Question: Do calculations to establish what is the permanent action ( dead load ) , G , you should use for design of the floor joists.
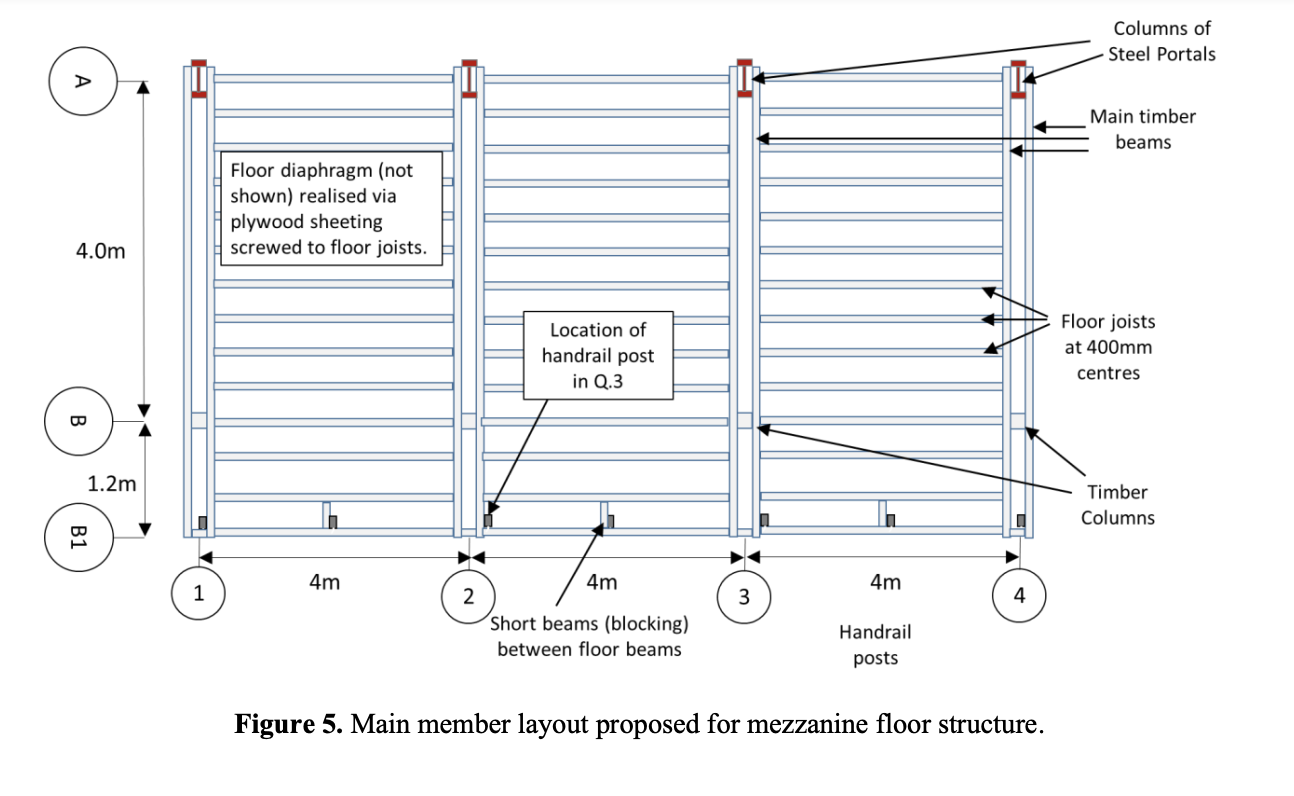
Do calculations to establish what is the permanent action dead load G you should use for design of the floor joists. Floor joists are spaced at mm centres with sawn timber NZ pine sections KNm The mezzanine floor area has mm pine plywood screwed on top of the floor joists that can be assumed to weigh kPa There is a mm plasterboard fibrous plaster ceiling screwed to the underside of the floor joists. Insulation and services within the floor structure can be assumed to add kPa to the floor dead load. Combine all dead load contributions and compute a uniformly distributed line load, in acting on the joists.Figure Main member layout proposed for mezzanine floor structure.
Broken up to answer this question:
a What is the dead load due to the selfweight of the floor joist? kNmdp
b What is the dead load due to other superimposed dead loads, such as flooring, ceiling, and service? kNmdp
c Combine all dead load contributions and compute a uniformly distributed line load, wG in kNm acting on the joists. kNmdp
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


