Question: DO NOT ANSWER THIS QUESTION WITHOUT MATLAB!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! I WILL DOWNVOTE IF YOU DO NOT USE MATLAB USE MATLAB TO PLOT THIS PROBLEM MY CODE ISN'T
DO NOT ANSWER THIS QUESTION WITHOUT MATLAB!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
I WILL DOWNVOTE IF YOU DO NOT USE MATLAB
USE MATLAB TO PLOT THIS PROBLEM

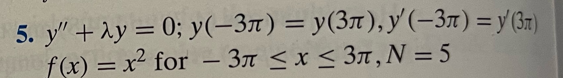
MY CODE ISN'T WORKING, SO COPY THE CODE BELOW AND FIX THE CODE
x = -3*pi:1:3*pi;
N = 5;
for n = 1:N
a0 = 3*pi^2;
an = (1*n^2)*36*(-1)^n;
F = a0 + an;
end
plot(x,F);
figure(3)
xlabel('x')
ylabel('y')
grid on
set(gca,'XAxisLocation','origin','YAxisLocation','origin')
ITS SOLUTION
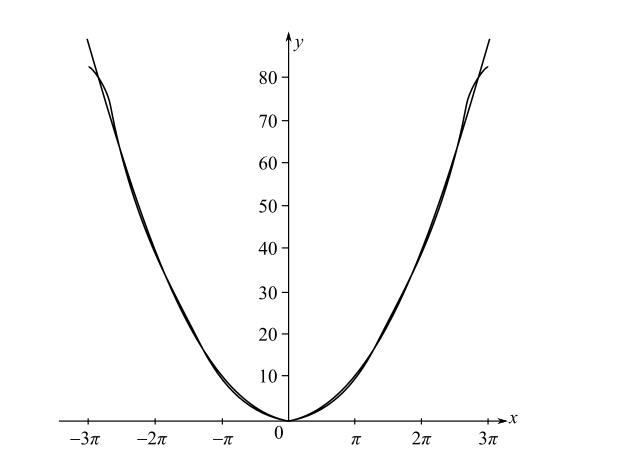
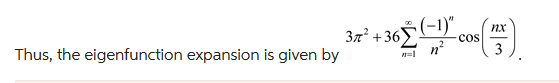
In each of Problems 1-6, find the expansion of f(x) in the eigenfunctions of the given Sturm-Liouville problem. Compare graphs of the function and the N th partial sums of the series for the given N. Also use the convergence theorem to determine what this eigenfunction expansion converges to on the relevant open interval. 5. y+y=0;y(3)=y(3),y(3)=y(3) f(x)=x2 for 3x3,N=5 32+36n=1n2(1)ncos(3nx)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


