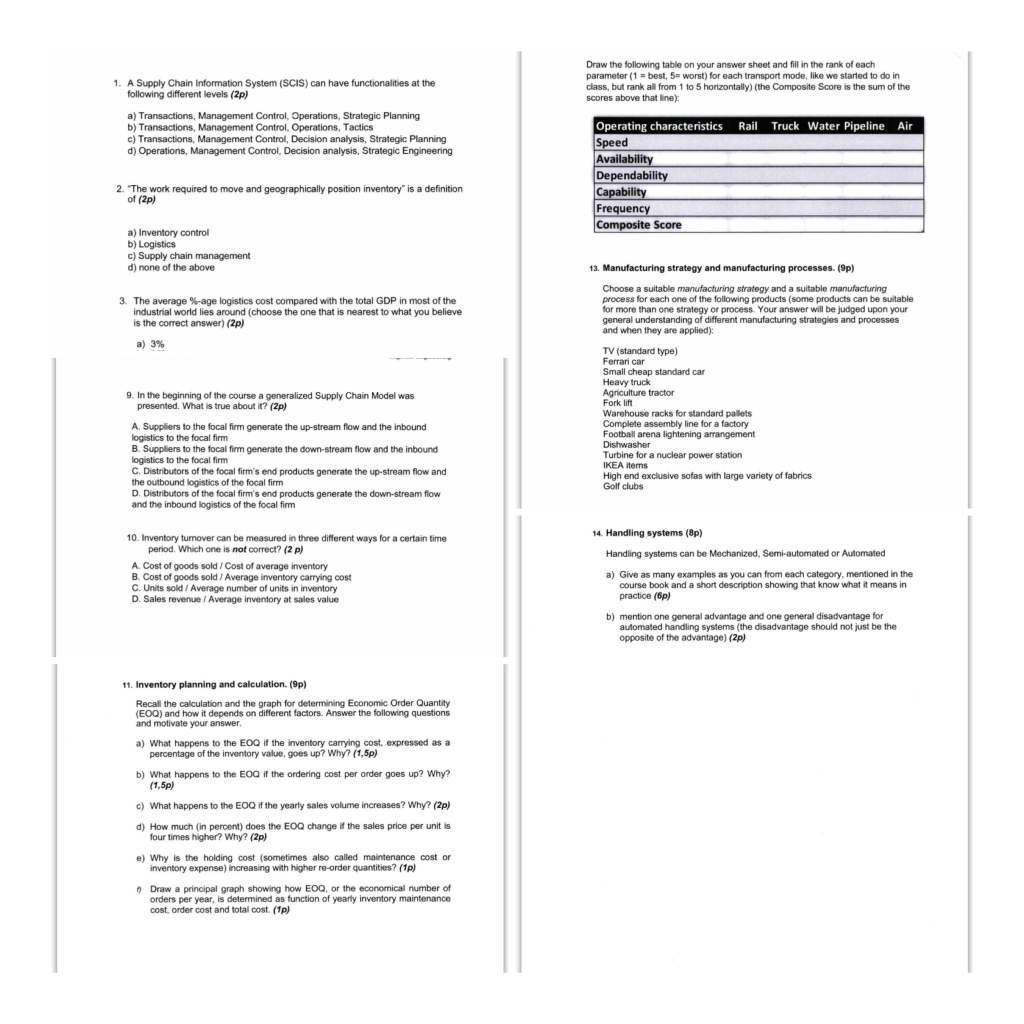
Draw the following table on your answer sheet and fill in the rank of each parameter (1 = best, 5= worst) for each transport mode, like we started to do in class, but rank all from 1 to 5 horizontally) (the Composite Score is the sum of the scores above that line): 1. A Supply Chain Information System (SCIS) can have functionalities at the following different levels (2p) a) Transactions, Management Control, Operations, Strategic Planning b) Transactions, Management Control, Operations, Tactics c) Transactions, Management Control, Decision analysis, Strategic Planning d) Operations, Management Control, Decision analysis, Strategic Engineering Operating characteristics Rail Truck Water Pipeline Air Speed Availability Dependability Capability Frequency Composite Score 2. The work required to move and geographically position inventory is a definition of (2p) a) Inventory control b) Logistics c) Supply chain management d) none of the above 3. The average %-age logistics cost compared with the total GDP in most of the industrial world lies around (choose the one that is nearest to what you believe is the correct answer) (2p) a) 3% 13. Manufacturing strategy and manufacturing processes. (Sp) Choose a suitable manufacturing strategy and a suitable manufacturing process for each one of the following products (some products can be suitable for more than one strategy or process. Your answer will be judged upon your general understanding of different manufacturing strategies and processes and when they are applied) TV (standard type) Ferrari car Small cheap standard car Heavy truck Agriculture tractor Forklift Warehouse racks for standard pallets Complete assembly line for a factory Football arena lightening arrangement Dishwasher Turbine for a nuclear power station IKEA items High end exclusive sofas with large variety of fabrics Golf clubs 9. In the beginning of the course a generalized Supply Chain Model was presented. What is true about it? (2p) A. Suppliers to the focal firm generate the up-stream flow and the inbound logistics to the focal firm B. Suppliers to the focal firm generate the down-stream flow and the inbound logistics to the focal firm C. Distributors of the focal firm's end products generate the up-stream flow and - the outbound logistics of the focal firm D. Distributors of the focal firm's end products generate the down-stream flow and the inbound logistics of the focal fimm 14. Handling systems (8) 10. Inventory turnover can be measured in three different ways for a certain time period. Which one is not correct? (2p) A. Cost of goods sold / Cost of average inventory B. Cost of goods sold / Average inventory carrying cost C. Units sold / Average number of units in inventory D. Sales revenue / Average inventory at sales value Handling systems can be Mechanized, Semi-automated or Automated , - a) Give as many examples as you can from each category, mentioned in the course book and a short description showing that know what it means in practice (6p) b) mention one general advantage and one general disadvantage for automated handling systems (the disadvantage should not just be the opposite of the advantage) (2p) 11. Inventory planning and calculation. (p) Recall the calculation and the graph for determining Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) and how it depends on different factors. Answer the following questions and motivate your answer. a) What happens to the EOQ if the inventory carrying cost, expressed as a percentage of the inventory value, goes up? Why? (1,5p) b) What happens to the EOg if the ordering cost per order goes up? Why? (1,5p) c) What happens to the EOQ if the yearly sales volume increases? Why? (2p) d) How much (in percent) does the EOQ change if the sales price per unit is four times higher? Why? (2p) e) Why is the holding cost (sometimes also called maintenance cost or inventory expense) increasing with higher re-order quantities? (p) Draw a principal graph showing how EOQ, or the economical number of orders per year, is determined as function of yearly inventory maintenance cost, order cost and total cost. (1p) Write your name on all sheets submitted! 