Question: File Tools View econ . Saved to this PC v X Question 1 (1 point) Because the perfectly competitive firm is a price-taker, its demand
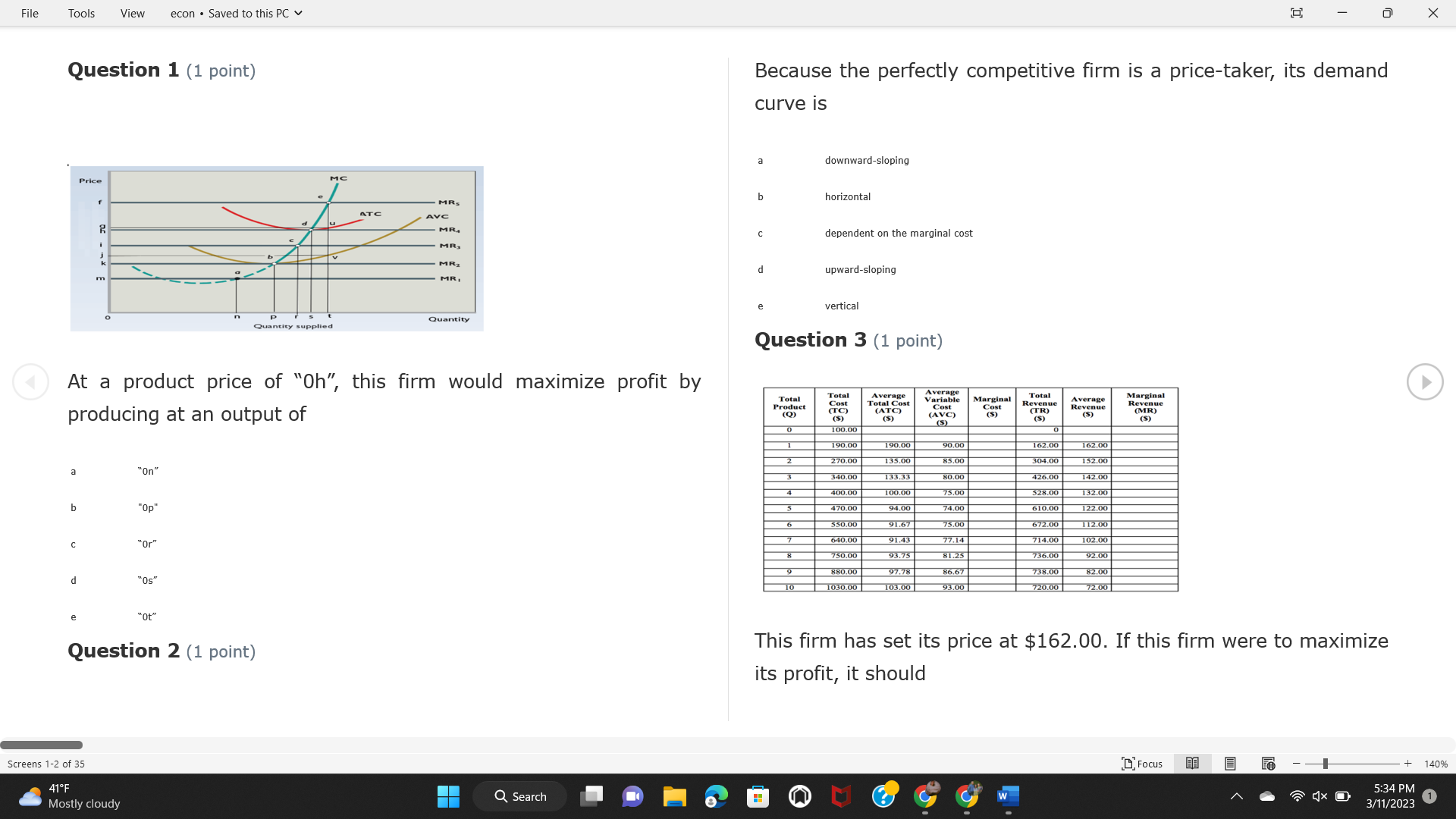
