Question: don't know how to do question 3 and 4 In our derivation of the BlackScholes equation we used the result that N(a:) +N(:1:) = 1
don't know how to do question 3 and 4
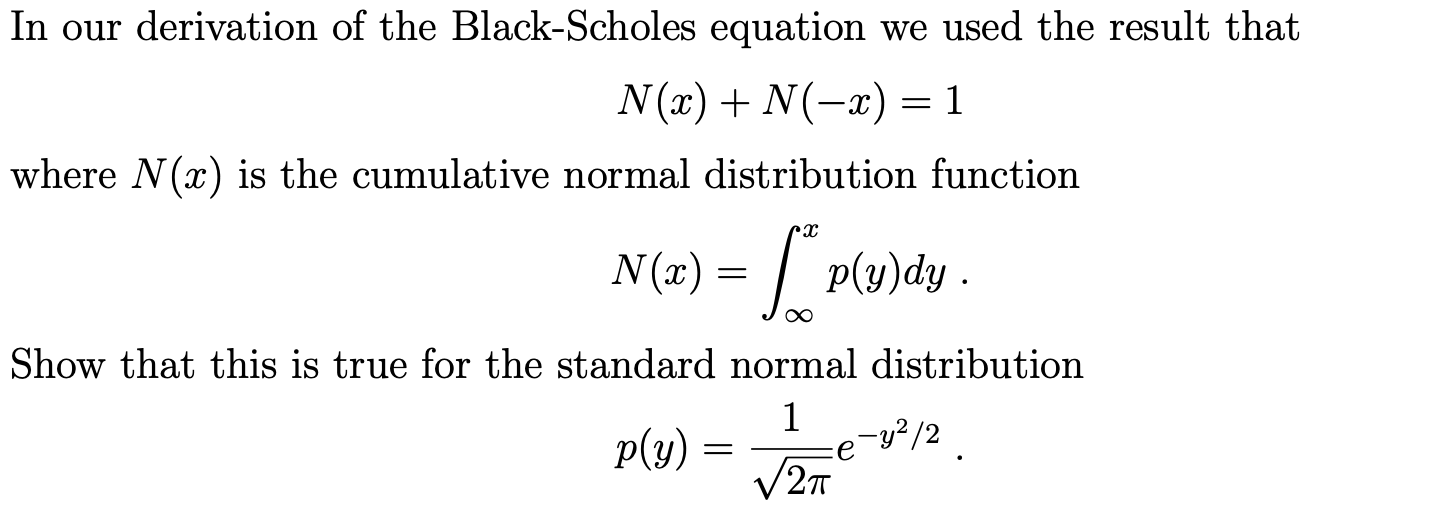
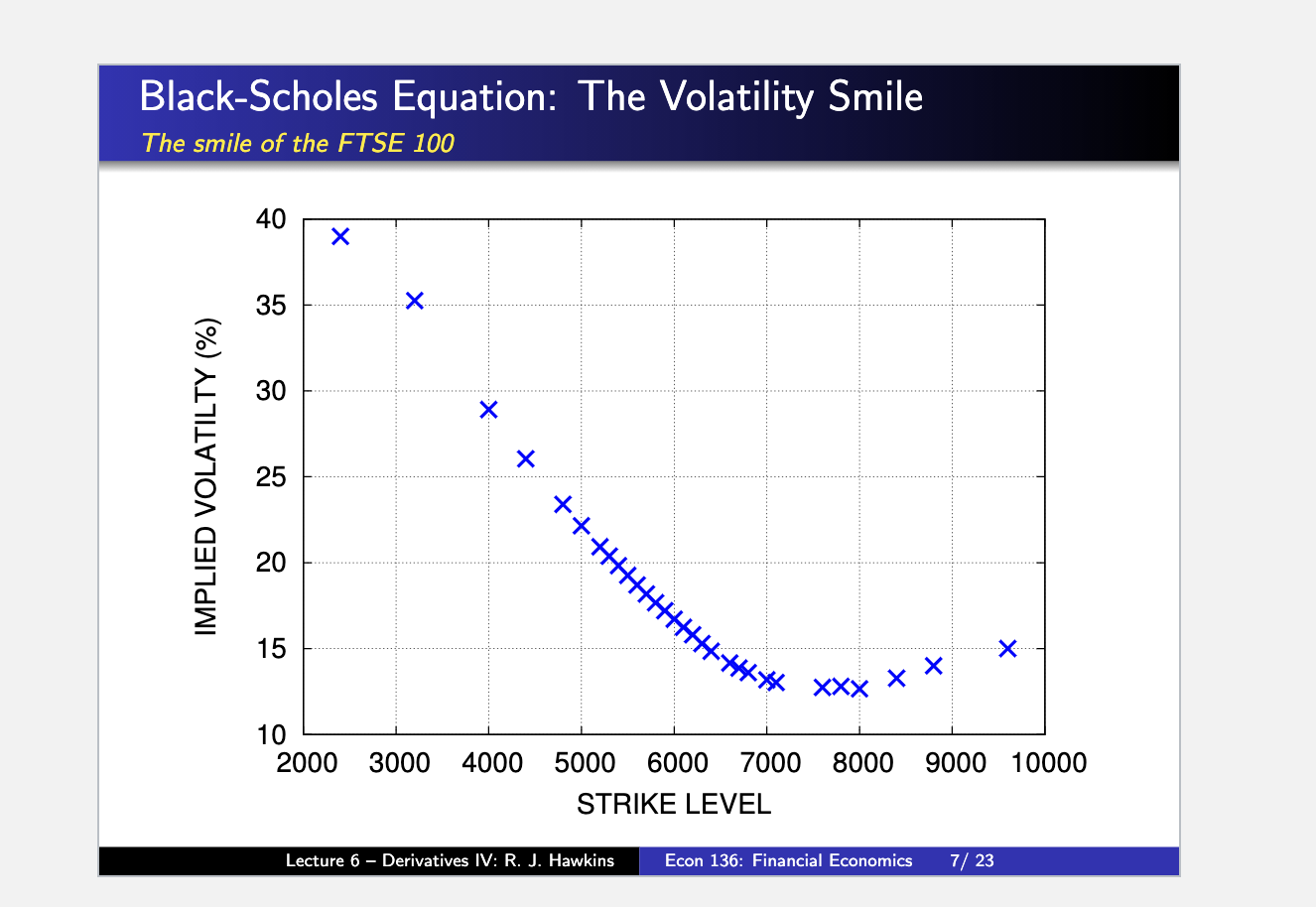
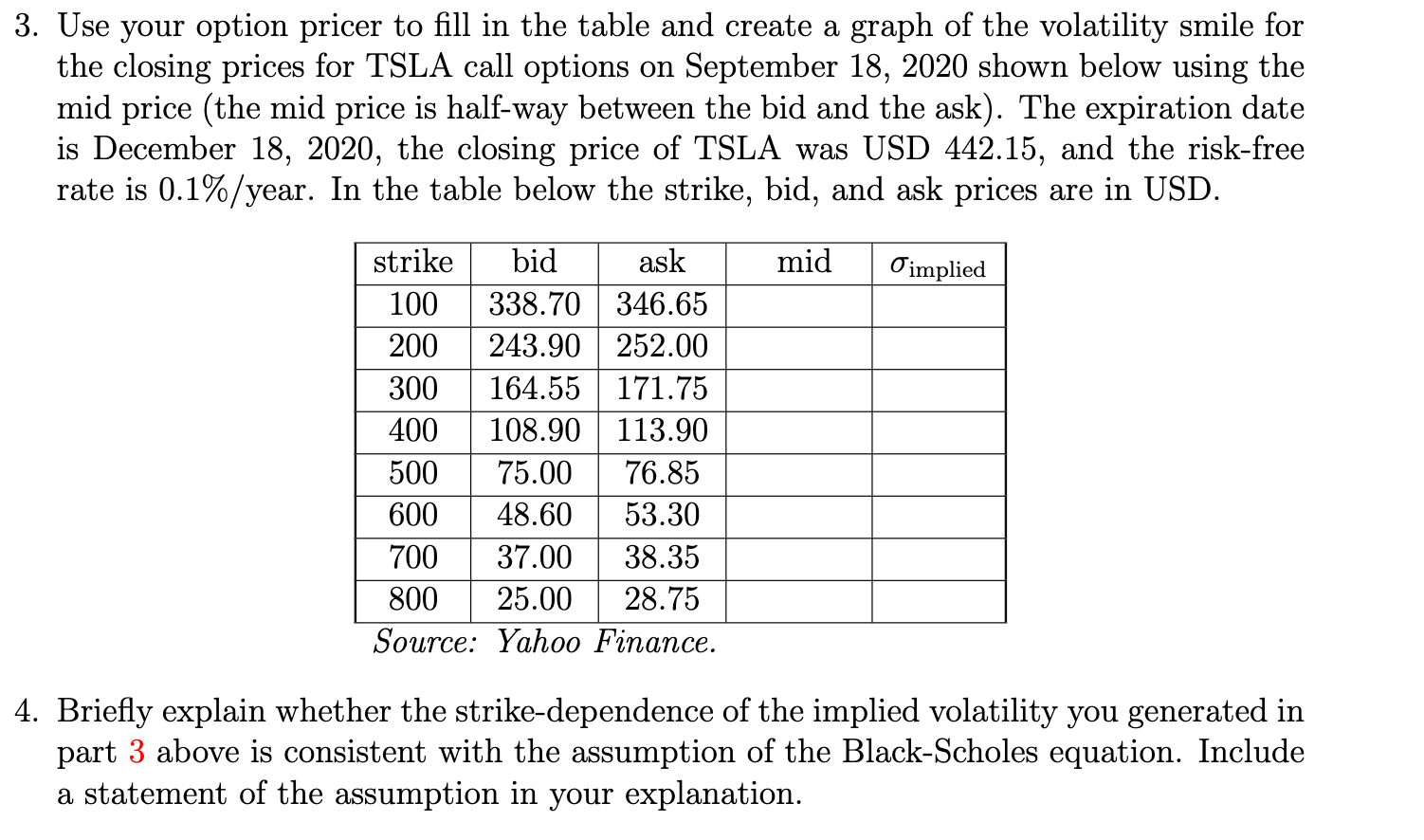
In our derivation of the BlackScholes equation we used the result that N(a:) +N(:1:) = 1 Where N (as) is the cumulative normal distribution function N (a?) = [$p(y)dy- 00 Show that this is true for the standard normal distribution 1 19(3)) 2 E6 92/2 . BIack-Scholes Equation: The Volatility Smile The smile of the FTSE 100 40 35 30 25 20 a}: E I It: _I O > D \"_J _| n. E 15 10 2000 3000 4000 5000 6000 7000 8000 9000 10000 STRIKE LEVEL Lecture 6 Derivatives IV: R. J. Econ 136: Financial Economics 7;" 23 3. Use your option pricer to ll in the table and create a graph of the volatility smile for the closing prices for TSLA call options on September 18, 2020 shown below using the mid price (the mid price is halfway between the bid and the ask). The expiration date is December 18, 2020, the closing price of TSLA was USD 442.15, and the riskfree rate is 0.1% / year. In the table below the strike, bid, and ask prices are in USD. bld ask m1d 0' implied 338.70 346.65 - 243-90 - 164-55 -_- 108.90 -- 75.00 48.60 -- 37.00 25.00 -- Source: Yahoo Finance. 4. Briey explain whether the strikedependence of the implied volatility you generated in part 3 above is consistent with the assumption of the BlackScholes equation. Include a statement of the assumption in your explanation
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