16. Production AB produce a popular game, called "Get your grade". Table 2 2 illustrates the aggregated demand for the game over the past 25 days. Table 3. Summary of Production AB's performance cycles over the past replenishments Performance Frequency cycle (days) 5 4 8 7 Section Ill: Calculation Questions, 45 points Make sure that is easy to understand your answer your solution and that you answer the actual question. Remember to use the righi unitspieces klo/SEK etc. An answer without or with the wrong unit is not approved. All abbreviations must be clarified. All calculations should follow in a logic sequence. Remember to clarity which part that is your answer For your convenience, a forme sheet is provided on the last page of this exam The answers should be on separate papers for each one of the numbered questions meaning that the answers for question 15, 16, 17 and 18 should each one start on a new paper. Solution and answers of the sub-problems a, b, c, d etc should be clearly separated from each other but may be on the same paper 7 9 9 8 10 Table 2. Demand for the past 25 days. Day Demand Day Demand 1 10 14 9 9 2 2 9 15 10 3 3 11 16 13 . 47 4 12 17 10 . 5 10 18 8 9 9 10 7 11 4 6 11 19 11 15. Fire AB buys 3 different products from 3 separate suppliers, see Table 1. The CEO of Fire AB has just hired you to investigate the inventory and she tells you that the company use an order cost of 250 SEK, and an inventory carrying cost percentage of 20%. The company sells products al 52 weeks of the year, and during all seven days of the week. Your first task for the day is to identify the following answers 7 7 20 10 8 10 21 8 d) Calculate the standard deviation for the performance cycle (2p) e) What is the combined standard deviation under conditions of demand and performance cycle uncertainties? (2p) The typical order quantity is 50 units, and Production AB strive to have a 95 percent product availability level. Calculate the required safety stock (2p) 9 22 11 10 12 23 12 11 10 9 Table 1. Information about the three different products Supplier Product Demand year Value/ unit (units) name (SEK) 1 PUR 15 000 10 2 KUR 10 000 15 3 TUR 20 000 5 24 25 11 9 12 13 8 17. Car-Isson produce an electric car called "Start-IT having a steady demand of 500 cars/week To manufacture one "Start-IT 4 tires are needed, these tires are ordered from a German supplier. Depending on the ordered quantity, it is possible to receive a discount. So, the company has two options when ordering the tires a . Option 1. Order less than 5000 tires at the time, each tire costs 400 SEK Option 2. Order 5000 or more tires time, the cost for each tire is instead 300 SEK a) What is the EOQ for the three separate products? (p) b) What is the average inventory level for the three separate products? (2p) a) Is the demand distribution normal? How do you know? (2p) b) Calculate the standard deviation for daily demand. Assume in this ca: ) that the performance cycle is constant (2) c) Is the performance cycle distribution normal? How do you know? (2 p c) What is the aggregated average inventory value? (2) d) What is the aggregated inventory expense? (2p) e) What is the throughput time for the three separate products? (3p) Carlsson do not use a safety stock since the lead-time for receiving the tires are just 1 day. They use an Inventory carrying cost percent of 15%, the ordering cost is 300 SEK/ order You have just been hired by Carlsson and your first task is to decide how many tires you should order based on lowest total cost, including the cost for order, cost for holding the inventory and the cost for buying the tires. Tip! Use the EOQ formula when appropriate. Motivate your answer. Assume that one year have 52 weeks. (12) a) Routine purchases could be a high level of supply risk b) Suppliers with high supply value are called leverage suppliers c) Items with high value to the firm and with high level of supply risk is a critical purchase which typically requires integration with suppliers d) High demand and high value results in bottleneck purchases d) 5. An Advanced Planning System (APS) aims primarily to (2p) 18. Christmas is on its way and it is time for the electronical store Lamp