Question: Figure 1 shows a beam under a linear vertical load. The equation for describing the elastic curve under this Problem 1 : Bisection Method [
Figure shows a beam under a linear vertical load. The equation for describing the elastic curve under this Problem : Bisection Method pt
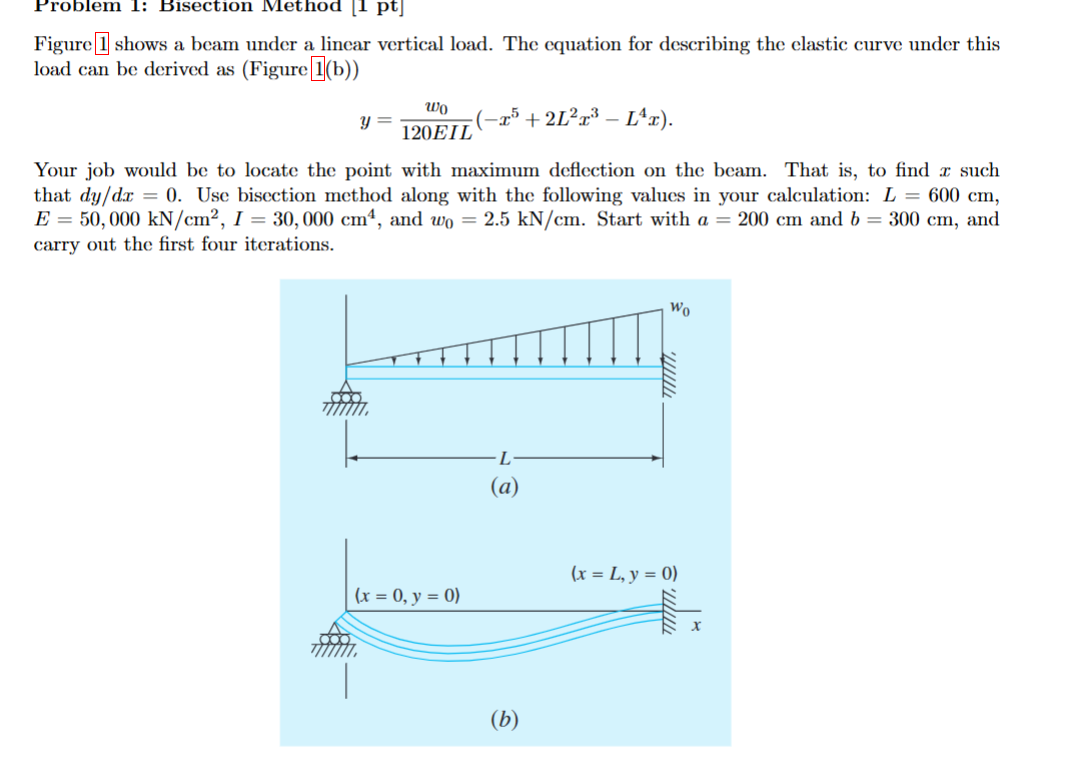
Figure shows a beam under a linear vertical load. The equation for describing the elastic curve under this load can be derived as Figure b
Your job would be to locate the point with maximum deflection on the beam. That is to find such that Use bisection method along with the following values in your calculation: and Start with and and carry out the first four iterations.
load can be derived as Figure b
y w
EIL xLx Lx
Your job would be to locate the point with maximum deflection on the beam. That is to find x such
that dydx Use bisection method along with the following values in your calculation: L cm
E kNcm I cm and w kNcm Start with a cm and b cm and
carry out the first four iterations.PROBLEMS
computation: L cm E kNcm
I
cm
and w kNcm
You buy a $ vehicle for nothing down at $
per year for years. Use the bisect function from Fig.
to determine the interest rate that you are paying. Employ
initial guesses for the interest rate of and and a stop
ping criterion of The formula relating present
worth P annual payments A number of years n and interest
rate i is
A P i in
The resistivity rho of doped si
charge q on an electron, the electron
tron mobility mu The electron densit
the doping density N and the intrinsic
electron mobility is described by the
erence temperature T and the refer
equations required to compute the res
rho
qnmu
where
n
N
N n
i
and
Determine N given T K
cm V s q times C
and a desired rho times V s
guesses of N and times
b the false position method.
A total charge Q is uniformly di
shaped conductor with radius a A c
distance x from the center of the ring
exerted on the charge by the ring is g
F
pi e
q Qx
x a
where etimes C
N m
Fi
the force is N if q and Q are times
radius of m
For fluid flow in pipes, friction
mensionless number, the Fanning fri
ning friction factor is dependent on a
related to the size of the pipe and
all be represented by another dime
Reynolds number Re A formula tha
w
L
a
x y
x L y
x
b
FIGURE P
chachqxd : AM Page
Figure : Beam deflection problem.
Problem : False Position Method pt
Determine the positive roots of the equation cosxx by using the false position method. Carry
out the first five iterations. Start with a and b
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


