Question: Determine the column allowable compressive force capacity, Pa for the given 3 x 8 S 4 S Douglas Fir sawn lumber column with an Fc
Determine the column allowable compressive force capacity, Pa for the given x SS Douglas Fir
sawn lumber column with an Fc psi and E x psi. Midheight bracing is provided for
the weak axis of buckling. Assume CM Ct CF Assume a day load duration. An
illustration of this column is found below. points total Use Table Aa on pg for the column
dimensional properties.
Hint: See Example problem on slide in the lecture PowerPoint presentation titled Chapter
REV wood only found in Module
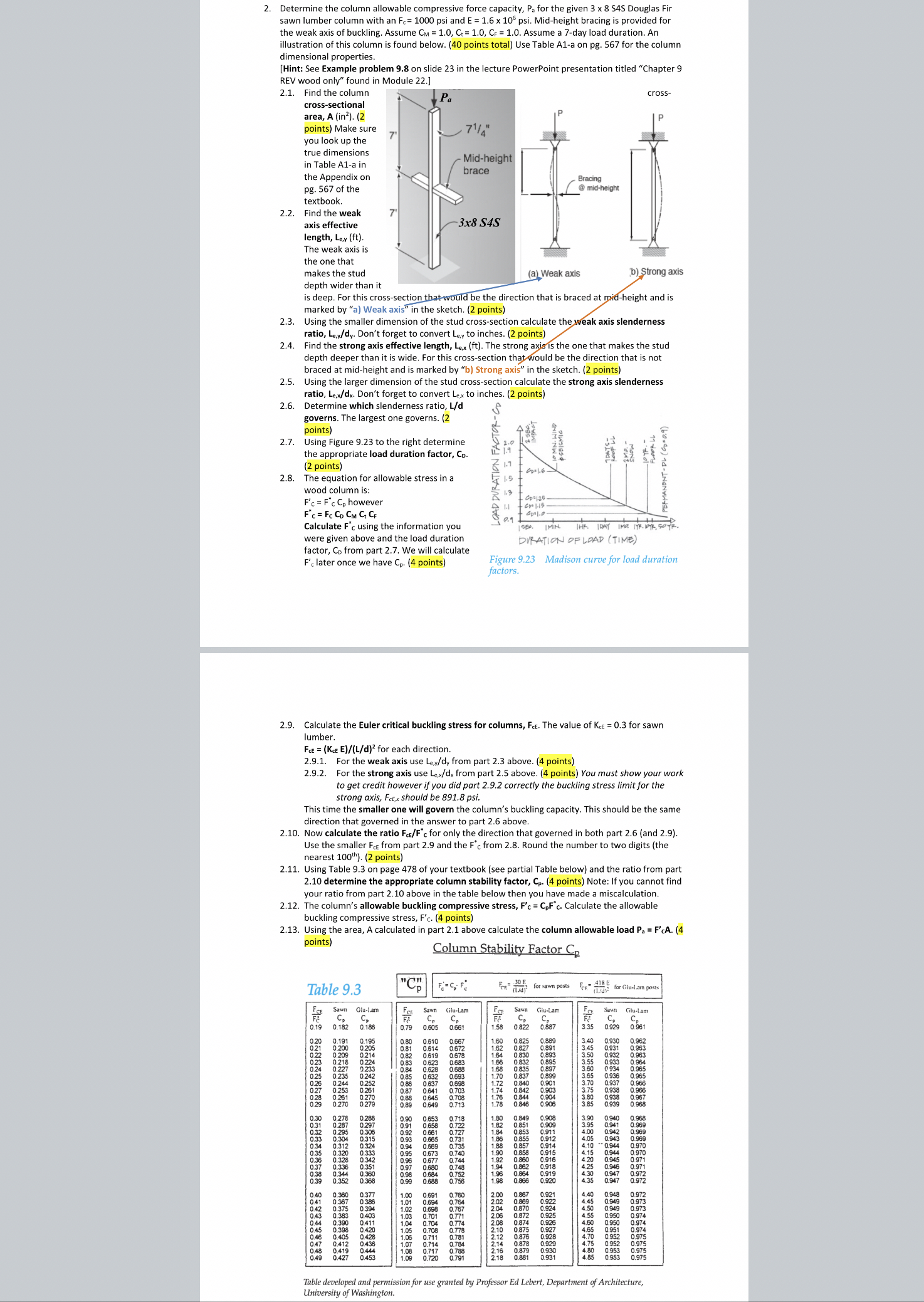
Find the column cross
crosssectional
area, A in
points Make sure
you look up the
true dimensions
in Table Aa in
the Appendix on
pg of the
textbook.
Find the weak
axis effective
length, Ley ft
The weak axis is
the one that
makes the stud
depth wider than it
is deep. For this crosssection that would be the direction that is braced at midheight and is
marked by a Weak axis in the sketch. points
Using the smaller dimension of the stud crosssection calculate the weak axis slenderness
ratio, Ley dy Dont forget to convert Ley to inches. points
Find the strong axis effective length, Lex ft The strong axis is the one that makes the stud
depth deeper than it is wide. For this crosssection that would be the direction that is not
braced at midheight and is marked by b Strong axis in the sketch. points
Using the larger dimension of the stud crosssection calculate the strong axis slenderness
ratio, Lex dx Dont forget to convert Lex to inches. points
Determine which slenderness ratio, Ld
governs. The largest one governs.
points
Using Figure to the right determine
the appropriate load duration factor, CD
points
The equation for allowable stress in a
wood column is:
FC FC Cp however
FC FC CD CM Ct CF
Calculate FC using the information you
were given above and the load duration
factor, CD from part We will calculate
Fc later once we have Cp points
x SS
Pa
Calculate the Euler critical buckling stress for columns, FcE The value of KcE for sawn
lumber.
FcE KcE ELd for each direction.
For the weak axis use Ley dy from part above. points
For the strong axis use Lex dx from part above. points You must show your work
to get credit however if you did part correctly the buckling stress limit for the
strong axis, FcE,x should be psi.
This time the smaller one will govern the columns buckling capacity. This should be the same
direction that governed in the answer to part above.
Now calculate the ratio FcE FC for only the direction that governed in both part and
Use the smaller FcE from part and the F C from Round the number to two digits the
nearest th points
Using Table on page of your textbook see partial Table below and the ratio from part
determine the appropriate column stability factor, Cp points Note: If you cannot find
your ratio from part above in the table below then you have made a miscalculation.
The columns allowable buckling compressive stress, FC Cp FC Calculate the allowable
buckling compressive stress, F C points
Using the area, A calculated in part above calculate the column allowable load Pa FC A
points
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