AB to plan how to distribute their product "Bright, Cool & Fantastic" (BCF) out to their distribution centers. The plant warehouse currently has 120 000 BCFs on stock and HR wants to use 5000 of them to give away as presents to the employees, the rest is to be distributed. Light AB have four distribution centers (DC) in Sweden. DC 1 has an inventory of 25 000 units and a daily demand of 3 000 units. DC 2 has an inventory of 35 000 units and daily demand of 15 000 units. DC 3 has an inventory of 15 000 units and a daily demand of 15 000 units Finally, DC 4 has an inventory of 20 000 units and a daily demand of 7 000 units. a) Eliminate the bullwhip effect by controlling supply chain movements based on customer demand b) Create supply chain visibility c) To control customer deliveries to be delivered on time d) Generate Purchase orders based on supply chain movements Given the above information use fair-share-allocation logic to answer the following questions. a) How many days will Lamp AB be able to sell the product BCF before they run out of stock, based on the assumed demands? ? (2p) 6. The elapsed time between order and shipment is called (2p) a. Leadtime b. Cash to cash conversion time, CCC C. Supply time d. Performance cycle time b) How many units shall each DC have delivered if fair-share-allocation logic is used? (2 p) c) If the daily demand increases by 5%, how many days will Light AB be able to sell before they run out of stock, and how many units should each DC have delivered if fair-share-allocation logic is used? (3 p) 7. According to the course, Network economics = (2p) a) Transportation economics + Warehousing economics b) Distribution economics + Inventory Economics c) Transportation economics + Inventory economics d) Inbound economics + Inventory economics + Outbound economics 8. Which inventory definition is NOT correct? (2p) a. Cycle inventory - average stock, resulting from replenishment b. Transit inventory = goods planned to be shipped c. Obsolete inventory stock out of date or without recent demand d. Inventory = all goods stocked in a company, including goods being Draw the following table on your answer sheet and fill in the rank of each parameter (1 = best, 5= worst) for each transport mode, like we started to do in class, but rank all from 1 to 5 horizontally) (the Composite Score is the sum of the scores above that line): 1. A Supply Chain Information System (SCIS) can have functionalities at the following different levels (2p) a) Transactions, Management Control, Operations, Strategic Planning b) Transactions, Management Control, Operations, Tactics c) Transactions, Management Control, Decision analysis, Strategic Planning d) Operations, Management Control, Decision analysis, Strategic Engineering Operating characteristics Rail Truck Water Pipeline Air Speed Availability Dependability Capability Frequency Composite Score 2. The work required to move and geographically position inventory is a definition of (2p) a) Inventory control b) Logistics c) Supply chain management d) none of the above 3. The average %-age logistics cost compared with the total GDP in most of the industrial world lies around (choose the one that is nearest to what you believe is the correct answer) (2p) a) 3% 13. Manufacturing strategy and manufacturing processes. (Sp) Choose a suitable manufacturing strategy and a suitable manufacturing process for each one of the following products (some products can be suitable for more than one strategy or process. Your answer will be judged upon your general understanding of different manufacturing strategies and processes and when they are applied) TV (standard type) Ferrari car Small cheap standard car Heavy truck Agriculture tractor Forklift Warehouse racks for standard pallets Complete assembly line for a factory Football arena lightening arrangement Dishwasher Turbine for a nuclear power station IKEA items High end exclusive sofas with large variety of fabrics Golf clubs 9. In the beginning of the course a generalized Supply Chain Model was presented. What is true about it? (2p) A. Suppliers to the focal firm generate the up-stream flow and the inbound logistics to the focal firm B. Suppliers to