Question: Exercise 1 1 Exercise 1 6 Exercises 1 9 , 2 0 , 2 1 Exercise 2 5 Exercise 3 2 algorithm. 4 . Write
Exercise
Exercise
Exercises
Exercise
Exercise
algorithm.
Write an Insertion Sort algorithm Insertion Sort is discussed in Section that uses Binary Search to find the position where the next insertion sould take place.
Determine the worstcase, averagecase, and bestcase time complexities for the basic Insertion Sort and for the version given in Exercise which uses Binary Search
Using the definitions of and show that
ninO but
The function belongs in which of the following complexity categories:
a
b
c
d
e
f None of these
The function belongs in which of the following complexity categories:
a
b
c
d
e
f None of these
The function belongs in which of the following complexity categories:
a
b
c
d
e
f None of these
Suppose you have a computer that requires minute to solve problem instances of size Suppose you buy a new computer that runs times faster than the old one. What instance sizes can be run in minute, assuming the following time complexities for our algorithm?
a
b
c
What is the time complexity of the nested loops below? For simplicity, you may assume that is a power of That is for some positive integer
for
;
while
body of the while loopNeeds
;
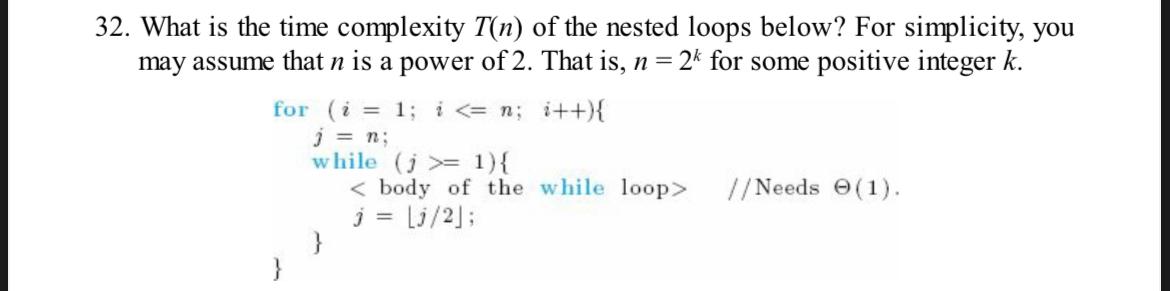
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


