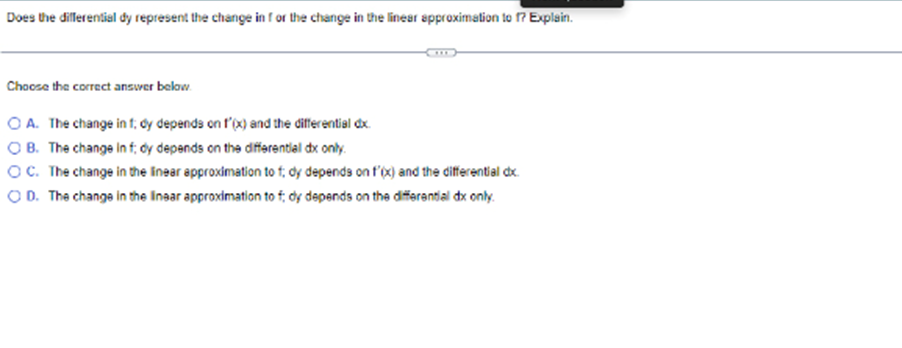
Question: Does the differential dy represent the change in for the change in the linear approximation to 7 Explain. Choose the correct answer below. ( A.




![[- 5,1] Select the correct choice below and, if necessary, fill in](https://s3.amazonaws.com/si.experts.images/answers/2024/06/667c05f446857_020667c05f4257a4.jpg)

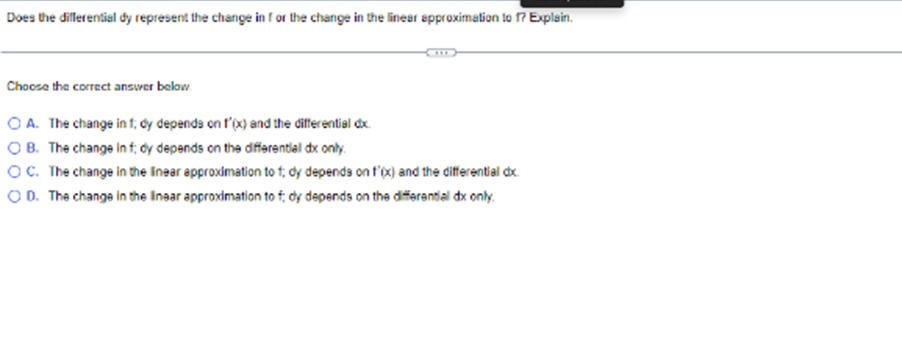
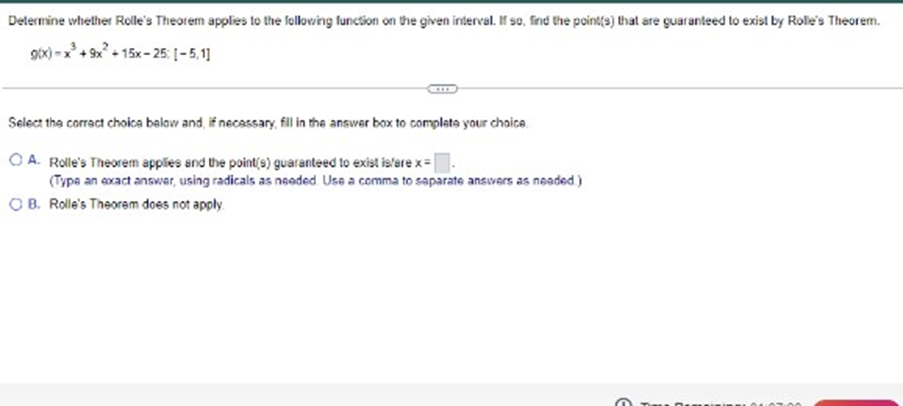
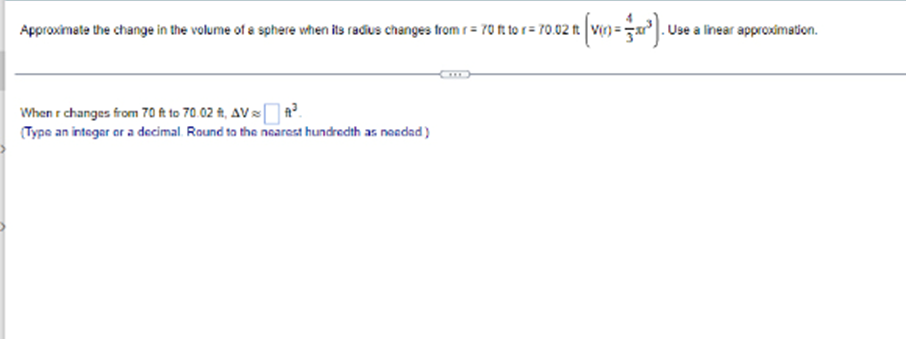




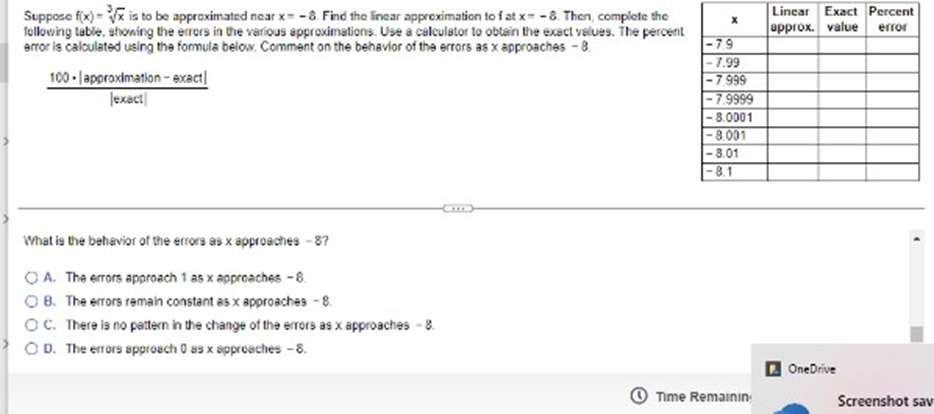
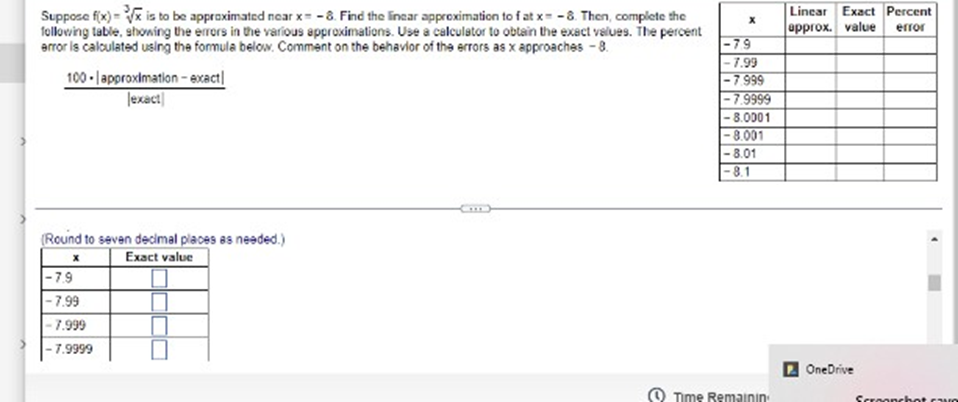
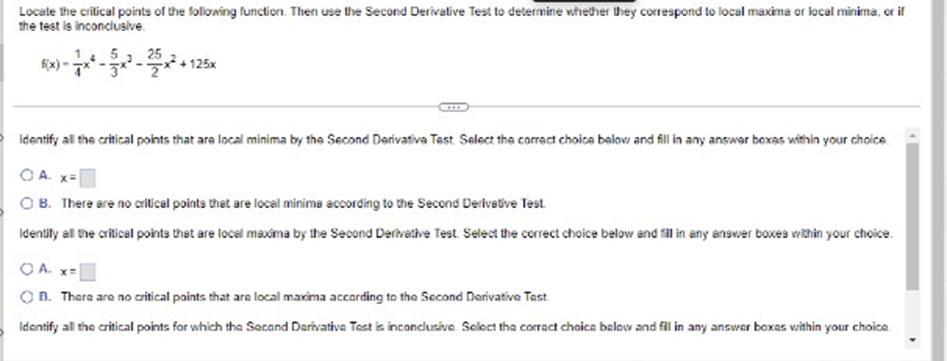

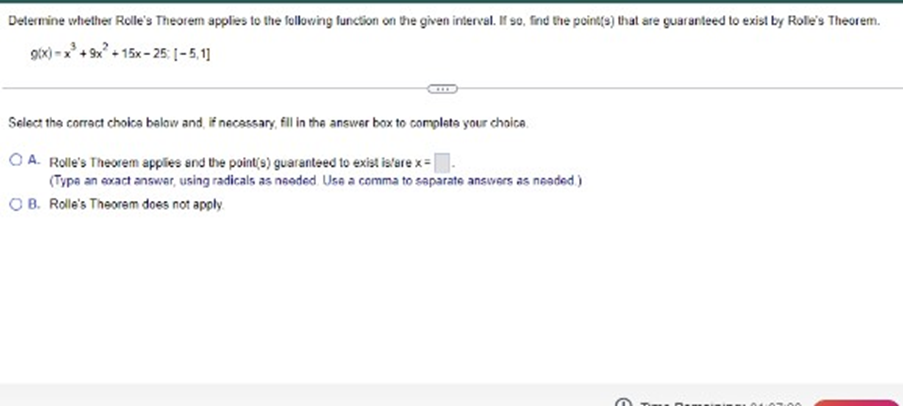
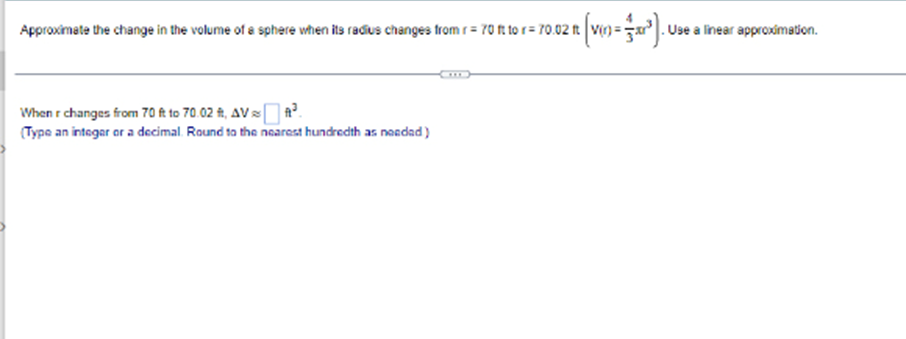
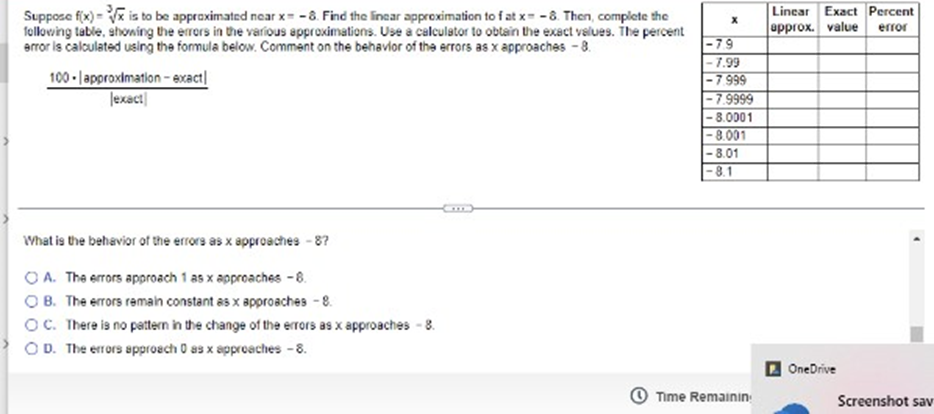
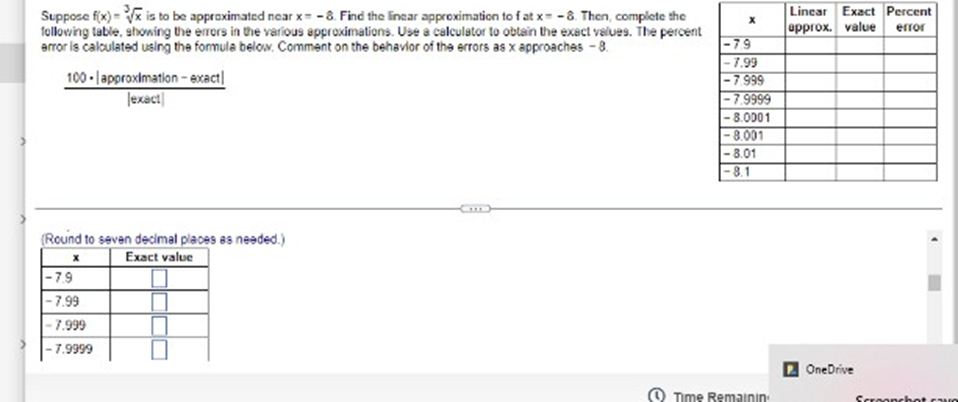
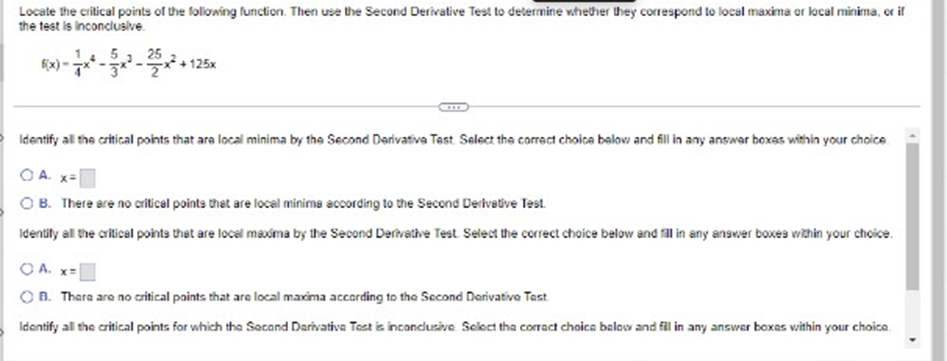
Does the differential dy represent the change in for the change in the linear approximation to 7 Explain. Choose the correct answer below. ( A. The change in f; dy depends on !'(x) and the differential dx. O B. The change In f; dy depends on the differential dx only. O C. The change in the linear approximation to f; dy depends on f'(x) and the differential dx. O D. The change in the Inear approximation to f; dy depends on the differential dx only.Determine whether Rolle's Theorem applies to the following function on the given interval. If so, find the point(s) that are guaranteed to exist by Role's Theorem. 