the focal firm generate the down-stream flow and the inbound logistics to the focal firm C. Distributors of the focal firm's end products generate the up-stream flow and - the outbound logistics of the focal firm D. Distributors of the focal firm's end products generate the down-stream flow and the inbound logistics of the focal fimm 14. Handling systems (8) 10. Inventory turnover can be measured in three different ways for a certain time period. Which one is not correct? (2p) A. Cost of goods sold / Cost of average inventory B. Cost of goods sold / Average inventory carrying cost C. Units sold / Average number of units in inventory D. Sales revenue / Average inventory at sales value Handling systems can be Mechanized, Semi-automated or Automated , - a) Give as many examples as you can from each category, mentioned in the course book and a short description showing that know what it means in practice (6p) b) mention one general advantage and one general disadvantage for automated handling systems (the disadvantage should not just be the opposite of the advantage) (2p) 11. Inventory planning and calculation. (p) Recall the calculation and the graph for determining Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) and how it depends on different factors. Answer the following questions and motivate your answer. a) What happens to the EOQ if the inventory carrying cost, expressed as a percentage of the inventory value, goes up? Why? (1,5p) b) What happens to the EOg if the ordering cost per order goes up? Why? (1,5p) c) What happens to the EOQ if the yearly sales volume increases? Why? (2p) d) How much (in percent) does the EOQ change if the sales price per unit is four times higher? Why? (2p) e) Why is the holding cost (sometimes also called maintenance cost or inventory expense) increasing with higher re-order quantities? (p) Draw a principal graph showing how EOQ, or the economical number of orders per year, is determined as function of yearly inventory maintenance cost, order cost and total cost. (1p) Write your name on all sheets submitted! 16. Production AB produce a popular game, called "Get your grade". Table 2 2 illustrates the aggregated demand for the game over the past 25 days. Table 3. Summary of Production AB's performance cycles over the past replenishments Performance Frequency cycle (days) 5 4 8 7 Section Ill: Calculation Questions, 45 points Make sure that is easy to understand your answer your solution and that you answer the actual question. Remember to use the righi unitspieces klo/SEK etc. An answer without or with the wrong unit is not approved. All abbreviations must be clarified. All calculations should follow in a logic sequence. Remember to clarity which part that is your answer For your convenience, a forme sheet is provided on the last page of this exam The answers should be on separate papers for each one of the numbered questions meaning that the answers for question 15, 16, 17 and 18 should each one start on a new paper. Solution and answers of the sub-problems a, b, c, d etc should be clearly separated from each other but may be on the same paper 7 9 9 8 10 Table 2. Demand for the past 25 days. Day Demand Day Demand 1 10 14 9 9 2 2 9 15 10 3 3 11 16 13 . 47 4 12 17 10 . 5 10 18 8 9 9 10 7 11 4 6 11 19 11 15. Fire AB buys 3 different products from 3 separate suppliers, see Table 1. The CEO of Fire AB has just hired you to investigate the inventory and she tells you that the company use an order cost of 250 SEK, and an inventory carrying cost percentage of 20%. The company sells products al 52 weeks of the year, and during all seven days of the week. Your first task for the day is to identify the following answers 7 7 20 10 8 10 21 8 d) Calculate the standard deviation for the performance cycle (2p) e) What is the combined standard deviation under conditions of demand and performance cycle uncertainties? (2p) The typical order quantity is 50 units, and Production AB strive to have a 95 percent product availability level. Calculate the required safety stock (2p) 9 22 11 10 12 23 12 11 10 9 Table 1. Information about the three different products Supplier Product Demand year Value/ unit (units) name (SEK) 1 PUR 