Question: Example 1 (Luenberger's Simplico Gold Mine) Gold can be extracted from the simplico gold mine at a rate of up to 10,000 ounces per
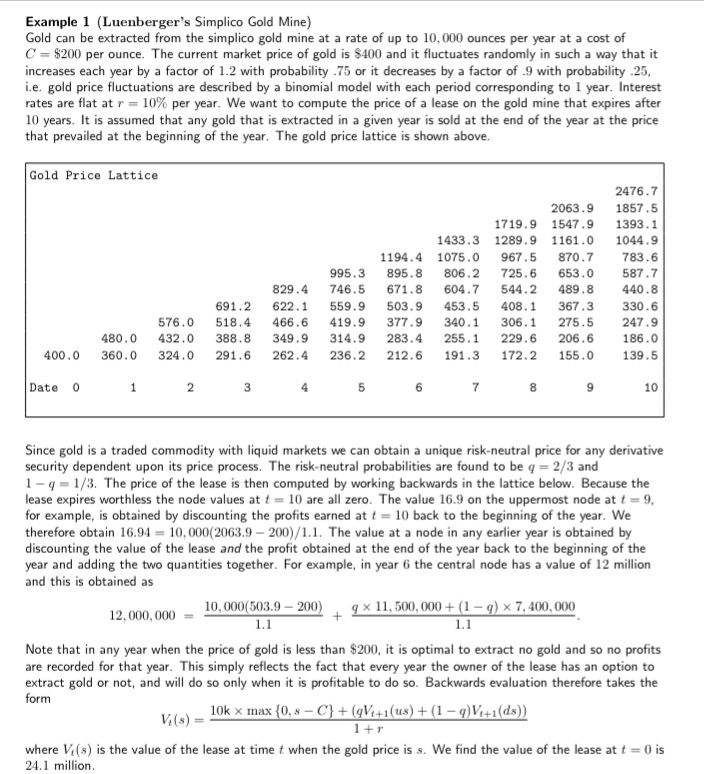
Example 1 (Luenberger's Simplico Gold Mine) Gold can be extracted from the simplico gold mine at a rate of up to 10,000 ounces per year at a cost of C $200 per ounce. The current market price of gold is $400 and it fluctuates randomly in such a way that it increases each year by a factor of 1.2 with probability .75 or it decreases by a factor of .9 with probability .25, i.e. gold price fluctuations are described by a binomial model with each period corresponding to 1 year. Interest rates are flat at r = 10% per year. We want to compute the price of a lease on the gold mine that expires after 10 years. It is assumed that any gold that is extracted in a given year is sold at the end of the year at the price that prevailed at the beginning of the year. The gold price lattice is shown above. Gold Price Lattice 1433.3 1719.9 1547.9 1289.9 1161.0 2476.7 2063.9 1857.5 1393.1 1044.9 829.4 995.3 746.5 1194.4 895.8 1075.0 806.2 725.6 967.5 870.7 783.6 653.0 587.7 671.8 604.7 544.2 489.8 440.8 400.0 360.0 480.0 432.0 324.0 691.2 622.1 576.0 518.4 466.6 388.8 349.9 291.6 262.4 559.9 419.9 314.9 236.2 503.9 453.5 408.1 367.3 330.6 377.9 340.1 306.1 275.5 247.9 283.4 255.1 229.6 206.6 186.0 212.6 191.3 172.2 155.0 139.5 Date 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Since gold is a traded commodity with liquid markets we can obtain a unique risk-neutral price for any derivative security dependent upon its price process. The risk-neutral probabilities are found to be q = 2/3 and 1 q 1/3. The price of the lease is then computed by working backwards in the lattice below. Because the lease expires worthless the node values at t=10 are all zero. The value 16.9 on the uppermost node at t = 9, for example, is obtained by discounting the profits earned at t=10 back to the beginning of the year. We therefore obtain 16.94 10,000(2063.9-200)/1.1. The value at a node in any earlier year is obtained by discounting the value of the lease and the profit obtained at the end of the year back to the beginning of the year and adding the two quantities together. For example, in year 6 the central node has a value of 12 million and this is obtained as 12,000,000 10,000(503.9-200) 1.1 q x 11,500,000+ (1 - q) x 7,400,000 1.1 Note that in any year when the price of gold is less than $200, it is optimal to extract no gold and so no profits are recorded for that year. This simply reflects the fact that every year the owner of the lease has an option to extract gold or not, and will do so only when it is profitable to do so. Backwards evaluation therefore takes the form 10k max {0, s C} + (qV+1(us) + (1 q)Vi+1(ds)) V(8)= 1+r where Vi(s) is the value of the lease at time t when the gold price is s. We find the value of the lease at t = 0 is 24.1 million.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
To evaluate the enhancement option for the Simplice goldmine we need to factor in the increase in extraction capacity from 10000 to 14000 ounces per y... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