9(x) - x + 9x + 15x - 25: [- 5,1] Select the correct choice below and, if necessary, fill in the answer box to complete your choice O A. Rolle's Theorem applies and the point(s) guaranteed to exist isfare x = (Type an exact answer, using radicals as needed. Use a comma to saparate answers as needed.) O) B. Rolle's Theorem does not apply.Approximate the change in the volume of a sphere when its radius changes fromr = 70 B tor= 70.02 1 V() = 3x . Use a linear approximation. When r changes from 70 ft to 70.02 #, AV (Type an integer or a decimal. Round to the nearest hundredth as needed )Suppose fix) = Vx is to be approximated near x= - 8. Find the linear approximation to f at x= - 8. Then, complete the Linear Exact Percent following table, showing the errors in the various approximations. Use a calculator to obtain the exact values. The percent approx. value error error is calculated using the formula below. Comment on the behavior of the errors as x approaches - 8. -79 . 7.99 100 . | approximation - exact| - 7.999 Jexact - 7.9999 8.0001 - 8.001 8.01 - 8.1 -7.9899 - 8.0001 - 8.001 - 8 01 - 8.1Suppose f(x) = Vx is to be approximated near x = - 8. Find the linear approximation to f at x = =8. Then, complete the Linear Exact Percent X following table, showing the errors in the various approximations. Use a calculator to obtain the exact values. The percent approx. value error error Is calculated using the formula below. Comment on the behavior of the errors as x approaches - 8. -79 - 7.99 100 - | approximation - exact| -7.999 exact - 7.9999 - 8.0001 - 8.001 - 8.01 - 8.1 - 8.0001 - 8.001 - 8.01 -8.1 Complete the percent error column of the table. OneDriveSuppose f(x) = Vx is to be approximated near x= - 8. Find the linear approximation to f at x = - 8. Then, complete the Linear Exact Percent X following table, showing the errors in the