Question: Do part C and D only plz Consider a graphite/epoxy composite laminate with the elastic constants as given in Table 2.1. The laminate has total

Do part C and D only plz
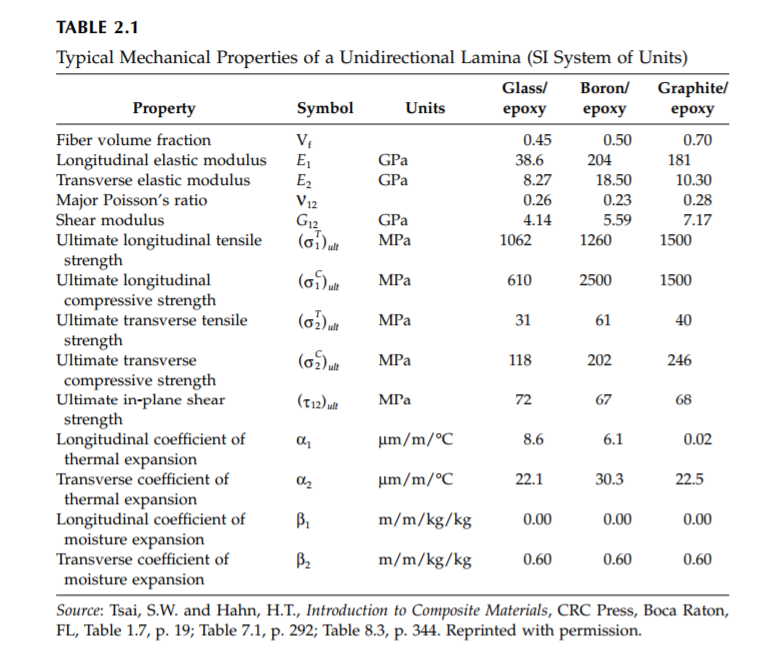
Consider a graphite/epoxy composite laminate with the elastic constants as given in Table 2.1. The laminate has total thickness of 0.9 mm and is stacked as a [0/-30/60] laminate, as shown in figure below 0 0.3 mm 30 0.3 mm 60 0.3 mm Figure: Thickness and coordinate locations of the three-ply laminate [0-30/60) Part A) Calculate the following: a) Find the reduced stiffness matrix [Q] for the 0 ply. Write a MATLAB function that calculates the reduced stiffness matrix [0]. Suggestion: name the function "ReducedStiffiness" Inputs to this function are E1, E2, V12 and G12 (from Table 2.1) and the output is [Q] matrix. Note: follow example 4.2 from Ref. |1| and example 7.1 from Ref. 2]. MATLAB function ReducedStiffness" is given on page 49 of Ref. [2 b) Find the transformed reduced stiffness matrices for angle plies-30 and 60. write a MATLAB function that calculates the transformed reduced stiffiness matrices [Q]. Suggestion: name the function "Qbar". Inputs to this function are [Q] and angle and the output is matrix for each angle ply. Note: follow example 4.2 from Ref. 1 and example 7.1 from Ref 121. MATLAB function Qbar" is given on page 62 of Ref. 121. Find the global strains (i.e., x, eyhy) at the top surface of the laminate (i.e., top surface of 0 ply) if the midplane strains and curvatures are given as follows: =400 x 10-6 and : Yoy-Kx-Ky-Kxy-0. write a MATLAB function that calculates strains at a given ply. Suggestion: name the function "Strains". Inputs to this function are .. ,Kg,Ky, Kry and distance z and the output is strain vector [Ex, yiYxy] for given ply. Note: follow example 7.1 from Ref. 121. MATLAB function Strains" is given on page 120 of Ref. 121 c) d) Use information in part c about the strain vector [Eg,Ey%y] to calculate the global stress vector [Oy; y.Tyy] at the top surface of the laminate, ie., top surface of the 0 ply. Note: follow example 7.1 from Ref,. 121 Consider a graphite/epoxy composite laminate with the elastic constants as given in Table 2.1. The laminate has total thickness of 0.9 mm and is stacked as a [0/-30/60] laminate, as shown in figure below 0 0.3 mm 30 0.3 mm 60 0.3 mm Figure: Thickness and coordinate locations of the three-ply laminate [0-30/60) Part A) Calculate the following: a) Find the reduced stiffness matrix [Q] for the 0 ply. Write a MATLAB function that calculates the reduced stiffness matrix [0]. Suggestion: name the function "ReducedStiffiness" Inputs to this function are E1, E2, V12 and G12 (from Table 2.1) and the output is [Q] matrix. Note: follow example 4.2 from Ref. |1| and example 7.1 from Ref. 2]. MATLAB function ReducedStiffness" is given on page 49 of Ref. [2 b) Find the transformed reduced stiffness matrices for angle plies-30 and 60. write a MATLAB function that calculates the transformed reduced stiffiness matrices [Q]. Suggestion: name the function "Qbar". Inputs to this function are [Q] and angle and the output is matrix for each angle ply. Note: follow example 4.2 from Ref. 1 and example 7.1 from Ref 121. MATLAB function Qbar" is given on page 62 of Ref. 121. Find the global strains (i.e., x, eyhy) at the top surface of the laminate (i.e., top surface of 0 ply) if the midplane strains and curvatures are given as follows: =400 x 10-6 and : Yoy-Kx-Ky-Kxy-0. write a MATLAB function that calculates strains at a given ply. Suggestion: name the function "Strains". Inputs to this function are .. ,Kg,Ky, Kry and distance z and the output is strain vector [Ex, yiYxy] for given ply. Note: follow example 7.1 from Ref. 121. MATLAB function Strains" is given on page 120 of Ref. 121 c) d) Use information in part c about the strain vector [Eg,Ey%y] to calculate the global stress vector [Oy; y.Tyy] at the top surface of the laminate, ie., top surface of the 0 ply. Note: follow example 7.1 from Ref,. 121
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


