Bytes Source Hardware Address 6 Bytes Frame Type Frame Data 2 Bytes 46-1500 Bytes Byte bit 0 12 3 45 678
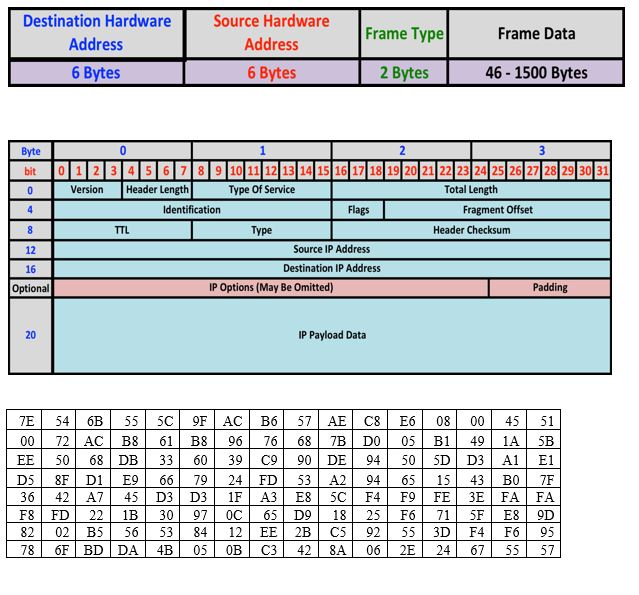

Destination Hardware Address 6 Bytes Source Hardware Address 6 Bytes Frame Type Frame Data 2 Bytes 46-1500 Bytes Byte bit 0 12 3 45 678 9110 11| 12 13 14 15 16117 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 VersionHeader Length Type Of Service Total Length Identification Flags Fragment Offset TTL Type Header Checksum Source IP Address 12 16 Optional Destination IP Address IP Options (May Be Omitted) Padding 20 IP Payload Data TE 54 | | 551 5C! 9F | AC B6 | 57| AEl C81 E6 | 08 | 00| 45| 51 00| 72| AC| B8| 61 | B8| 96| 76| 681 7B DOI 05 | B1 | 491 1A1 5B EE | 501 68|DB | 33| 60| 39| C9| 90| DE 94| 50| 5Di D3| All E1 DSI 8F D| E9 | 66| 79| 24 | FD 53 | A2| 94| 65 | 15| 43 | BO 7F F8 FD 22B 30 970C 65 D9 18 25F6 71 5FE8 9D 82 | 02 | B5| 56| 53| 84 | 12 | EE| 2Bl C5| 92 | 55| 3D| F4l Fol 95 78| 6F | BD DA 4B | 05 | 0B C31 421 8A 061 2E | 24 | 67| 55| 57 1. Find the source hardware address 2. Find the destination hardware address. 3. What type of frame is this? 4. What Flag(s) are set? 5. What is the fragment offset? 6. What is the TTL count? 7. What is the Header Checksum? 8. If the header includes no options or padding, what are the first five bytes of the datagram data? 9. Find the destination IP address. 10.What class is the destination IP address? 11.What is the network ID in the destination address? 12.What is the host IID in the destination address? 13.Write the destination IP address in dotted decimal notation 14.Find the source IP address. 15.What class is the source IP address? 16.What is the network ID in the source address? 17.What is the host ID in the source address? 18.Write the source IP address in dotted decimal notation 19.Can this message be delivered directly by the source to the destination, or will it require routers to handle the message e Explain how the ARP Protocol works. What problem does it solve? How does it solve the problem? Give examples and be as specific as possible Suppose machine C receives an ARP request sent from A looking for target B and suppose C has the binding for IPB to HWB in its ARP cache. Should C answer the request? Explain why or why not. Destination Hardware Address 6 Bytes Source Hardware Address 6 Bytes Frame Type Frame Data 2 Bytes 46-1500 Bytes Byte bit 0 12 3 45 678 9110 11| 12 13 14 15 16117 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 VersionHeader Length Type Of Service Total Length Identification Flags Fragment Offset TTL Type Header Checksum Source IP Address 12 16 Optional Destination IP Address IP Options (May Be Omitted) Padding 20 IP Payload Data TE 54 | | 551 5C! 9F | AC B6 | 57| AEl C81 E6 | 08 | 00| 45| 51 00| 72| AC| B8| 61 | B8| 96| 76| 681 7B DOI 05 | B1 | 491 1A1 5B EE | 501 68|DB | 33| 60| 39| C9| 90| DE 94| 50| 5Di D3| All E1 DSI 8F D| E9 | 66| 79| 24 | FD 53 | A2| 94| 65 | 15| 43 | BO 7F F8 FD 22B 30 970C 65 D9 18 25F6 71 5FE8 9D 82 | 02 | B5| 56| 53| 84 | 12 | EE| 2Bl C5| 92 | 55| 3D| F4l Fol 95 78| 6F | BD DA 4B | 05 | 0B C31 421 8A 061 2E | 24 | 67| 55| 57 1. Find the source hardware address 2. Find the destination hardware address. 3. What type of frame is this? 4. What Flag(s) are set? 5. What is the fragment offset? 6. What is the TTL count? 7. What is the Header Checksum? 8. If the header includes no options or padding, what are the first five bytes of the datagram data? 9. Find the destination IP address. 10.What class is the destination IP address? 11.What is the network ID in the destination address? 12.What is the host IID in the destination address? 13.Write the destination IP address in dotted decimal notation 14.Find the source IP address. 15.What class is the source IP address? 16.What is the network ID in the source address? 17.What is the host ID in the source address? 18.Write the source IP address in dotted decimal notation 19.Can this message be delivered directly by the source to the destination, or will it require routers to handle the message e Explain how the ARP Protocol works. What problem does it solve? How does it solve the problem? Give examples and be as specific as possible Suppose machine C receives an ARP request sent from A looking for target B and suppose C has the binding for IPB to HWB in its ARP cache. Should C answer the request? Explain why or why not
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