various approximations. Use a calculator to obtain the exact values. The percent approx. value error error Is calculated using the formula below. Comment on the behavior of the errors as x approaches - 8. -79 -7.99 100 . | approximation - exact | - 7.999 Jexact - 7.9999 - 8.0001 - 8.001 - 8.01 - 8.1 - 8.0501 - 8.001 - 8.01 - 8.1 What is the behavior of the errors as x approaches - 87 OneDriveSuppose f(x) = Vx is to be approximated near x= = 8. Find the linear approximation to f at x = = 8. Then, complete the Linear Exact Percent X following table, showing the errors in the various approximations. Use a calculator to obtain the exact values. The percent approx. value error error Is calculated using the formula below. Comment on the behavior of the errors as x approaches - 8. -79 7.99 100 - | approximation - exact| 7.999 [exact] - 7.9999 - 8.0001 - 8.001 - 8.01 - 8.1 Complete the percent error column of the table (Use scientific notation. Use the multiplication symbol in the math palette as needed. Do not round until the final answer. Then round to one decimal place as needed.) X Percent error 7.9 . 7.99 - 7.999Suppose fix) = Vx is to be approximated near x = - 8. Find the linear approximation to f at x= = 8. Then, complete the Linear Exact Percent X following table, showing the errors in the various approximations. Use a calculator to obtain the exact values. The percent approx. value error error Is calculated using the formula below. Comment on the behavior of the errors as x approaches - 8. -79 -7.99 100 . | approximation - exact| - 7.999 Jexact - 7.9999 - 8.0001 - 8.001 8.01 - 8.1 What is the behavior of the errors as x