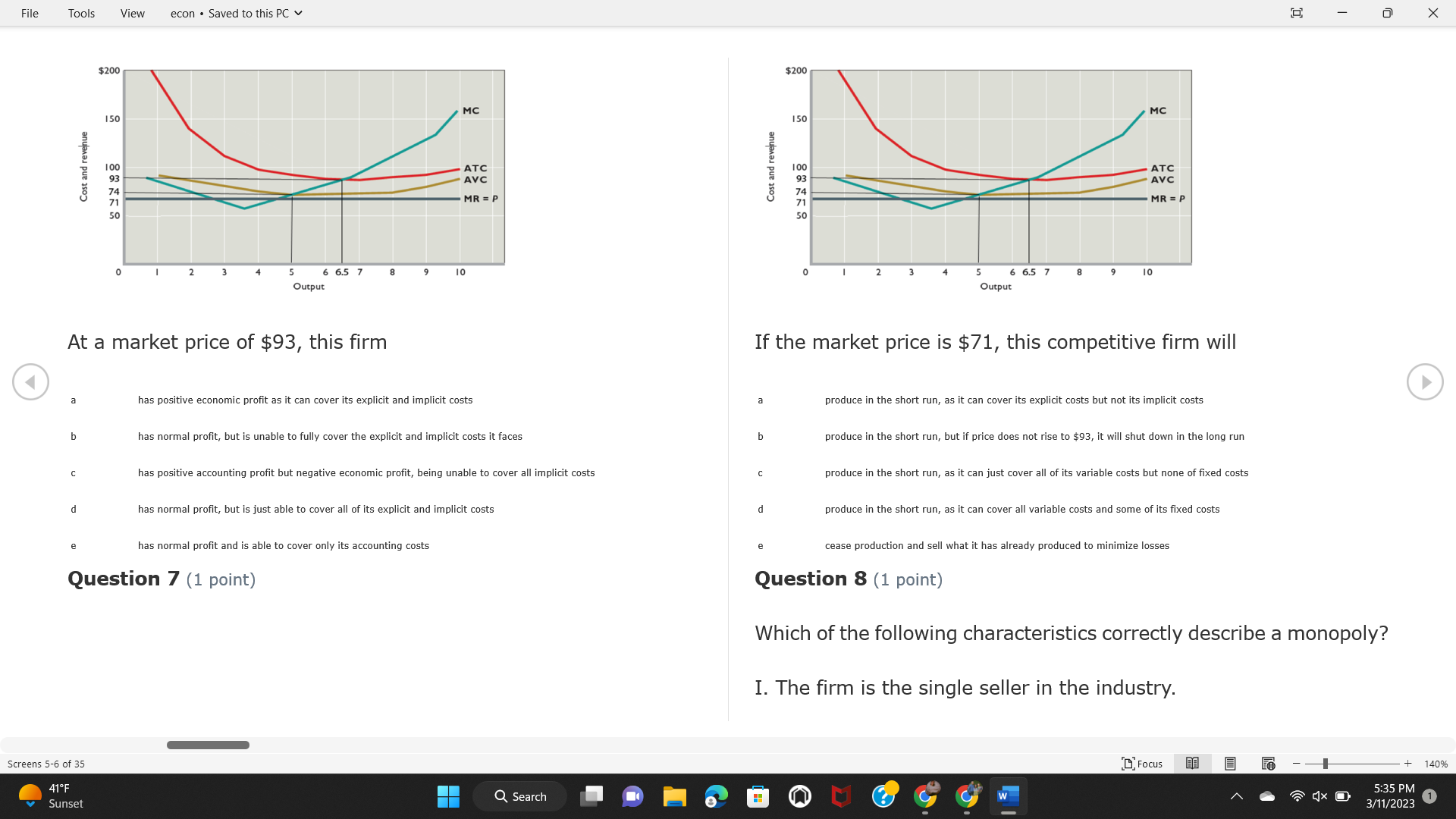
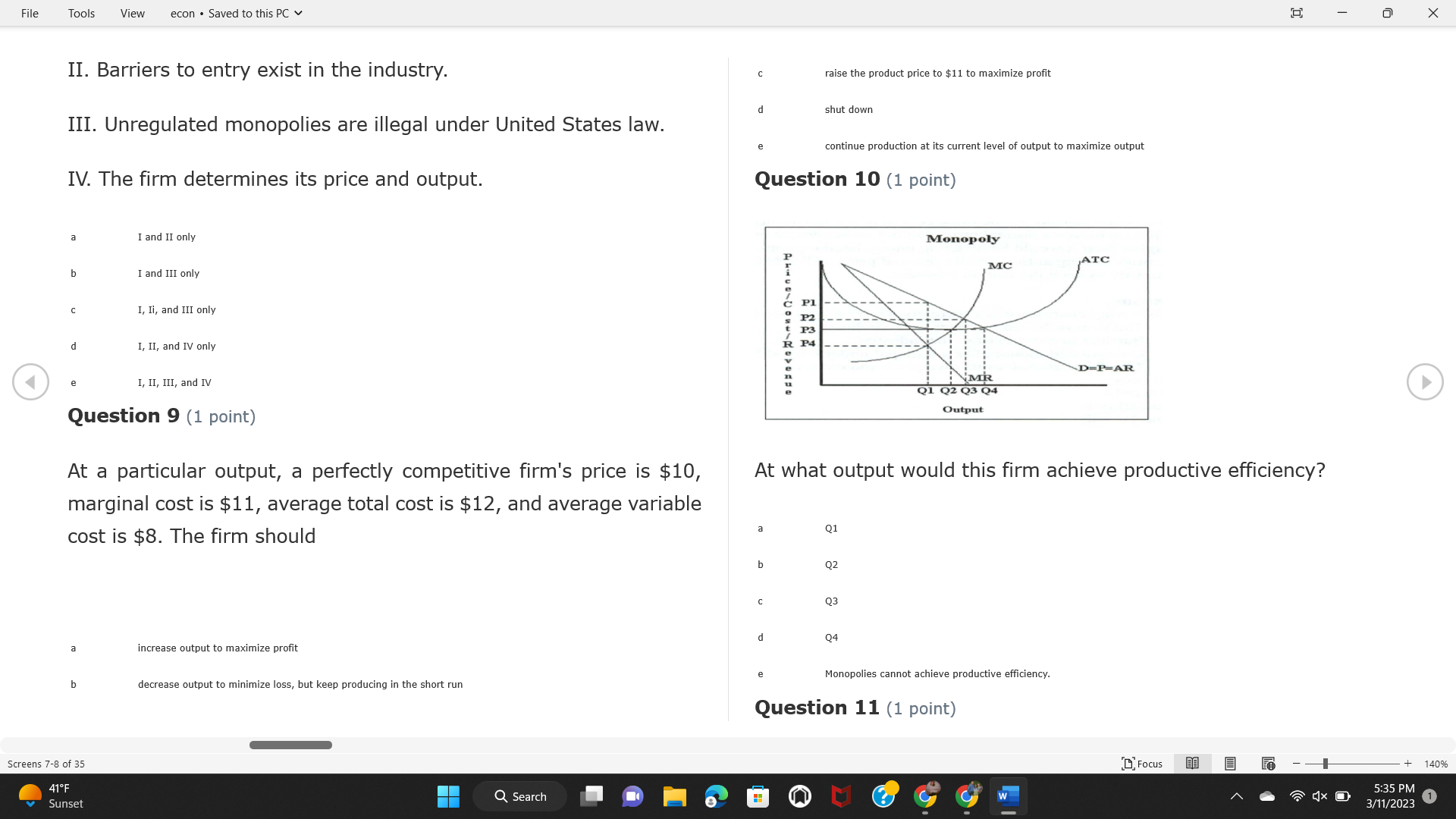
