Question: Exercise 1: 1: 2: LD MOV Stall Consider following assembly-language program: R3, R7 R8, (R3) R3, R3, 4 3: ADD 4: LOAD R9, (R3)
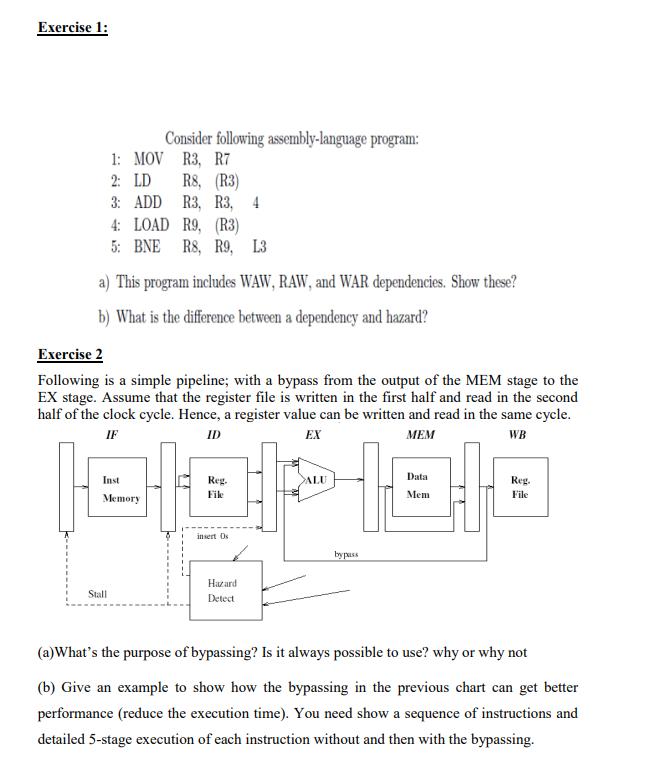
Exercise 1: 1: 2: LD MOV Stall Consider following assembly-language program: R3, R7 R8, (R3) R3, R3, 4 3: ADD 4: LOAD R9, (R3) 5: BNE R8, R9, L3 a) This program includes WAW, RAW, and WAR dependencies. Show these? b) What is the difference between a dependency and hazard? Exercise 2 Following is a simple pipeline; with a bypass from the output of the MEM stage to the EX stage. Assume that the register file is written in the first half and read in the second half of the clock cycle. Hence, a register value can be written and read in the same cycle. IF ID EX MEM WB Inst Memory Reg. File insert Os Hazard Detect ALU bypass Data Mem Reg. File (a) What's the purpose of bypassing? Is it always possible to use? why or why not (b) Give an example to show how the bypassing in the previous chart can get better performance (reduce the execution time). You need show a sequence of instructions and detailed 5-stage execution of each instruction without and then with the bypassing.
Step by Step Solution
3.38 Rating (145 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Part A WAW occurs when arrangements of instruction will affect final output value of a variable WAR ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


