Question: Exercise 4 Choose the letter of the correct answer. Write your answer on the line before each number. 1. A monopolist is in equilibrium if


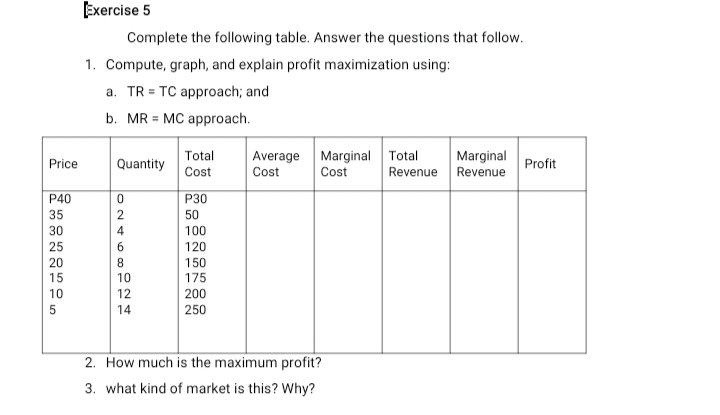






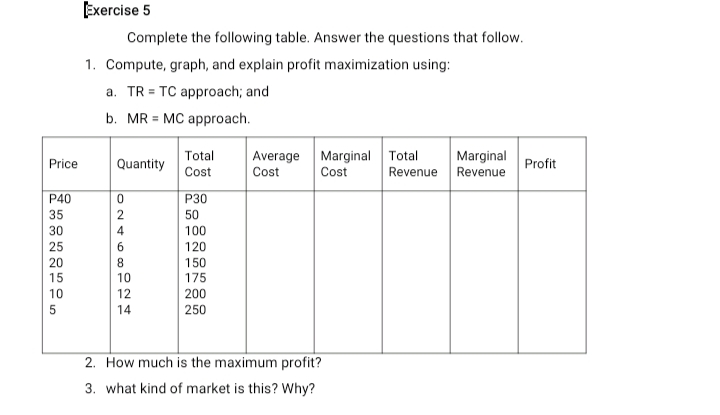




Exercise 4 Choose the letter of the correct answer. Write your answer on the line before each number. 1. A monopolist is in equilibrium if a. his profits are in excess of normal b. his price causes sales of the quality at which MR = MC. c. consumers are satisfied with his price d. he sells the amount at which MR crosses the quantity axis 2. One oligopolist is in equilibrium if _ a. it does not exist b. it may be altered depending on the reactions of his rivals c. it represents the demand for the whole industry d. it may be altered since conditions constantly change 3. Freedom of entry in monopolistic competition is a. a limiting force in excessive profits b. significantly inhibited because of complex technical requirements c. denied by collusion d. expensive because of fixed cost 4. Which is a characteristic of an oligopoly? a. an open market for the best interests of consumers b. a market situation with no competition c. a market situation with only one buyer d. a market situation with only a few competing sellers 5. In the kinked demand curve model of simple oligopoly, the price established in the industry will not fall because if one firm attempts to a. increase price, other firms will follow b. decrease price, other firms will not follow c. decrease price, other firms will follow to start a price war d. decrease price, other firms will increase price 6. Nonprice competition often takes the form of a. homogeneous products b. price wars c. product differentiation6. Nonprice competition often takes the form of a. homogeneous products b. price wars c. product differentiation d. collusion 7. The marginal revenue product is equal to a. a summation of the variable and fixed cost b. the marginal product times the price of the output c. price times marginal cost d. the interaction of demand and supply 8. The marginal revenue product declines because of a. increasing returns to scale b. diminishing returns to scale c. the falling price of the input d. interaction of marginal utility and marginal cost 9. A monopoly finds that its present level of output and sales revenue are equal to P5 and marginal cost is P4.10. Which of the following maximizes profits? a. leave price and leave output unchanged b. increase price and leave output unchanged c. increase price and decrease output d. increase price and increase output 10. Price leadership in oligopoly means a. one firm sets new prices b. one firm alters price c. all firms collude d. small firms make price changesExercise 5 Complete the following table. Answer the questions that follow. 1. Compute, graph, and explain profit maximization using: a. TR = TC approach; and b. MR = MC approach. Total Price Quantity Average Marginal Total Marginal Cost Cost Cost Profit Revenue Revenue P40 P30 35 ANO 50 30 100 25 6 120 20 8 150 15 10 175 10 12 200 5 14 250 2. How much is the maximum profit? 3. what kind of market is this? Why?VII. ASSIGNMENT Choose the letter of the correct answer. 1 . can also cause an upward shift in the budget line. a. Higher prices b. Higher indifference curve C. Higher utility d. Lower prices 2. The rate of substitution alo9ng the indifference curve implies. a. Utility trade-off b. Commodity trade-off C. Relative prices d. Relative utility of commodities 3. Another indifference curve corresponds to another level of satisfaction because of the change in _ a. Budget b. Prices C. Consumption level d. Utility 4. The maximum satisfaction point of a budget line is where it is tangent to an indifference curve because a. Higher indifference curve yields more satisfaction b. Budget can only buy the satisfaction of the indifference curve within it. C. The highest indifference curve within a budget line is