approaches - 87 O A. The errors approach 1 as x approaches - 8. O B. The errors remain constant as x approaches - 8. O C. There is no pattern in the change of the errors as x approaches - 8. O D. The errors approach 0 as x approaches - 8. OneDrive Time Remaining Screenshot savSuppose fix) = Vx is to be approximated near x = - 8. Find the linear approximation to f at x = - 8. Then, complete the Linear Exact Percent X following table, showing the errors in the various approximations. Use a calculator to obtain the exact values. The percent approx. value error error Is calculated using the formula below. Comment on the behavior of the errors as x approaches - 8. -79 - 7.99 100 . | approximation - exact| - 7.999 Jexact -7.9999 8.0001 - 8.001 - 8.01 -8.1 (Round to seven decimal places as needed.) X Exact value -7.9 -7.99 7.999 -7.9999 OneDrive Time RemaininLocate the critical points of the following function. Then use the Second Derivative Test to determine whether they correspond to local maxima or local minima, or if the test is Inconclusive. 5 25 + 125x Identify all the critical points that are local minima by the Second Derivative Test Select the correct choice below and fill in any answer boxes within your choice O A. x= O B. There are no critical points that are local minime according to the Second Derivative Test. Identify all the critical points that are locel moodma by the Second Derivative Test. Select the correct choice below and fill in any answer boxes within your choice. O A. x= O B. There are no critical points that are local maxima according to the Second Derivative Test Identify all the critical points for which