15 000 10 2 KUR 10 000 15 3 TUR 20 000 5 24 25 11 9 12 13 8 17. Car-Isson produce an electric car called "Start-IT having a steady demand of 500 cars/week To manufacture one "Start-IT 4 tires are needed, these tires are ordered from a German supplier. Depending on the ordered quantity, it is possible to receive a discount. So, the company has two options when ordering the tires a . Option 1. Order less than 5000 tires at the time, each tire costs 400 SEK Option 2. Order 5000 or more tires time, the cost for each tire is instead 300 SEK a) What is the EOQ for the three separate products? (p) b) What is the average inventory level for the three separate products? (2p) a) Is the demand distribution normal? How do you know? (2p) b) Calculate the standard deviation for daily demand. Assume in this ca: ) that the performance cycle is constant (2) c) Is the performance cycle distribution normal? How do you know? (2 p c) What is the aggregated average inventory value? (2) d) What is the aggregated inventory expense? (2p) e) What is the throughput time for the three separate products? (3p) Carlsson do not use a safety stock since the lead-time for receiving the tires are just 1 day. They use an Inventory carrying cost percent of 15%, the ordering cost is 300 SEK/ order You have just been hired by Carlsson and your first task is to decide how many tires you should order based on lowest total cost, including the cost for order, cost for holding the inventory and the cost for buying the tires. Tip! Use the EOQ formula when appropriate. Motivate your answer. Assume that one year have 52 weeks. (12) a) Routine purchases could be a high level of supply risk b) Suppliers with high supply value are called leverage suppliers c) Items with high value to the firm and with high level of supply risk is a critical purchase which typically requires integration with suppliers d) High demand and high value results in bottleneck purchases d) 5. An Advanced Planning System (APS) aims primarily to (2p) 18. Christmas is on its way and it is time for the electronical store Lamp AB to plan how to distribute their product "Bright, Cool & Fantastic" (BCF) out to their distribution centers. The plant warehouse currently has 120 000 BCFs on stock and HR wants to use 5000 of them to give away as presents to the employees, the rest is to be distributed. Light AB have four distribution centers (DC) in Sweden. DC 1 has an inventory of 25 000 units and a daily demand of 3 000 units. DC 2 has an inventory of 35 000 units and daily demand of 15 000 units. DC 3 has an inventory of 15 000 units and a daily demand of 15 000 units Finally, DC 4 has an inventory of 20 000 units and a daily demand of 7 000 units. a) Eliminate the bullwhip effect by controlling supply chain movements based on customer demand b) Create supply chain visibility c) To control customer deliveries to be delivered on time d) Generate Purchase orders based on supply chain movements Given the above information use fair-share-allocation logic to answer the following questions. a) How many days will Lamp AB be able to sell the product BCF before they run out of stock, based on the assumed demands? ? (2p) 6. The elapsed time between order and shipment is called (2p) a. Leadtime b. Cash to cash conversion time, CCC C. Supply time d. Performance cycle time b) How many units shall each DC have delivered if fair-share-allocation logic is used? (2 p) c) If the daily demand increases by 5%, how many days will Light AB be able to sell before they run out of stock, and how many units should each DC have delivered if fair-share-allocation logic is used? (3 p) 7. According to the course, Network economics = (2p) a) Transportation economics + Warehousing economics b) Distribution economics + Inventory Economics c) Transportation economics + Inventory economics d) Inbound economics + Inventory economics + Outbound economics 8. Which inventory definition is NOT correct? (2p) a. Cycle inventory - average stock, resulting from replenishment b. Transit inventory = goods planned to be shipped c. Obsolete inventory stock out of date or without recent demand d. Inventory = all goods stocked in a company, including goods being






