Question: Discrete math Let us consider a floor covered with square tiles, all the tiles have the same size, with Width= Height=A. We drop a coin
 Discrete math
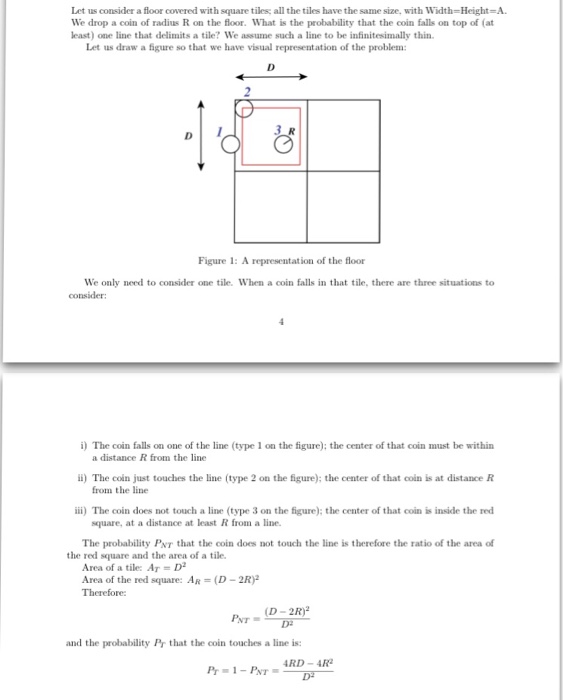
Discrete math Let us consider a floor covered with square tiles, all the tiles have the same size, with Width= Height=A. We drop a coin of radius R on the floor. What is the probability that the coin falls on top of (at least) one line that delimits a tile We assume such a line to be infinitesimally thin Let us draw a figure so that we have visual representation of the problem: Figure 1: A representation of the floor We only need to consider one tile. When a coin falls in that tile, there are three situations to consider i) The coin falls on one of the line (type 1 on the figure): the center of that coin must be within a distance R from the line i) The coln just touches the line (type 2 on the figure); the center of that coin is at distance R iii) The coin does not touch a line (type 3 on the figure): the center of that coin is inside the red from the line square, at a distance at least R from a line. The probability PNT that the coin does not touch the line is therefore the ratio of the area of the red l square and the area of a tile Area of a tile: AT = Area of the red square: AR( Therefore D-2R and the probability Pr that the coin touches a line is: RD-4R Let us consider a floor covered with square tiles, all the tiles have the same size, with Width= Height=A. We drop a coin of radius R on the floor. What is the probability that the coin falls on top of (at least) one line that delimits a tile We assume such a line to be infinitesimally thin Let us draw a figure so that we have visual representation of the problem: Figure 1: A representation of the floor We only need to consider one tile. When a coin falls in that tile, there are three situations to consider i) The coin falls on one of the line (type 1 on the figure): the center of that coin must be within a distance R from the line i) The coln just touches the line (type 2 on the figure); the center of that coin is at distance R iii) The coin does not touch a line (type 3 on the figure): the center of that coin is inside the red from the line square, at a distance at least R from a line. The probability PNT that the coin does not touch the line is therefore the ratio of the area of the red l square and the area of a tile Area of a tile: AT = Area of the red square: AR( Therefore D-2R and the probability Pr that the coin touches a line is: RD-4R
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


