Question: Exercise 2 We can now use the zero-coupon yield from Exercise 1 to price a bond. Suppose, we have a 5% coupon bond (paid semi-annually)
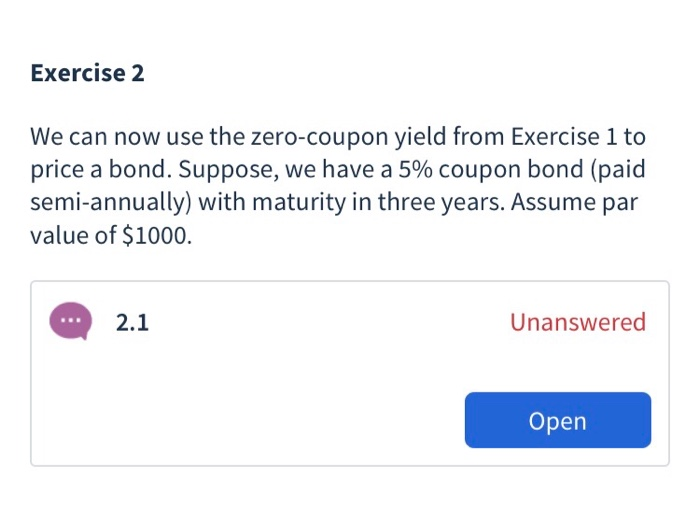
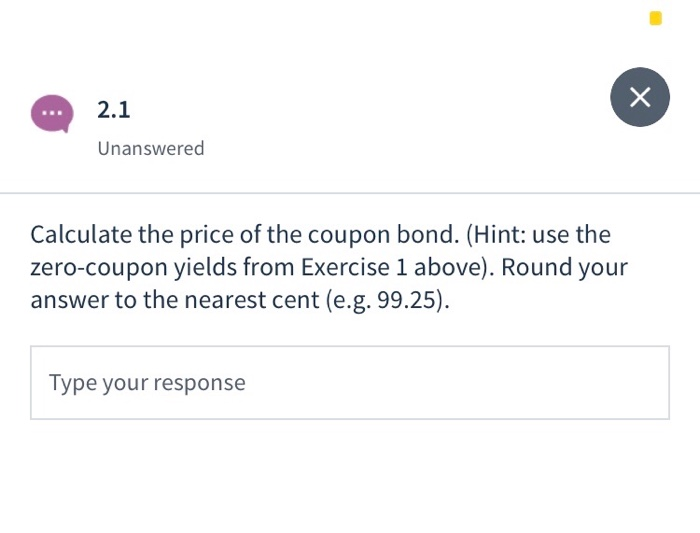
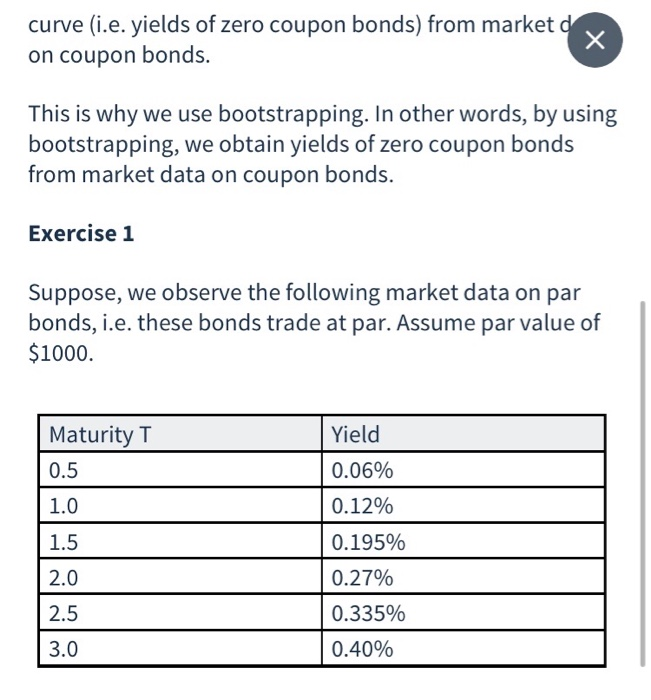
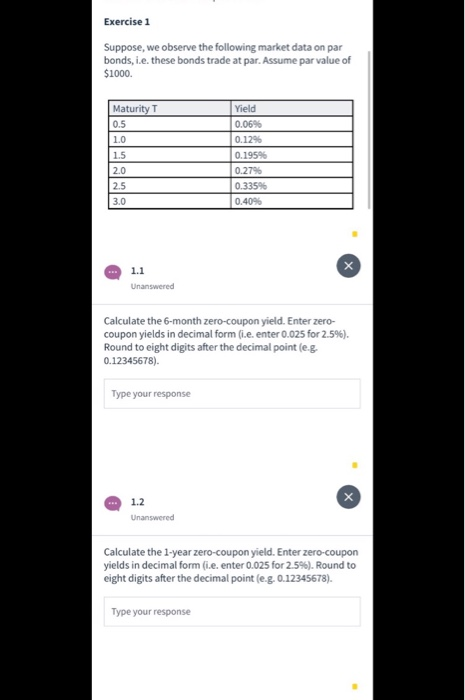
Exercise 2 We can now use the zero-coupon yield from Exercise 1 to price a bond. Suppose, we have a 5% coupon bond (paid semi-annually) with maturity in three years. Assume par value of $1000. 2.1 Unanswered Open 2.1 Unanswered Calculate the price of the coupon bond. (Hint: use the zero-coupon yields from Exercise 1 above). Round your answer to the nearest cent(e.g. 99.25). Type your response curve (i.e. yields of zero coupon bonds) from market d. on coupon bonds. This is why we use bootstrapping. In other words, by using bootstrapping, we obtain yields of zero coupon bonds from market data on coupon bonds. Exercise 1 Suppose, we observe the following market data on par bonds, i.e. these bonds trade at par. Assume par value of $1000. Maturity T 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 Yield 0.06% 0.12% 0.195% 0.27% 0.335% 0.40% 3.0 Exercise 1 Suppose, we observe the following market data on par bonds, i.e. these bonds trade at par. Assume par value of $1000 Maturity T 0.5 10 15 Yield 0.06% 0.12% 0.195% 0.2796 0.335% 0.40% Unanswered Calculate the 6-month zero-coupon yield. Enter zero- coupon yields in decimal form (i.e. enter 0.025 for 2.5%). Round to eight digits after the decimal point (e.g. 0.12345678). Type your response - 1.2 Unanswered Calculate the 1-year zero-coupon yield. Enter zero-coupon yields