Question: Escape problem (problem 26-1 from Thomas Cormen, et al., Introduction to Algorithms, 3rd edition, The MIT Press, 2009) An nn grid is an undirected graph
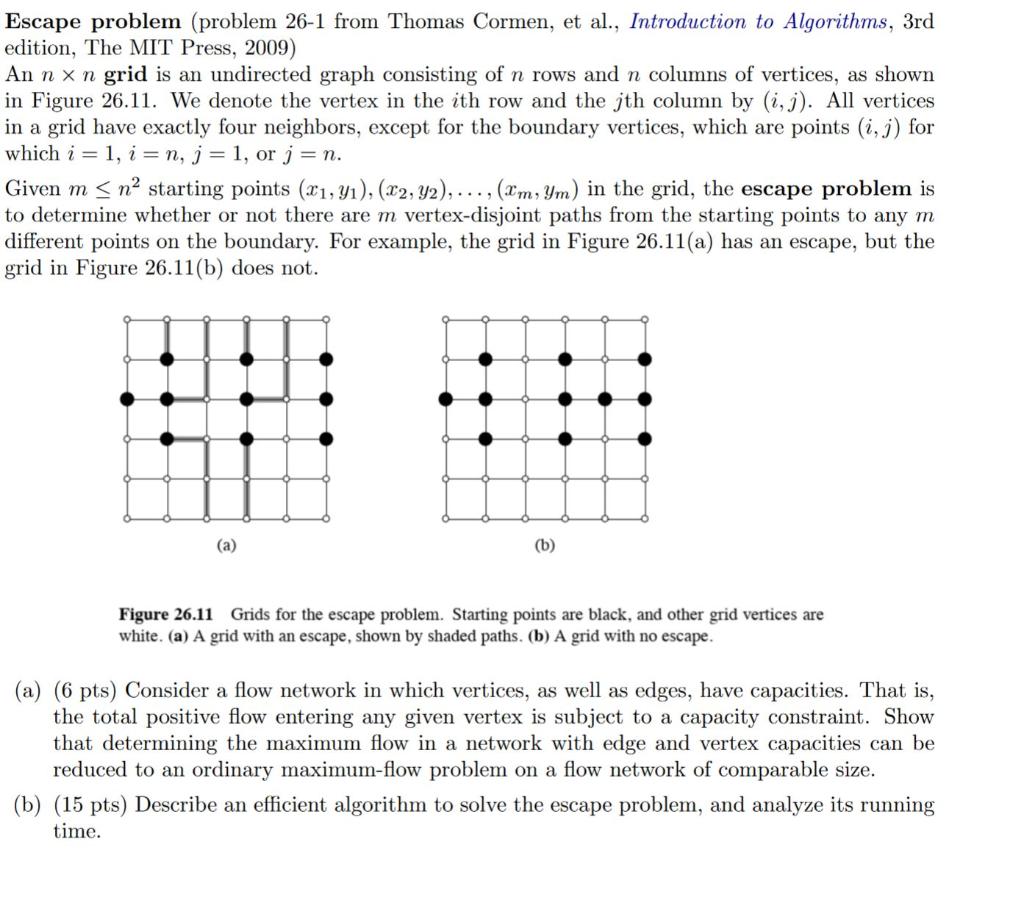
Escape problem (problem 26-1 from Thomas Cormen, et al., Introduction to Algorithms, 3rd edition, The MIT Press, 2009) An nn grid is an undirected graph consisting of n rows and n columns of vertices, as shown in Figure 26.11. We denote the vertex in the i th row and the j th column by (i,j). All vertices in a grid have exactly four neighbors, except for the boundary vertices, which are points (i,j) for which i=1,i=n,j=1, or j=n. Given mn2 starting points (x1,y1),(x2,y2),,(xm,ym) in the grid, the escape problem is to determine whether or not there are m vertex-disjoint paths from the starting points to any m different points on the boundary. For example, the grid in Figure 26.11(a) has an escape, but the grid in Figure 26.11(b) does not. (b) Figure 26.11 Grids for the escape problem. Starting points are black, and other grid vertices are white. (a) A grid with an escape, shown by shaded paths. (b) A grid with no escape. (a) (6 pts) Consider a flow network in which vertices, as well as edges, have capacities. That is, the total positive flow entering any given vertex is subject to a capacity constraint. Show that determining the maximum flow in a network with edge and vertex capacities can be reduced to an ordinary maximum-flow problem on a flow network of comparable size. (b) (15 pts) Describe an efficient algorithm to solve the escape problem, and analyze its running time
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