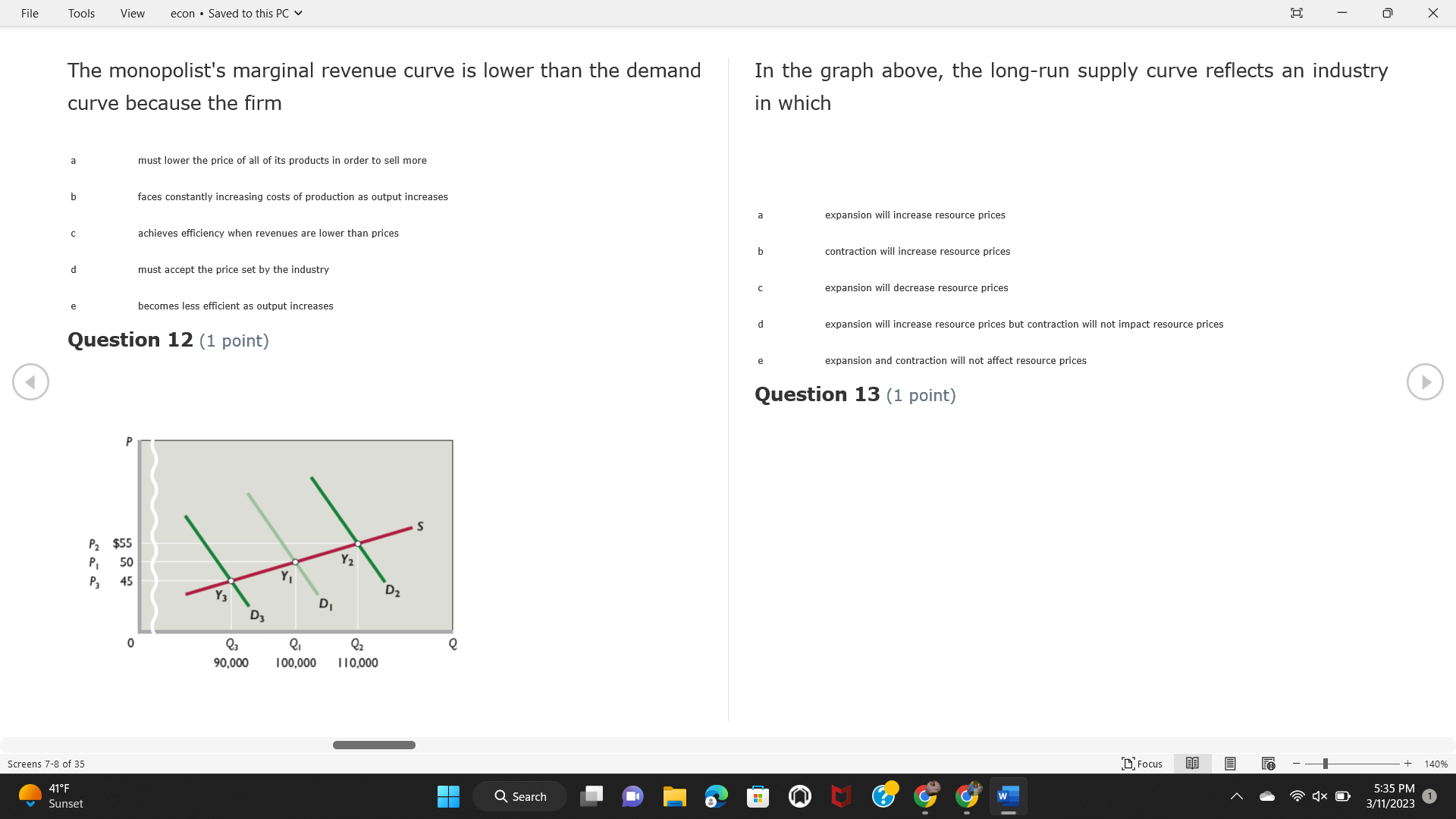
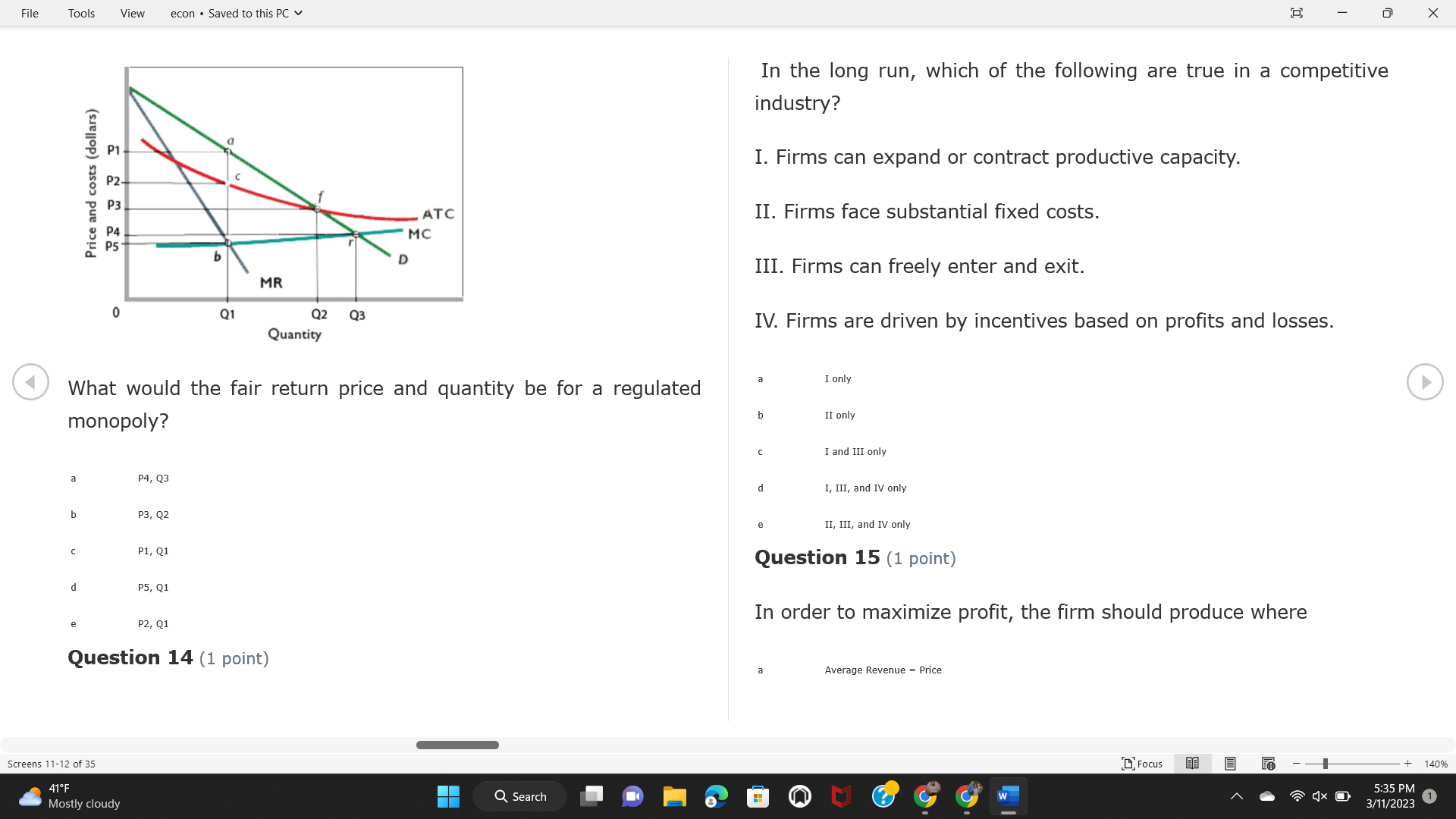
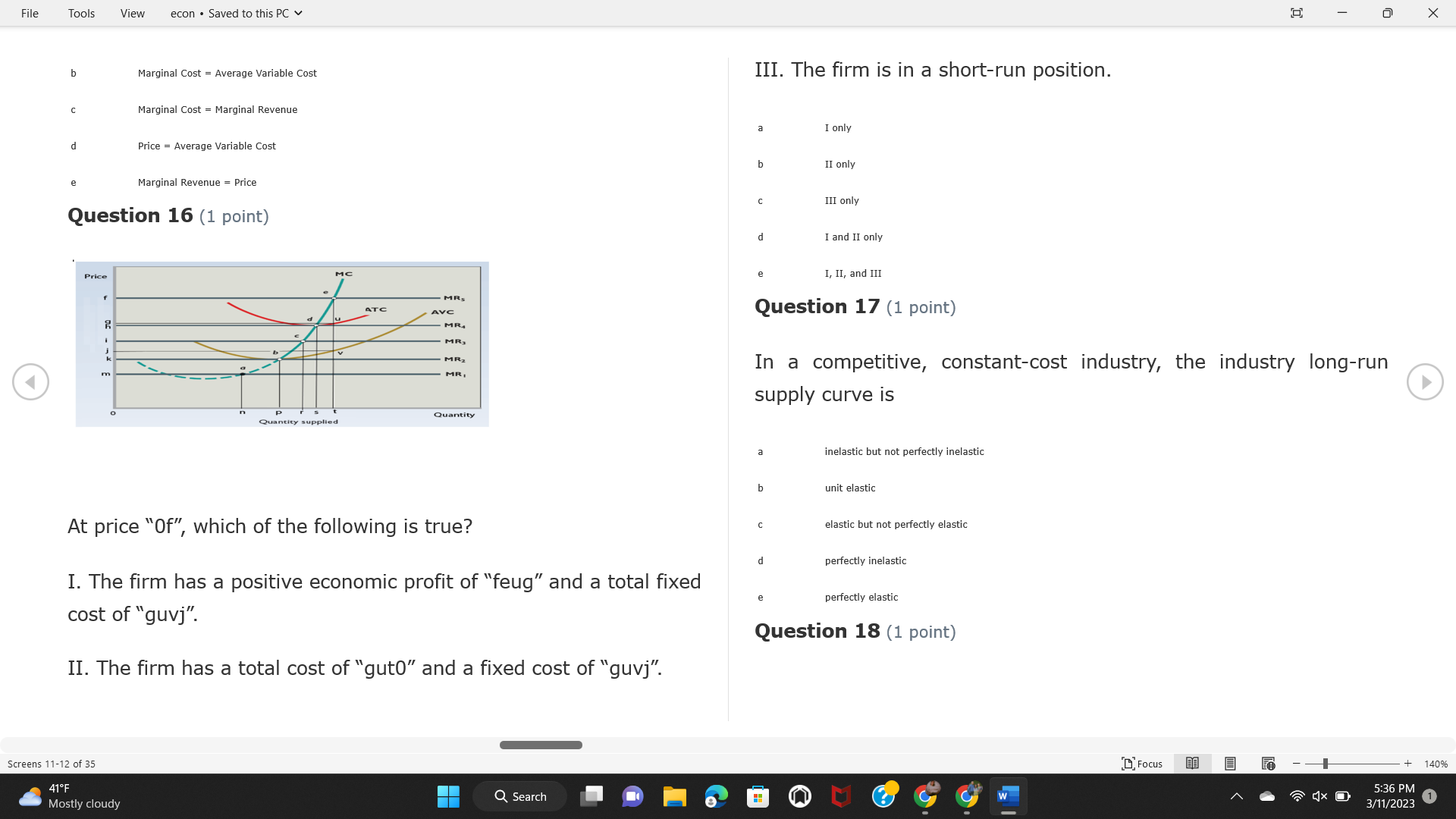
