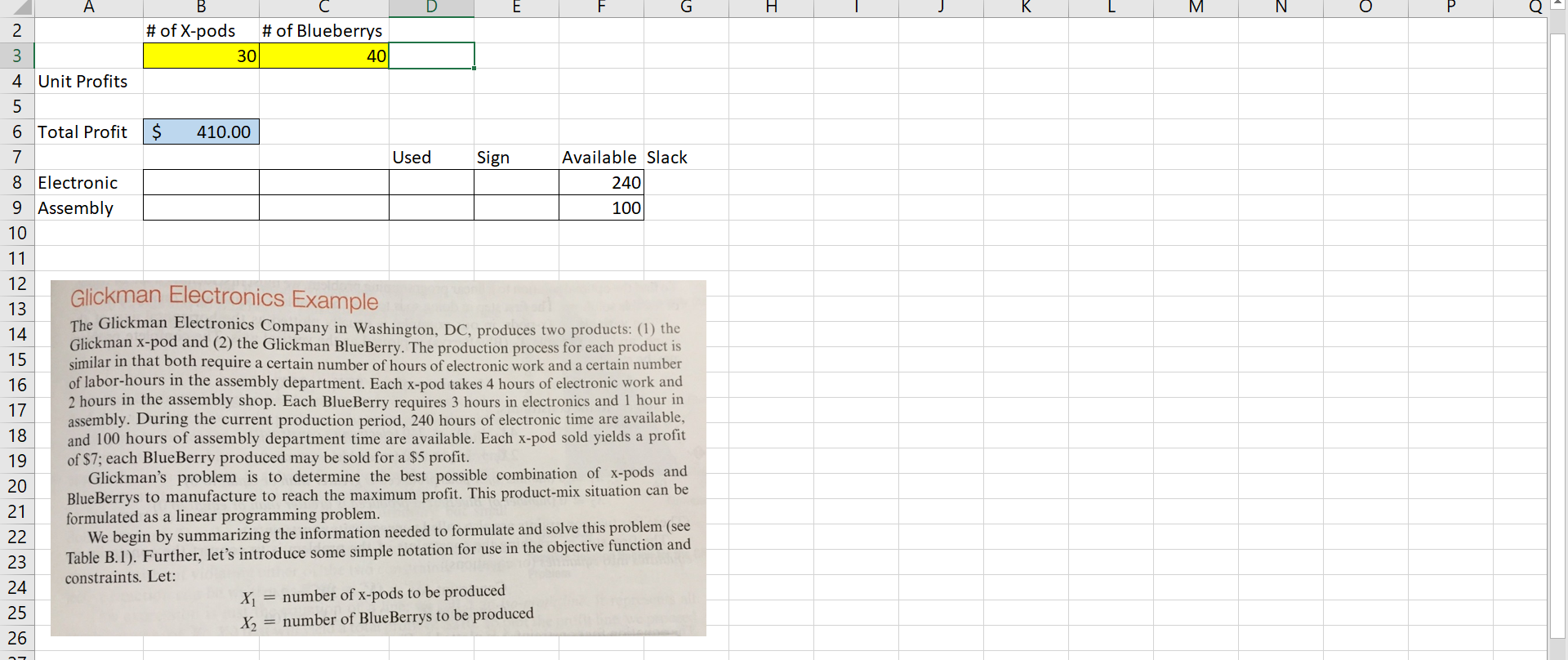
Question: . E F G H M N. O B # of X-pods # of Blueberrys 30 40 2 3 4 Unit Profits 5 6 Total
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


