Question: DO NOT COPY ANSWERS FROM OTHERS OR ELSE THUMB DOWN!! A fluid with constant flow rate m[kg/h] enters a tube with circular cross section of
![with constant flow rate m[kg/h] enters a tube with circular cross section](https://s3.amazonaws.com/si.experts.images/answers/2024/09/66d899712404f_08866d899705ba88.jpg) DO NOT COPY ANSWERS FROM OTHERS OR ELSE THUMB DOWN!!
DO NOT COPY ANSWERS FROM OTHERS OR ELSE THUMB DOWN!!
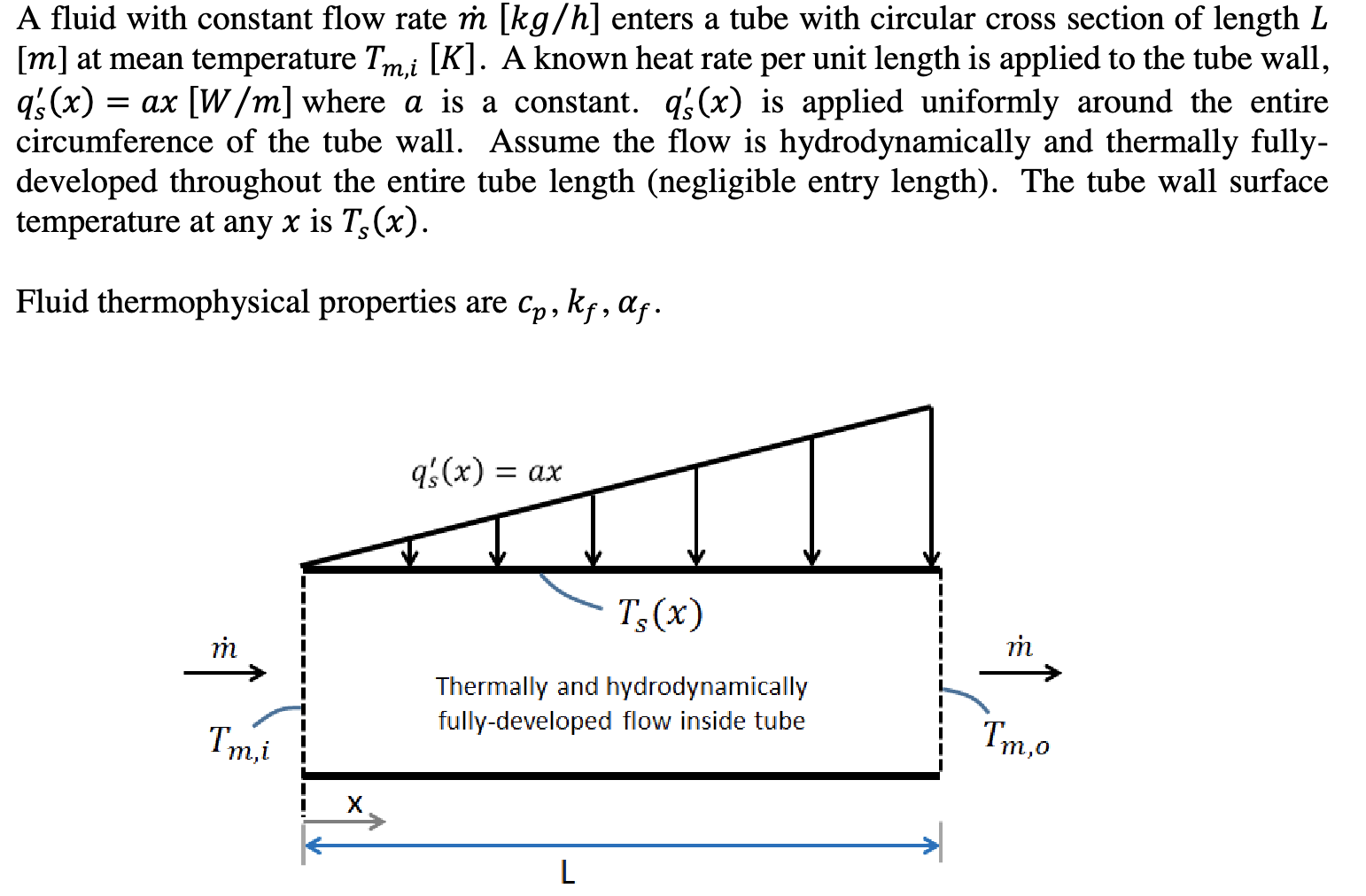
A fluid with constant flow rate m[kg/h] enters a tube with circular cross section of length L [m] at mean temperature Tm,i[K]. A known heat rate per unit length is applied to the tube wall, qs(x)=ax[W/m] where a is a constant. qs(x) is applied uniformly around the entire circumference of the tube wall. Assume the flow is hydrodynamically and thermally fullydeveloped throughout the entire tube length (negligible entry length). The tube wall surface temperature at any x is Ts(x). (a) If x is measured in meters, what are the units of the constant a in the equation given above for qs(x)? (b) Draw a differential element within the fluid and apply conservation of energy to it to write a differential equation for dTm/dx that describes the steady-state balance of energy. The equation given in part (b) above should guide you for this differential energy balance. (c) From your differential equation in part (c) above, derive an expression for the mean temperature distribution Tm(x). (d) For the given wall heating condition and fully-developed flow condition stated for this problem, does the temperature difference [Ts(x)Tm(x)] increase with x in a linear, quadratic, or exponential manner? Write linear, quadratic, or exponential and give a brief mathematical justification
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