the Second Derivative Test is inconclusive. Select the correct choice below and fill in any answer boxes within your choiceUse the derivative f'(x)=>"(x-5)(x + 1) to determine the local maxima and minima off and the intervals of increase and decrease. Sketch a possible graph of f (f is not unique) The local maximum/maxima is/are at x =] (Use a comma to separate answers as needed.] The local minimum/minima is/are at x=] (Use a comma to separate answers as needed.) The interval(s) of increase is/are]. (Type your answer in interval notation Use a comma to separate answers as needed ) The interval(s) of decrease is(are) (Type your answer in interval notation. Use a comma to separate answers as needed.) Which is a possible graph of 17 O A. O B. OC. OD. OLocate the critical points of the following function. Then use the Second Derivative Test to determine whether they correspond to local maxima or local minima, or if the test is Inconclusive 5 25 2 + 125x O) B. There are no critical points that are local minima according to the Second Derivative Tast Identify all the critical points that are local maxima by the Second Derivative Test Select the correct choice below and fill in any answer boxes within your choice O A. x= O B. There are no critical points that are local maxima according to the Second Derivative Test Identify all the critical points for which the Second Derivative Test is inconclusive. Select the correct choice below and fill in any answer boxes within your choice. O A. x= O B. There are no critical points for which the Second Derivative Test is inconclusive
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


