Question: Exercise 1 1. What does linearization mean, in the case of multidimensional storage? 2. Explain why dimension order is important when storing multidimensional data in
Exercise 1
1. What does linearization mean, in the case of multidimensional storage?
2. Explain why dimension order is important when storing multidimensional data in a linearized array.
Exercise 2
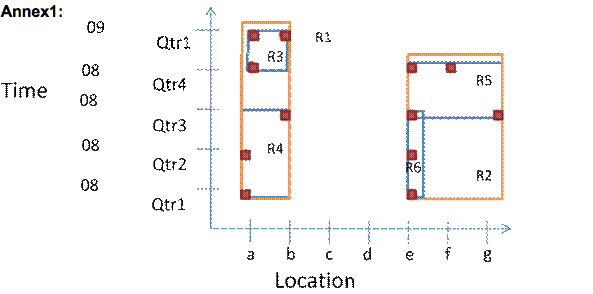
Considering the R-Tree graphically represented through the MBR with a maximal node size of 3, in Annex 1, perform the following tasks:
a. Insert, in this order the following data (each of them will be represented as the small red squares): (08 Qtr2, b), (08 Qtr2, c), (09 Qtr1, c). Represent each step graphically, evidencing the produced split. As split method use the linear cost algorithm and as heuristics, the least enlargement criterion.
b. Draw the R-Tree according to the obtained graphical representation of the MBR, after performing exercise 2.a.
c. Graphically represent (as in the lecture) the following search ([08 Qtr 2, 08 Qtr 3], [a,c]) on both the MBR representation obtained from exercise 2.a, as well as on the R-Tree representation obtained from 2.b.
Exercise 3
1. UB-Trees:
a. What is an UB-Tree and why does it use a Z-curve?
b. How big should Z-Regions be and why?
c. What mechanism can we use to allow hierarchy restrictions and still obtain good performance with UB-Tree based indexes, and how does it work?
2. Bitmap indexes:
a. What is a multi-component bitmap index and why is it useful?
b. What is the idea behind range-encoded bitmap indexes and why are they useful?
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