that which is tangent to it. d. All of the above 5. Deviation from the quasi-marginal condition results in less satisfaction because of _ a. Relative prices b. Commodity trade off C. Relative utility of commodities d. Utility trade off 6. Substitution effect results from a . a. Change in marginal utility b. Change in relative marginal utility C. Decrease in the marginal utility of one commodity Change in total satisfaction 7. There is consumer surplus when one a. Pays less for succeeding consumption b. Pays less for preceding consumption C. Pays more for succeeding consumption d. None of the above 8. Water is cheaper than diamond because of a. Need b. Utility in use C. Utility in exchange d. Purchasing power9. The marginal rate of substitution of Product A for Product B is __ when there is more preference for the farmer. a. Higher b. Unchanged c. Varied d. Lower 10. The budget line when incomes increase. a. Shifts upward b. Shifts downward c. Does not change d. Varies Identify what is being described 1. Change in overall consumption due to a change in price. 2. Change in consumption mix due to a change in price. 3. Equality in the marginal utilities of a commodity item. 4. One factor that changes the consumption mix favors the commodity over another. 5. Causes total satisfaction to change. 6. It is the basis of consumption and demand behavior. 7. The proponent of Theory of Motivation, which explains the psychological factors that affect consumer behavior. 8. the psychological law that is based on subjective valuation of satisfaction. 9. Term in economics for satisfaction. 10. It depicts the combination that does nor yield any difference in satisfaction. 11. Social group that has a direct or indirect influence on one's consumer behavior. 12. Complete description of an indifference curve's shape. 13. The relationship of these two graphical illustrations tells the best combination in the consumption of times following a limited budget. 14. What MRS stands for. 15. The potential consumption of a certain tem on its market price and the income of its buyers. 16. Principles behind a consumer finding a consumption mix that will garner him the highest level of satisfaction. 17. Formula for marginal utility. 18. It is the function of the units of consumption. 19. The set of activities a person is expected to perform. 20.it is the function of the units of consumption.Choose the letter of the correct answer. _ 1 . The use of something should pay for its opportunity foregone to indicate _. a. Addition b. Reduction c. Change d. Net change _ 2. Based on the foregoing. the best alternative is hat which _. a. Gives the most benefit b. Gives the most addition to benefit c. Has the most opportunity cost :1. El and c e. A and c _ 3. It causes total cost to change with output. a. Fixed cost b. 'v'ariable cost c. Average variable cost d. Average fixed cost _ 4. Average fixed cost _ as output decreases. a. Increases b. Decrease c. Remains constant d. None of the above _ 5. Average cost eventually increases as output decreases because of _. a. 'v'ariable cost b. Fixed cost c. Opportunity cost :1. Imputed cost _ 6. The condition that underlies the shape of the average cost curve. a. Returns to scale b. Law of Diminishing returns c. Shutdown price d. Long-run cost curves |7. When marginal cost increases, marginal product in the production function a. Decreases b. Increases c. Does not change d. Is zero 8. Given a certain price, profit decreases when the output level causes MC to be gre affecting a. Revenue and variable cost b. Revenue and fixed cost C. Least of the lowest cost d. Fixed cost 9. The most efficient plant is characterized by . a. Least cost b. Bigger capacity c. Least of the lowest cost d. More production 10. Producing short of MR=MC means lower profit because a. MC is greater than MR b. MR is greater than MC C. Revenue is less d. Of lower cost
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