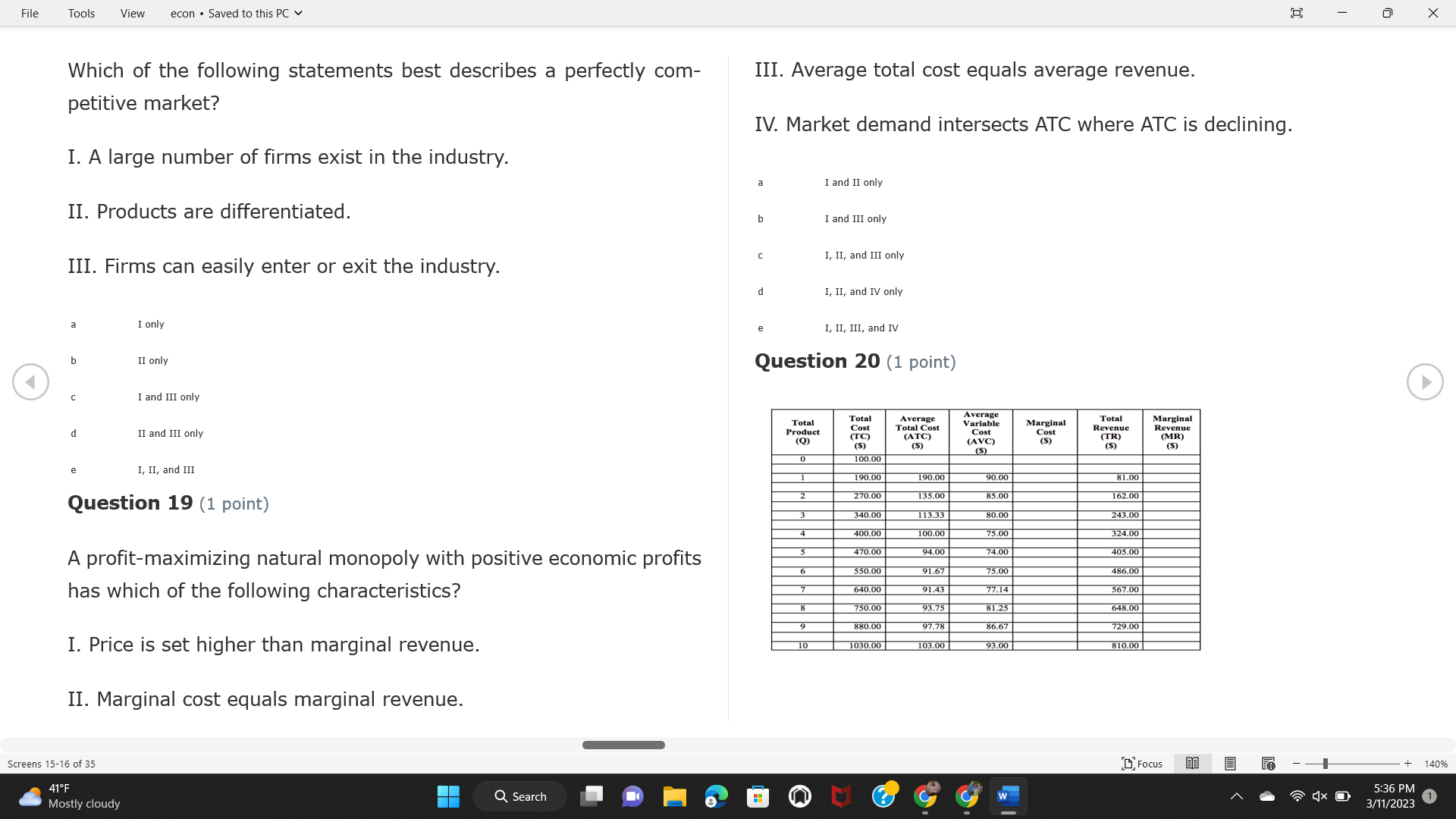
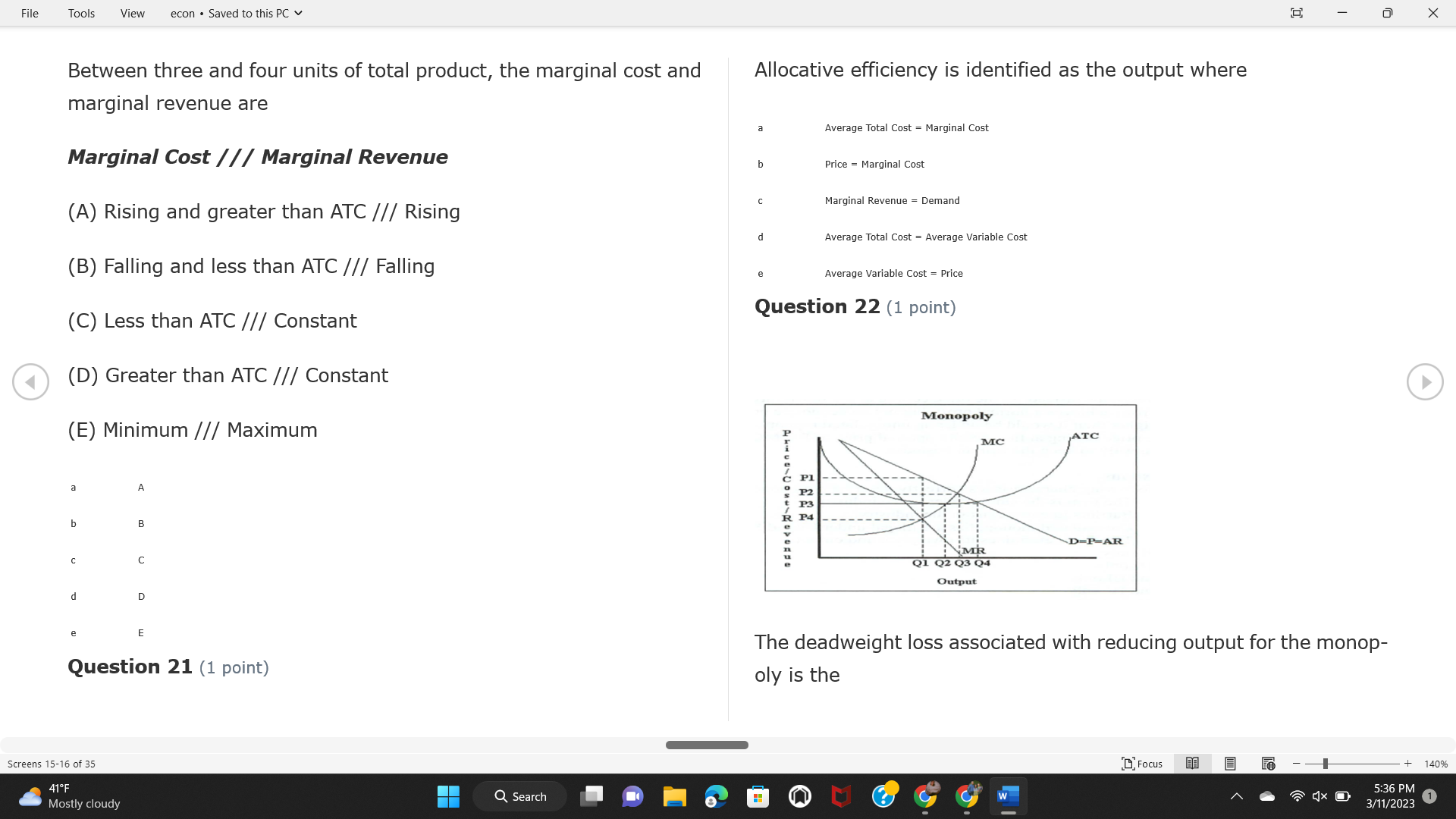
