Question: Exercise 3 Bonus. The energy function (called a Hamiltonian) for a classical diatomic molecule vibrating is (4) where x, p; are position (displacement from the
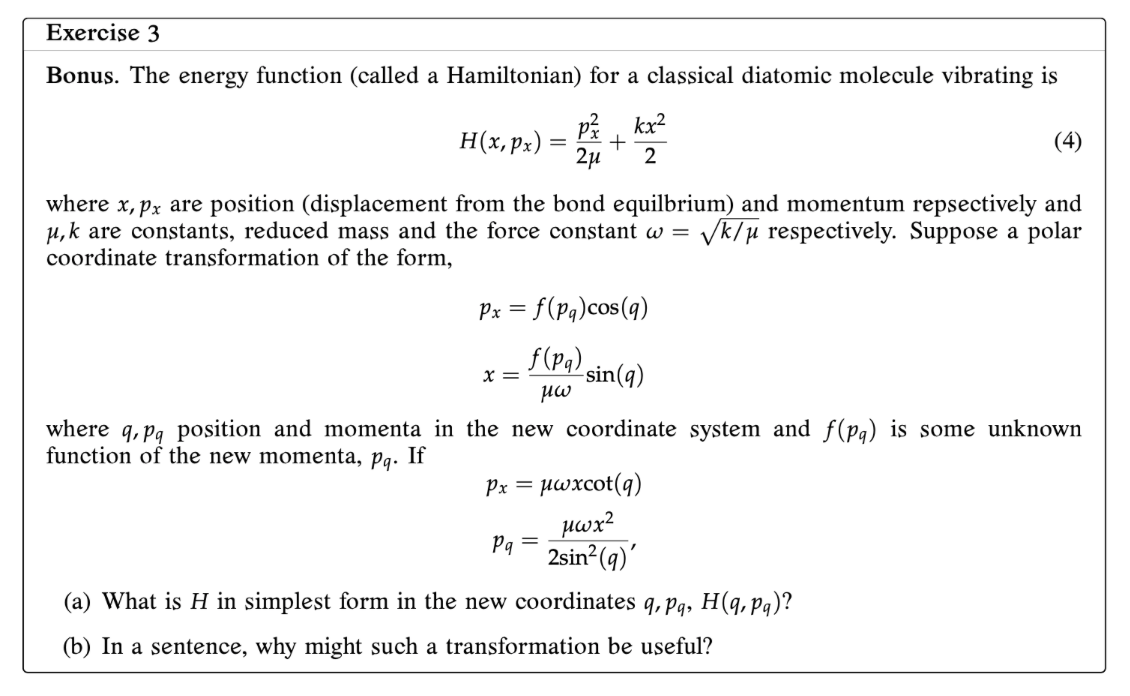
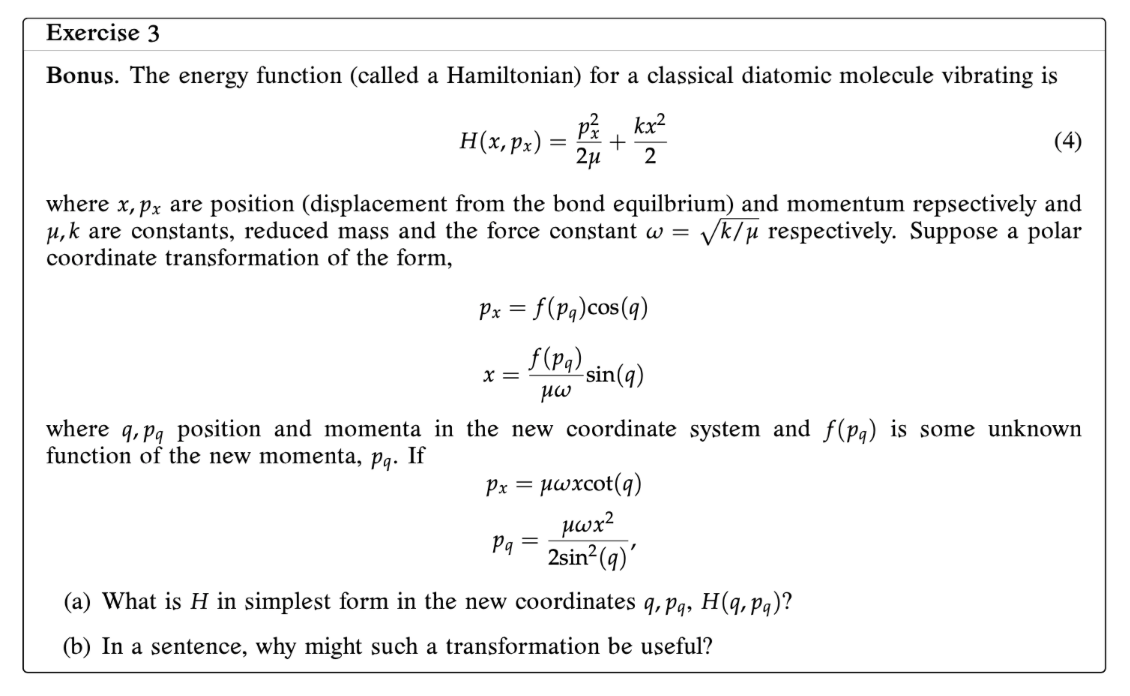
Exercise 3 Bonus. The energy function (called a Hamiltonian) for a classical diatomic molecule vibrating is (4) where x, p; are position (displacement from the bond equilbrium) and momentum repsectively and ink are constants, reduced mass and the force constant to = Mic/y respectively. Suppose a polar coordinate transformation of the form, Px = f(Pq)C5('i) Hm) ya; x = sin(q) where mpg position and momenta in the new coordinate system and f(pq) is some unknown function of the new momenta, pq. If p; = pwxcot(q) (a) What is H in simplest form in the new coordinates :3, pg, H (4;, pg)? 03) In a sentence, why might such a transformation be useful
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


