Question: EXERCISE - INDIVIDUAL: Create a Binary File Write a C program, create_binary_file, which takes at least one argument: a filename, and subsequently, integers in
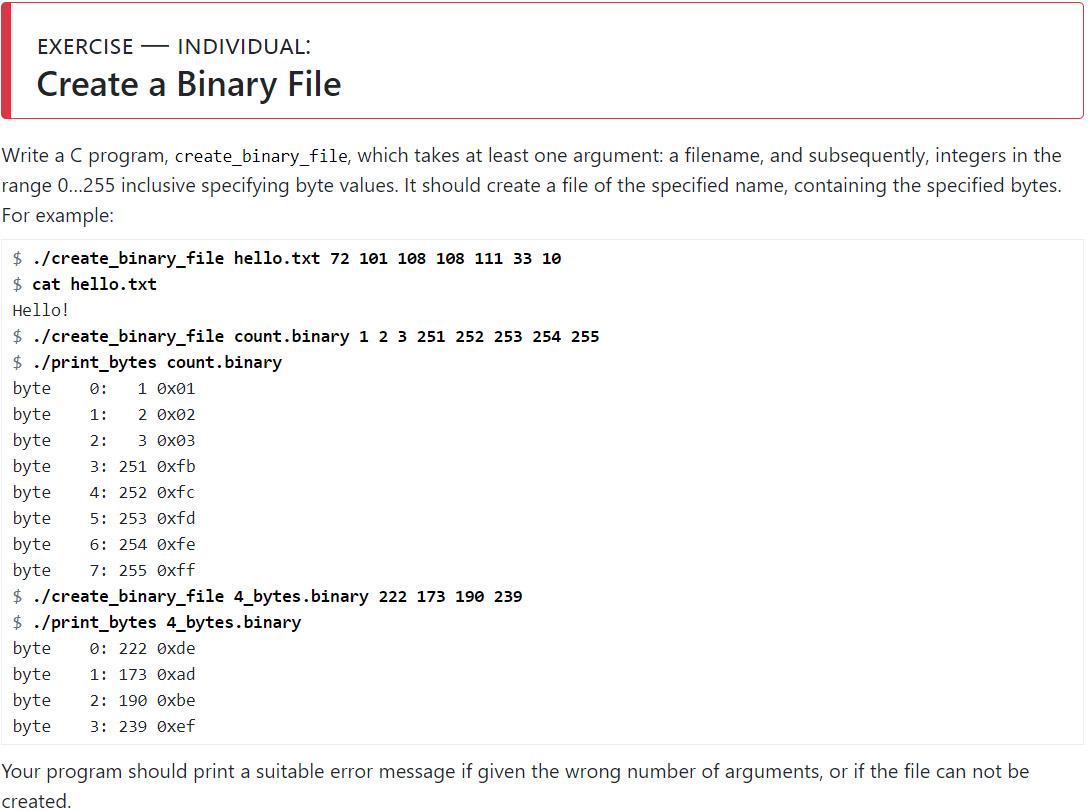
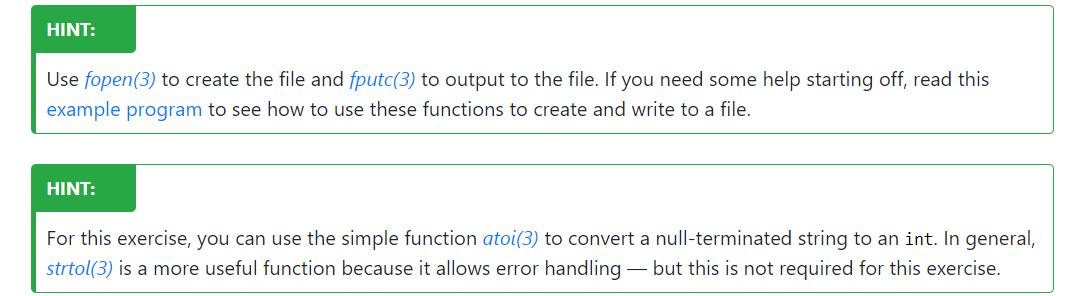
EXERCISE - INDIVIDUAL: Create a Binary File Write a C program, create_binary_file, which takes at least one argument: a filename, and subsequently, integers in the range 0...255 inclusive specifying byte values. It should create a file of the specified name, containing the specified bytes. For example: $ ./create_binary_file hello.txt 72 101 108 108 111 33 10 $cat hello.txt Hello! $ ./create_binary_file count.binary 1 2 3 251 252 253 254 255 $ ./print_bytes count. binary byte 1 0x01 byte 1: 2 0x02 byte 2: 3 0x03 byte 3: 251 Oxfb byte 4: 252 0xfc byte 5: 253 0xfd byte 6: 254 Oxfe byte 7: 255 0xff $ ./create_binary_file 4_bytes.binary 222 173 190 239 $ ./print_bytes 4_bytes.binary 0: 222 Oxde 1: 173 Oxad 2: 190 Oxbe 3: 239 Oxef byte byte byte byte Your program should print a suitable error message if given the wrong number of arguments, or if the file can not be created. HINT: Use fopen(3) to create the file and fputc(3) to output to the file. If you need some help starting off, read this example program to see how to use these functions to create and write to a file. HINT: For this exercise, you can use the simple function atoi(3) to convert a null-terminated string to an int. In general, strtol(3) is a more useful function because it allows error handling - but this is not required for this exercise.
Step by Step Solution
3.45 Rating (145 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
include include include int mainint argc cha... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


