Question: Figure 3 below illustrates an example timing diagram for the Distributed Coordination Function (Basic Access mode) in IEEE 802.11 wireless LANs. It shows the procedure
Figure 3 below illustrates an example timing diagram for the Distributed Coordination Function (Basic Access mode) in IEEE 802.11 wireless LANs. It shows the procedure for Station A sending a DATA frame (with payload = 500 bytes) to Station B, which is subsequently acknowledged. Make the following assumptions: All Stations can hear each others transmissions Backoff interval = Slottime x Random(0,63) Random(n,m) = function that generates a random integer between n and m Output of Random(0,63) for station C = 40 Output of Random(0,63) for station D = 20 Station C has a DATA frame ready to transmit to D at the point marked x on station C line Station D has a DATA frame ready to transmit to A at the point marked x on station D line Complete the timing diagram for the transmissions of Stations C and D by drawing a diagram as in figure below, and show where necessary the DIFS, SIFS, ACK, DATA, Backoff and Deference for ALL stations. Your diagram does not have to be to scale, but the ordering of events must be clear (e.g. in the current diagram it is clear that the SIFS at station B starts at the same time the DATA from station A is completed).
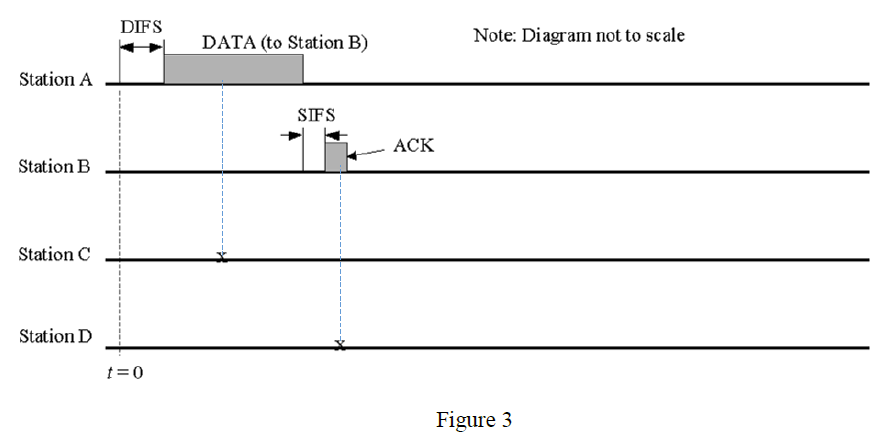
DIFS DATA (to Station B) Note: Diagram not to scale Station A SIFS ACK Station EB Station C Station D! 1-0 Figure 3 DIFS DATA (to Station B) Note: Diagram not to scale Station A SIFS ACK Station EB Station C Station D! 1-0 Figure 3
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