in decimal form (e.enter 0.025 for 2.5%). Round to eight digits after the decimal point(e.g. 0.12345678). Type your response Exercise 2 We can now use the zero-coupon yield from Exercise 1 to price a bond. Suppose, we have a 5% coupon bond (paid semi-annually) with maturity in three years. Assume par value of $1000. 2.1 Unanswered Open 2.1 Unanswered Calculate the price of the coupon bond. (Hint: use the zero-coupon yields from Exercise 1 above). Round your answer to the nearest cent(e.g. 99.25). Type your response curve (i.e. yields of zero coupon bonds) from market d. on coupon bonds. This is why we use bootstrapping. In other words, by using bootstrapping, we obtain yields of zero coupon bonds from market data on coupon bonds. Exercise 1 Suppose, we observe the following market data on par bonds, i.e. these bonds trade at par. Assume par value of $1000. Maturity T 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 Yield 0.06% 0.12% 0.195% 0.27% 0.335% 0.40% 3.0 Exercise 1 Suppose, we observe the following market data on par bonds, i.e. these bonds trade at par. Assume par value of $1000 Maturity T 0.5 10 15 Yield 0.06% 0.12% 0.195% 0.2796 0.335% 0.40% Unanswered Calculate the 6-month zero-coupon yield. Enter zero- coupon yields in decimal form (i.e. enter 0.025 for 2.5%). Round to eight digits after the decimal point (e.g. 0.12345678). Type your response - 1.2 Unanswered Calculate the 1-year zero-coupon yield. Enter zero-coupon yields in decimal form (e.enter 0.025 for 2.5%). Round to eight digits after the decimal point(e.g. 0.12345678). Type your response
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


