Question: Exercise 2. Use the Black-Scholes formula to find the value of a call option on the following stock: So $50 X $50 7 (annualized) 3%
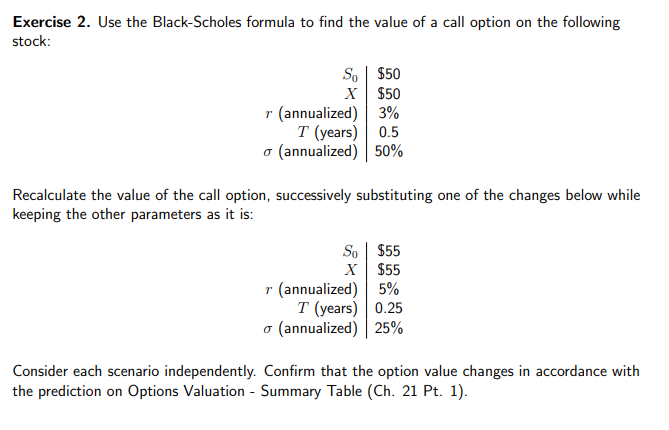

Exercise 2. Use the Black-Scholes formula to find the value of a call option on the following stock: So $50 X $50 7 (annualized) 3% T (years) 0.5 (annualized) 50% Recalculate the value of the call option, successively substituting one of the changes below while keeping the other parameters as it is: So $55 X $55 7 (annualized) 5% T (years) 0.25 (annualized) |25% Consider each scenario independently. Confirm that the option value changes in accordance with the prediction on Options Valuation - Summary Table (Ch. 21 Pt. 1).Exercise 3. Adapting the Black-Scholes formula for pricing an European call option we defined in class, we can obtain the pricing formula, given parameters (St, X, r, o), for a call selling at time t and expiring at T: C+(St) = S.Q(di) - Xe "(T-1)4(dz) where d1 = In($t/ x) + (r + 0' /2) (T - t) OVT d2 = di - ovT-t And @(.) is the cumulative distribution function of a standard normal. From the formula obtained in Exercise 2. you can obtain a pricing formula for a European put option at time t, with matu- rity T, similar to the one above. We will use the Black-Scholes formula to price put options on the S&P 500 with maturity 1 year and different strike prices, and compare them to the actual prices of the options. Go to CBOE or something similar (remember to disclose your source) and get data on prices and "implied volatil- ity" of put options on the S&P 500 with strike prices of 2000, 2200, 2400, 2600, 2800, and 3000 and maturity as close to 1 year as you can find (so about July 2021). Next, using the current level of the S&P 500 as S,, the current fed funds rate as r, T = 1 and t = 0 (for maturity one year), and volatility o = 0.18 (about the historical annual volatility of the S&P 500), calculate the Black-Scholes prices, Pots, of each of the put options with their strike prices. Then, calculate the percent change from the actual option price, Po, to the Black-Scholes price, i.e., %AP = AP PB-S - Po Po Which options does the Black-Scholes price miss by the largest percentages? (Present all the changes in a table.) Lastly, create two graphs: On the first, put strike prices on the X-axis and plot lines for the ac- tual prices and the Black-Scholes prices. On the second, put strike prices on the X-axis and plot lines for the implied volatilities and our assumed volatility (a straight line at 0.18). Discuss your findings in a few sentences
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