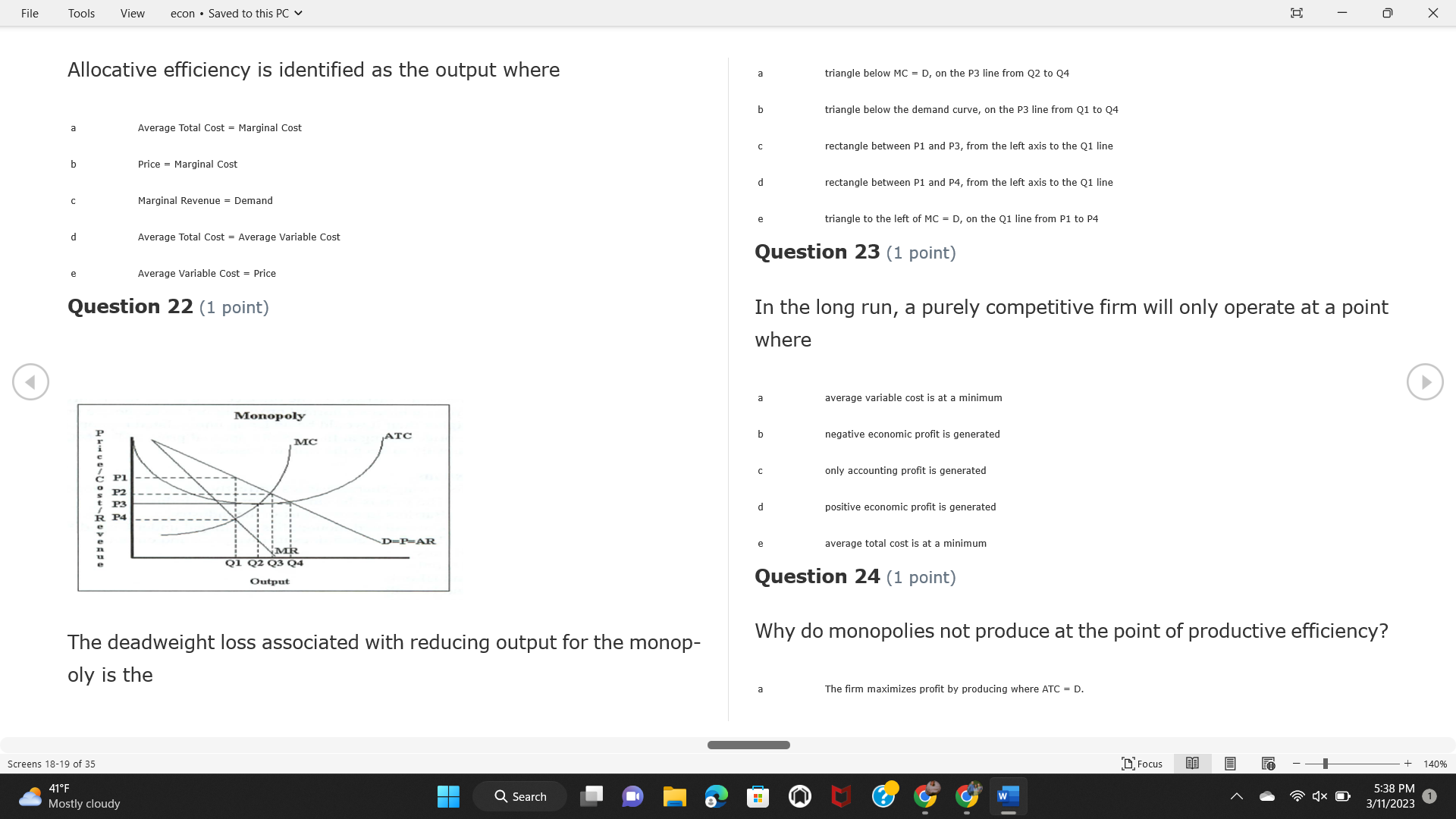
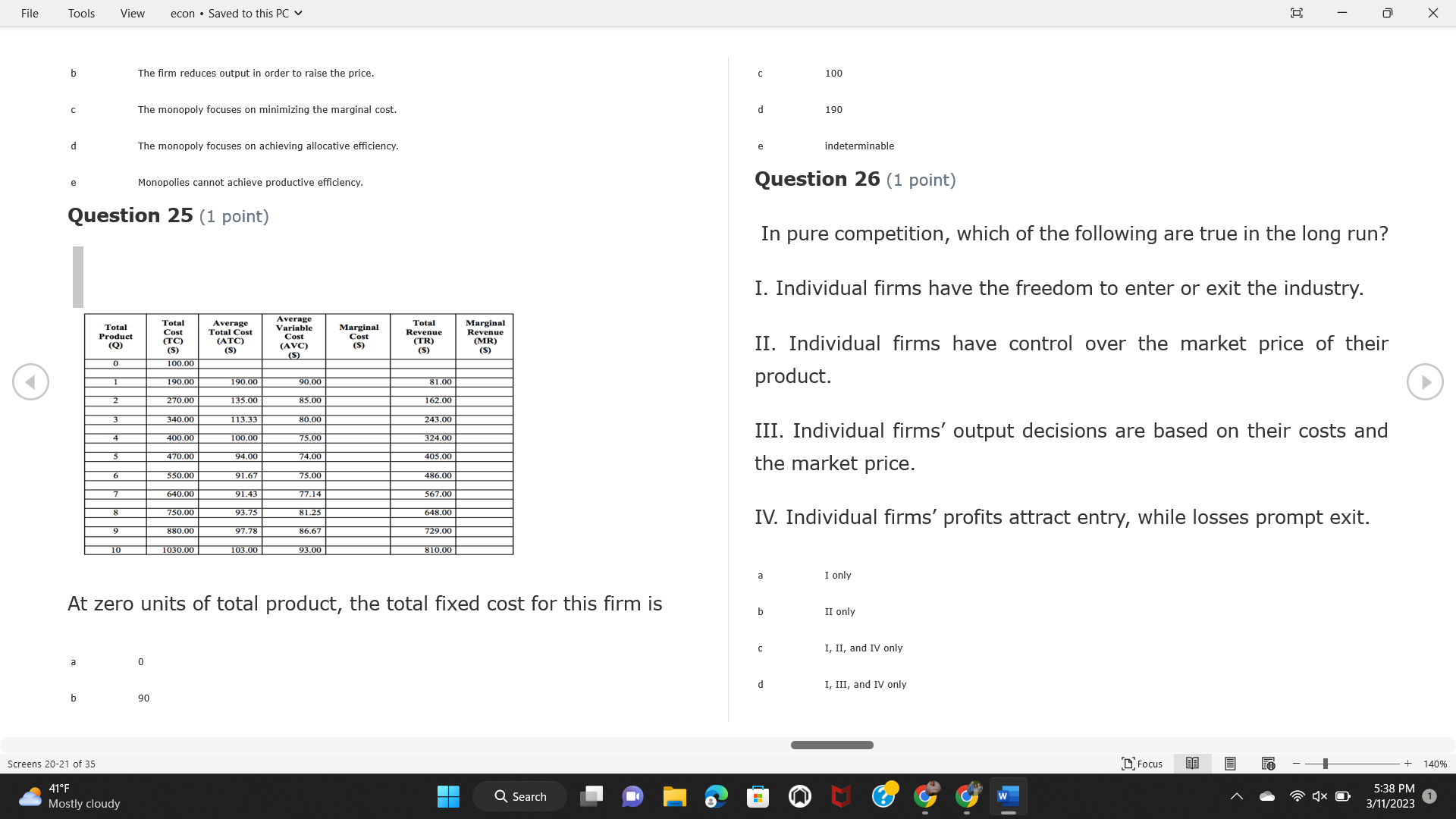
