Question: Develop the TreeADT as an array-based concrete implementation. Create the Array-based Tree ADT, Run it with TestTreeADT.java to ensure it works. TestTreeADT: 2. Additional Instructions
Develop the TreeADT as an array-based concrete implementation. Create the Array-based Tree ADT, Run it with TestTreeADT.java to ensure it works.


TestTreeADT:
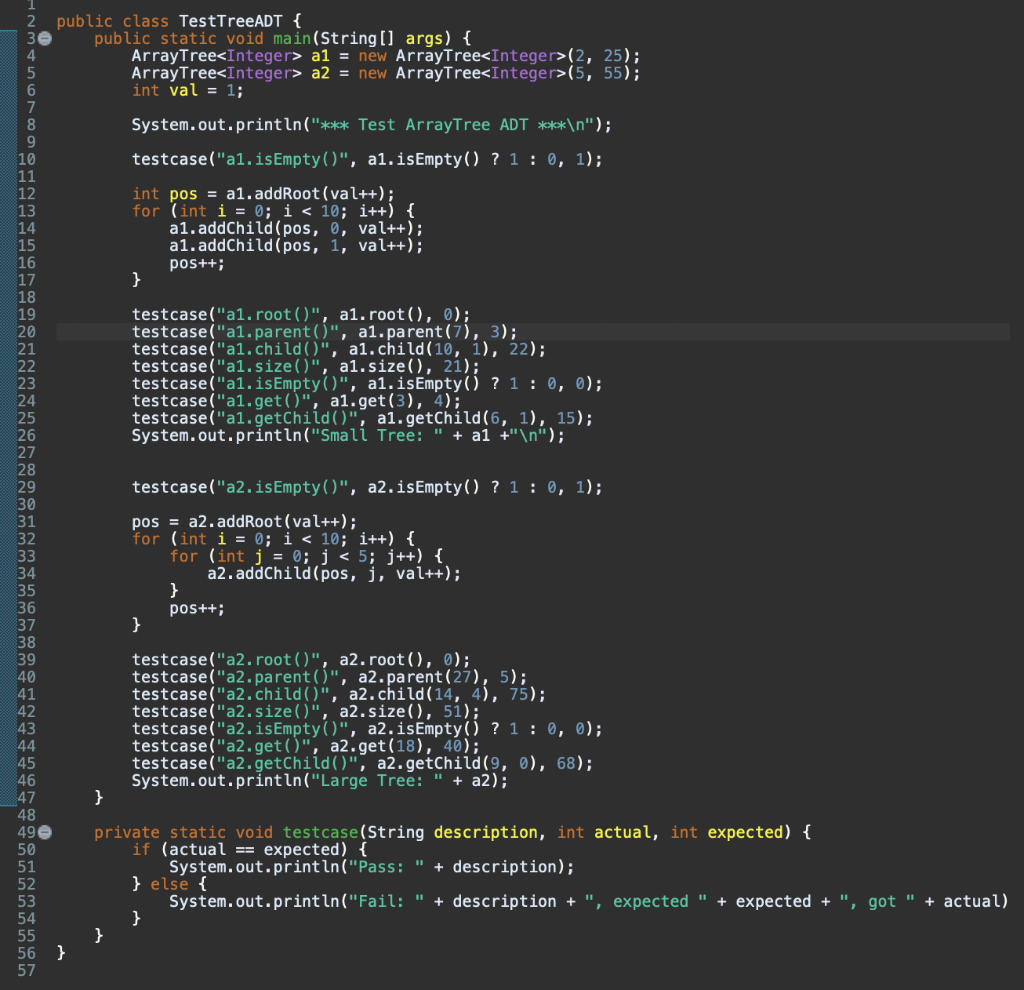
2. Additional Instructions 2.1. Basic Level: Array Tree ADT Develop an ArrayTree class to meet the design shown here. It should not implement the Tree interface we discussed in class. The behavior of each method should be clear from our discussion in class. While the class is generic (element is type E), the positions are all primitive integers. The default order is 2 and the default capacity is 1000. toString() should print a summary of the data elements as shown in the sample output below: ArrayTree -arrayl: E -count: int -size: int -order: int +ArrayTree(order: int, capacity: int) +ArrayTreel) +root: int +parent(p:int); int +child(p: parent, cint); int +size()int +isEmptyO:boolean +addRoot(e: E): int +get(pos: int): E addChild(parent: int child: Inte: E): int +getChildparent: int, child: int): E +toString(): String Running your ArrayTree with TestTreeADT.java should result in the following output. Note: it's ok that you get one Fail in testing a2. You should understand why that is correct as you implement the TreeADT. *** Test ArrayTree ADT *** Pass: a1.isEmpty() Pass: a1.root() Pass: a1.parent() Pass: a1.child() Pass: a1.size() Pass: a1.isEmpty() Pass: a1.get() Pass: a1.getChild() Small Tree: [ArrayTree: order=2, count=21, size=25, array={1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 - --- }] Pass: a2.isEmpty() Pass: a2. root() Pass: a2.parent() Fail: a2.child(), expected 75, got -1 Pass: a2.size() Pass: a2.isEmpty() Pass: a2.get() Pass: a2.getChild() Large Tree: [ArrayTree: order=5, count=51, size=55, array={22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 - - - - }] public class TestTreeADT { public static void main(String[] args) { ArrayTree a1 = new ArrayTree(2, 25); ArrayTree a2 = new ArrayTree(5, 55); int val = 1; 8 9 System.out.println("*** Test ArrayTree ADT *** "); testcase("a1.isEmpty()", a1.isEmpty() ? 1 : 0, 1); int pos = a1.addRoot(val++); for (int i = 0; i






