Question: doesnt allow me to make the image bigger.. i know when i zoom in on my laptop screen with (Command & +) its readable. not
doesnt allow me to make the image bigger.. i know when i zoom in on my laptop screen with (Command & +) its readable. not sure how else to make the image bigger? 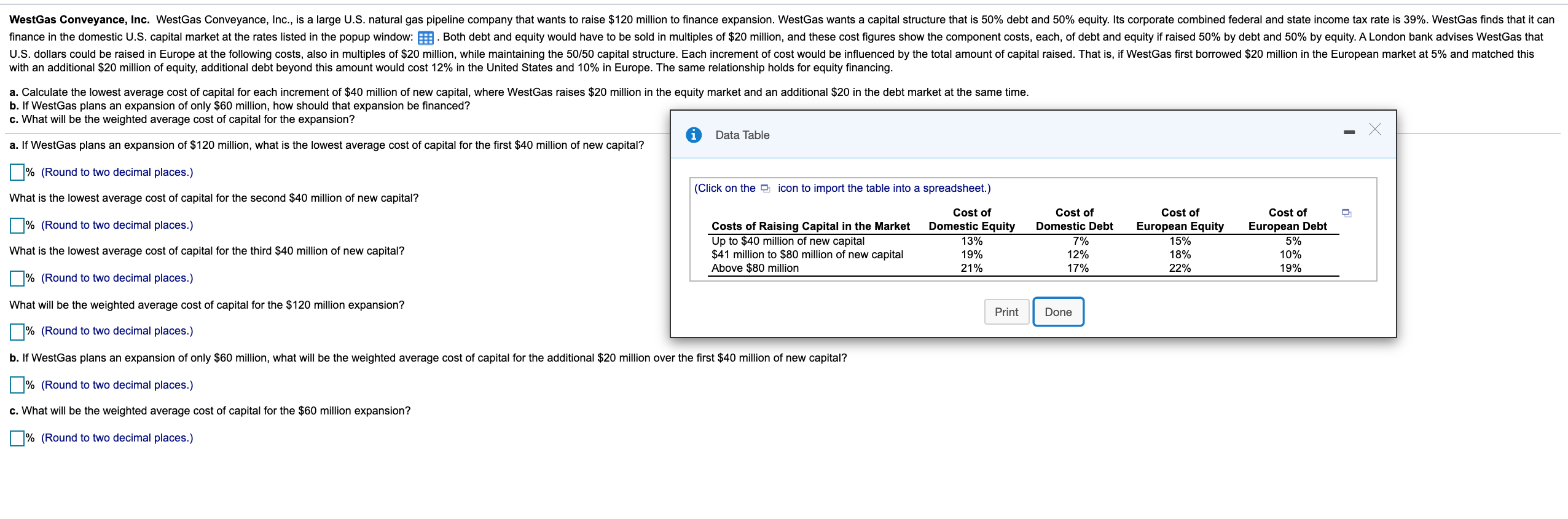
WestGas Conveyance, Inc. WestGas Conveyance, Inc., is a large U.S. natural gas pipeline company that wants to raise $120 million to finance expansion. WestGas wants a capital structure that is 50% debt and 50% equity. Its corporate combined federal and state income tax rate is 39%. WestGas finds that it can finance in the domestic U.S. capital market at the rates listed in the popup window: :. Both debt and equity would have to be sold in multiples of $20 million, and these cost figures show the component costs, each, of debt and equity if raised 50% by debt and 50% by equity. A London bank advises WestGas that U.S. dollars could be raised in Europe at the following costs, also in multiples of $20 million, while maintaining the 50/50 capital structure. Each increment of cost would be influenced by the total amount of capital raised. That is, if WestGas first borrowed $20 million in the European market at 5% and matched this with an additional $20 million of equity, additional debt beyond this amount would cost 12% in the United States and 10% in Europe. The same relationship holds for equity financing. a. Calculate the lowest average cost of capital for each increment of $40 million of new capital, where WestGas raises $20 million in the equity market and an additional $20 in the debt market at the same time. b. If WestGas plans an expansion of only $60 million, how should that expansion be financed? c. What will be the weighted average cost of capital for the expansion? Data Table a. If WestGas plans an expansion of $120 million, what is the lowest average cost of capital for the first $40 million of new capital? % (Round to two decimal places.) (Click on the icon to import the table into a spreadsheet.) What is the lowest average cost of capital for the second $40 million of new capital? | % (Round to two decimal places.) Cost of Cost of Domestic EquityDomestic Debt 7% 19% 21% 17% 13% Costs of Raising Capital in the Market Up to $40 million of new capital $41 million to $80 million of new capital Above $80 million Cost of European Equity 15% 18% 22% Cost of European Debt 5% 10% 19% What is the lowest average cost of capital for the third $40 million of new capital? 12% | % (Round to two decimal places.) What will be the weighted average cost of capital for the $120 million expansion? Print Print Done Done % (Round to two decimal places.) b. If WestGas plans an expansion of only $60 million, what will be the weighted average cost of capital for the additional $20 million over the first $40 million of new capital? | % (Round to two decimal places.) c. What will be the weighted average cost of capital for the $60 million expansion? % (Round to two decimal places.) WestGas Conveyance, Inc. WestGas Conveyance, Inc., is a large U.S. natural gas pipeline company that wants to raise $120 million to finance expansion. WestGas wants a capital structure that is 50% debt and 50% equity. Its corporate combined federal and state income tax rate is 39%. WestGas finds that it can finance in the domestic U.S. capital market at the rates listed in the popup window: :. Both debt and equity would have to be sold in multiples of $20 million, and these cost figures show the component costs, each, of debt and equity if raised 50% by debt and 50% by equity. A London bank advises WestGas that U.S. dollars could be raised in Europe at the following costs, also in multiples of $20 million, while maintaining the 50/50 capital structure. Each increment of cost would be influenced by the total amount of capital raised. That is, if WestGas first borrowed $20 million in the European market at 5% and matched this with an additional $20 million of equity, additional debt beyond this amount would cost 12% in the United States and 10% in Europe. The same relationship holds for equity financing. a. Calculate the lowest average cost of capital for each increment of $40 million of new capital, where WestGas raises $20 million in the equity market and an additional $20 in the debt market at the same time. b. If WestGas plans an expansion of only $60 million, how should that expansion be financed? c. What will be the weighted average cost of capital for the expansion? Data Table a. If WestGas plans an expansion of $120 million, what is the lowest average cost of capital for the first $40 million of new capital? % (Round to two decimal places.) (Click on the icon to import the table into a spreadsheet.) What is the lowest average cost of capital for the second $40 million of new capital? | % (Round to two decimal places.) Cost of Cost of Domestic EquityDomestic Debt 7% 19% 21% 17% 13% Costs of Raising Capital in the Market Up to $40 million of new capital $41 million to $80 million of new capital Above $80 million Cost of European Equity 15% 18% 22% Cost of European Debt 5% 10% 19% What is the lowest average cost of capital for the third $40 million of new capital? 12% | % (Round to two decimal places.) What will be the weighted average cost of capital for the $120 million expansion? Print Print Done Done % (Round to two decimal places.) b. If WestGas plans an expansion of only $60 million, what will be the weighted average cost of capital for the additional $20 million over the first $40 million of new capital? | % (Round to two decimal places.) c. What will be the weighted average cost of capital for the $60 million expansion? % (Round to two decimal places.)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