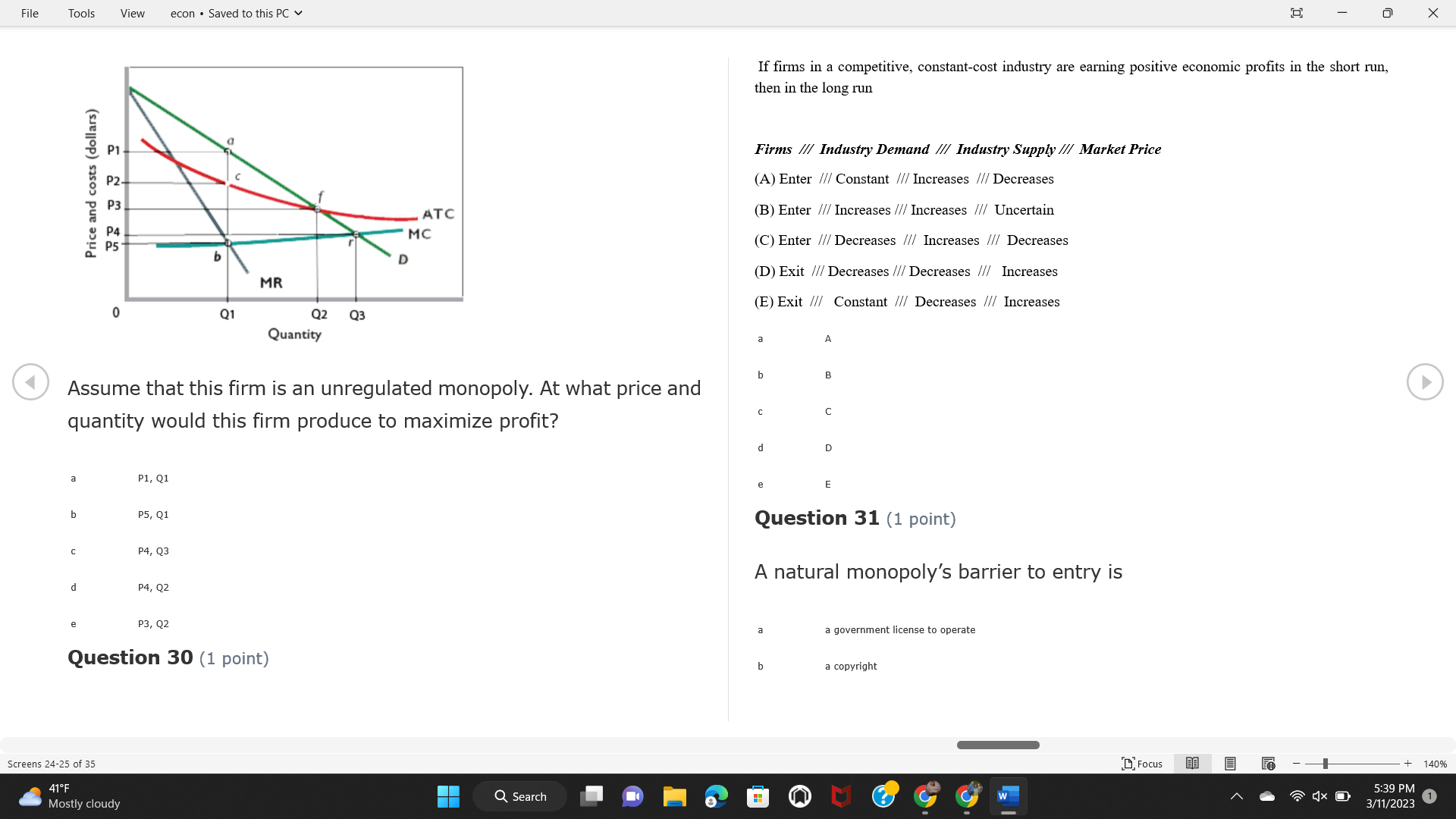
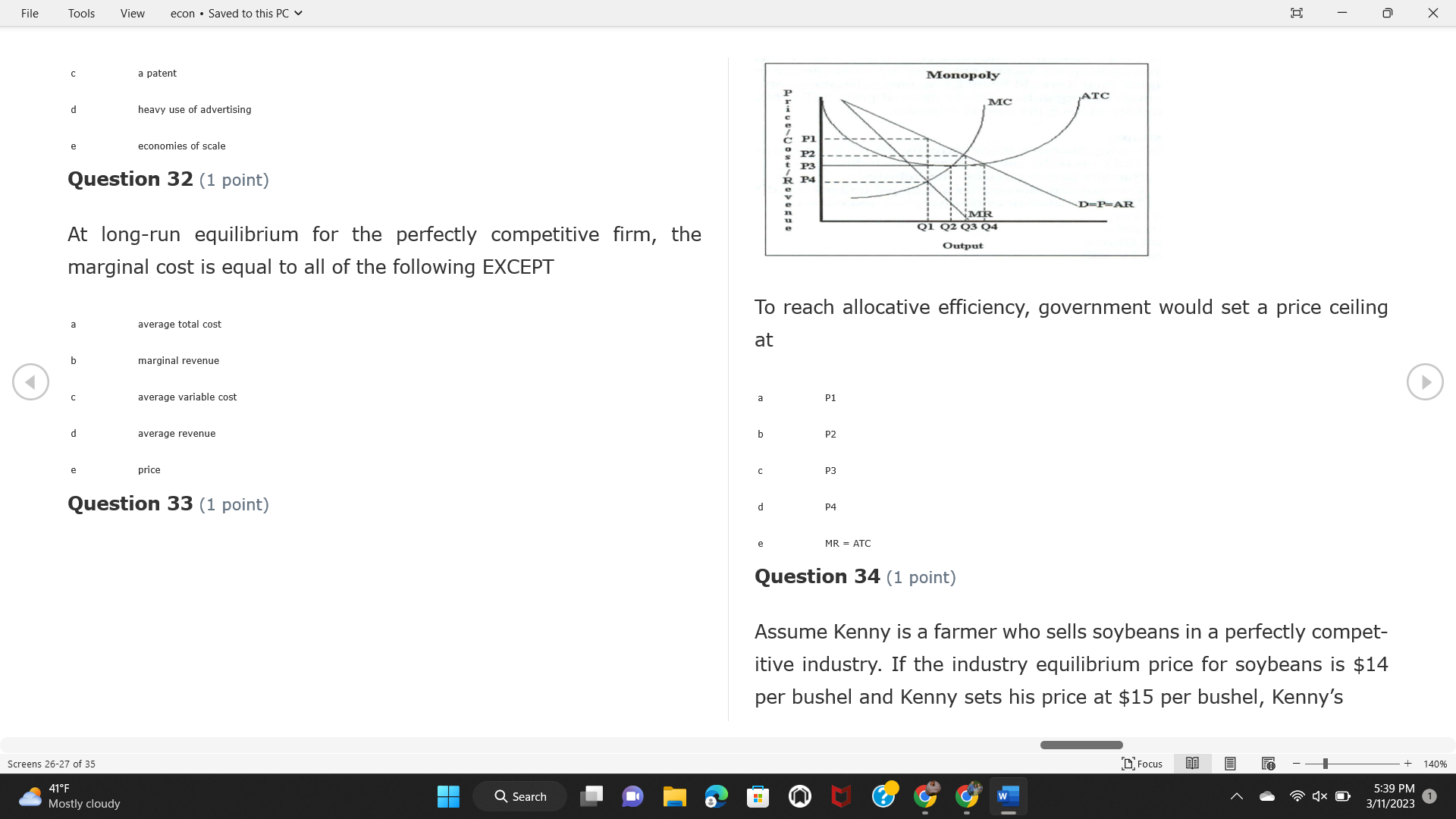
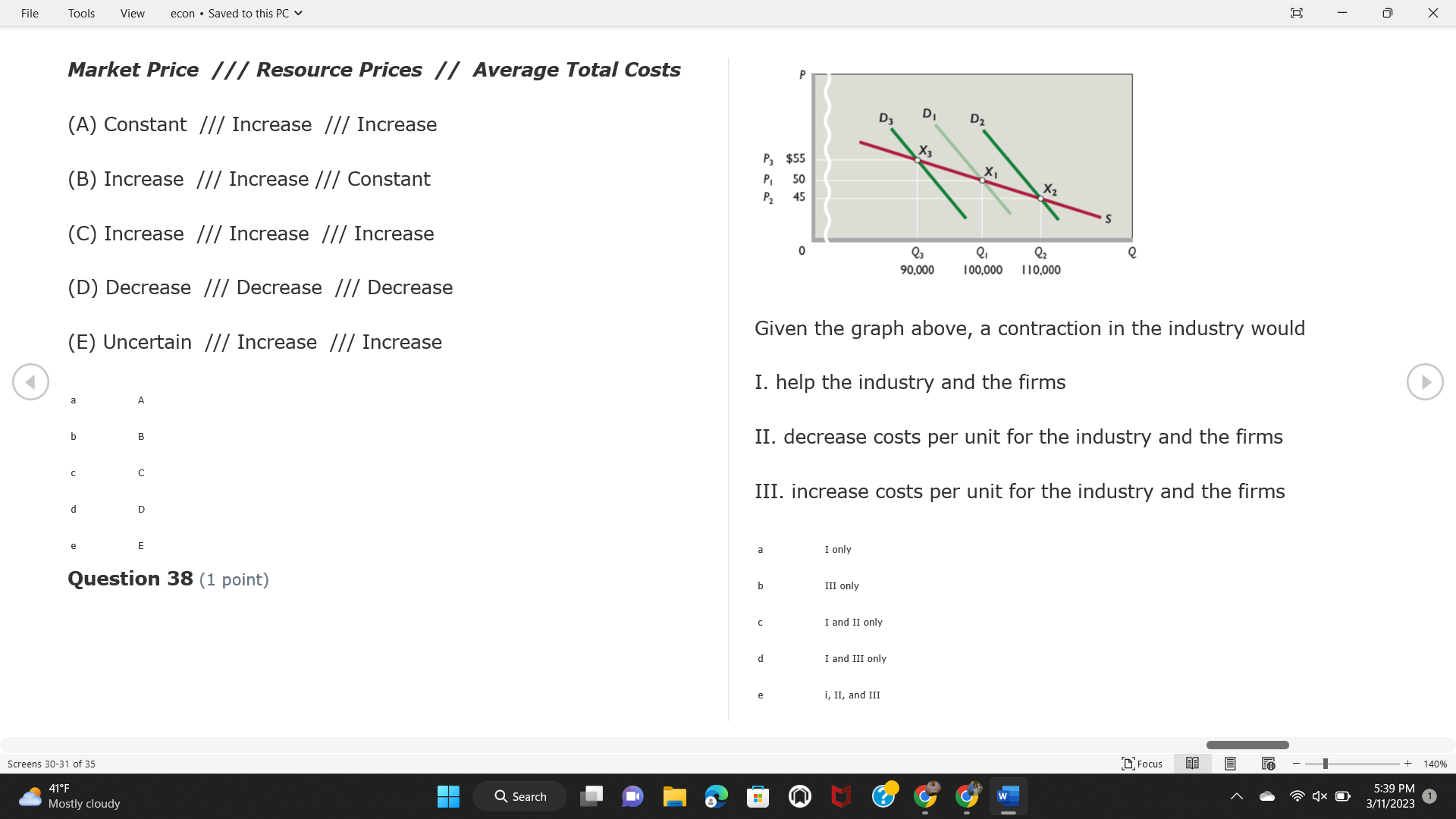
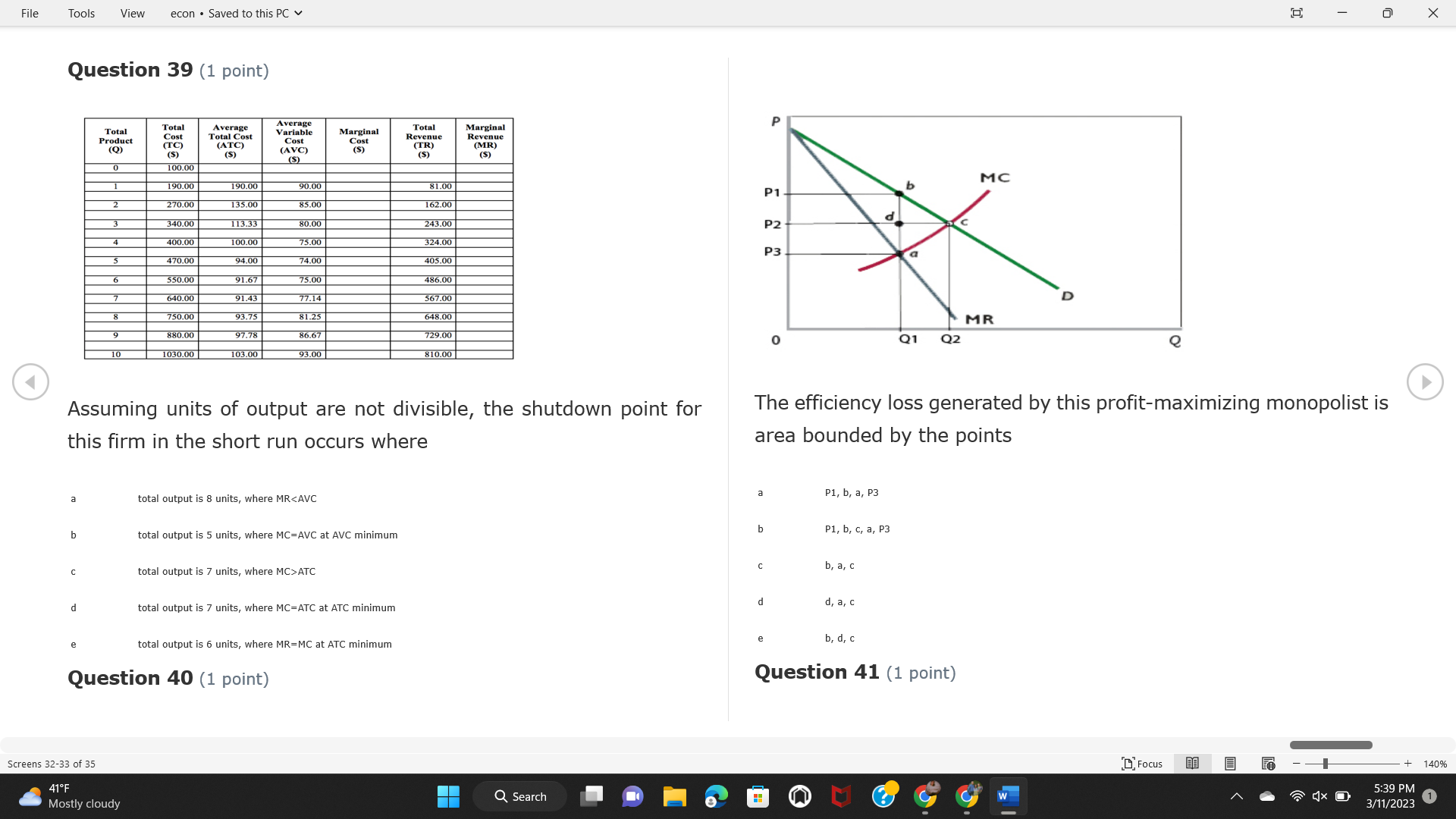
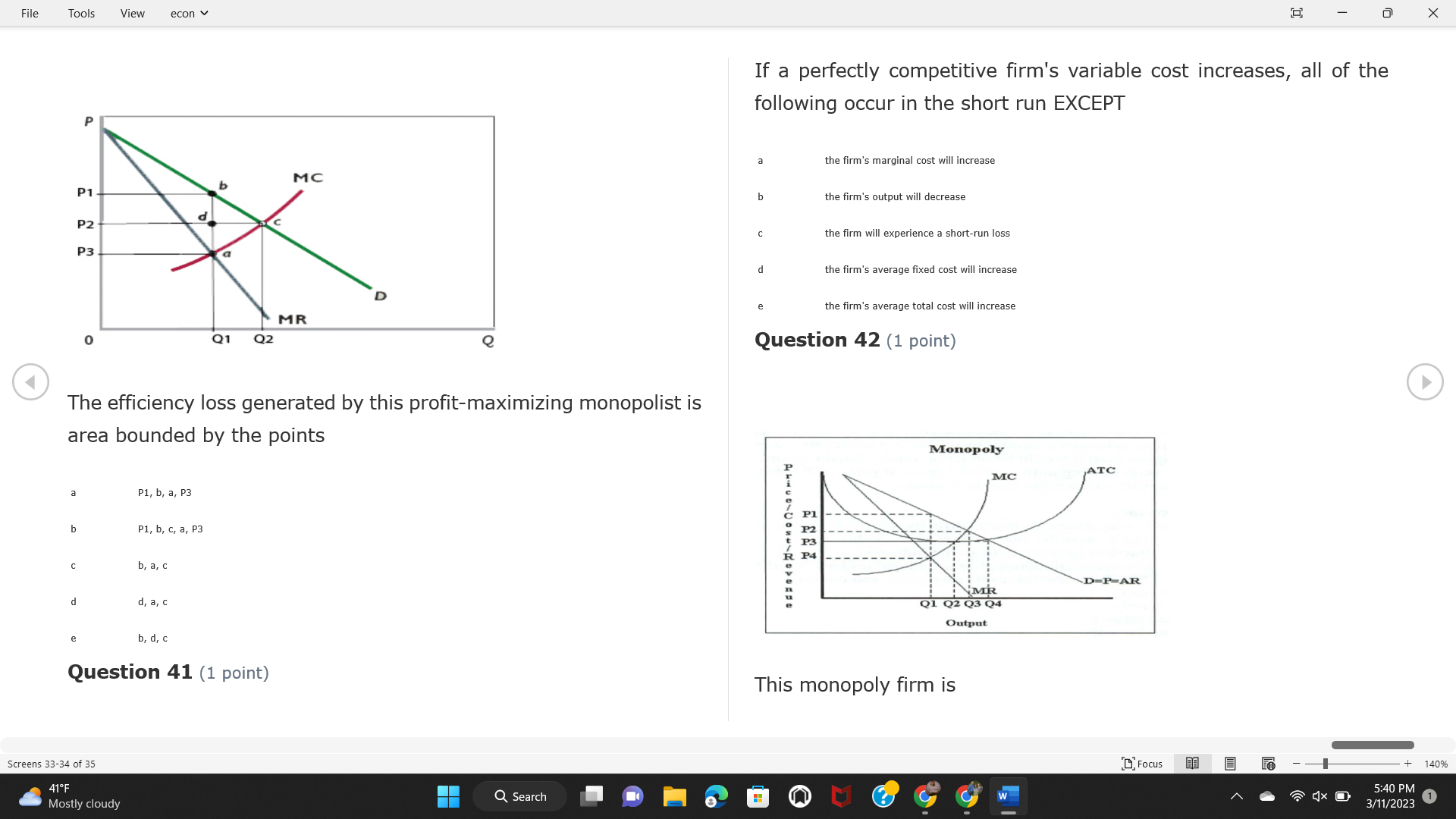
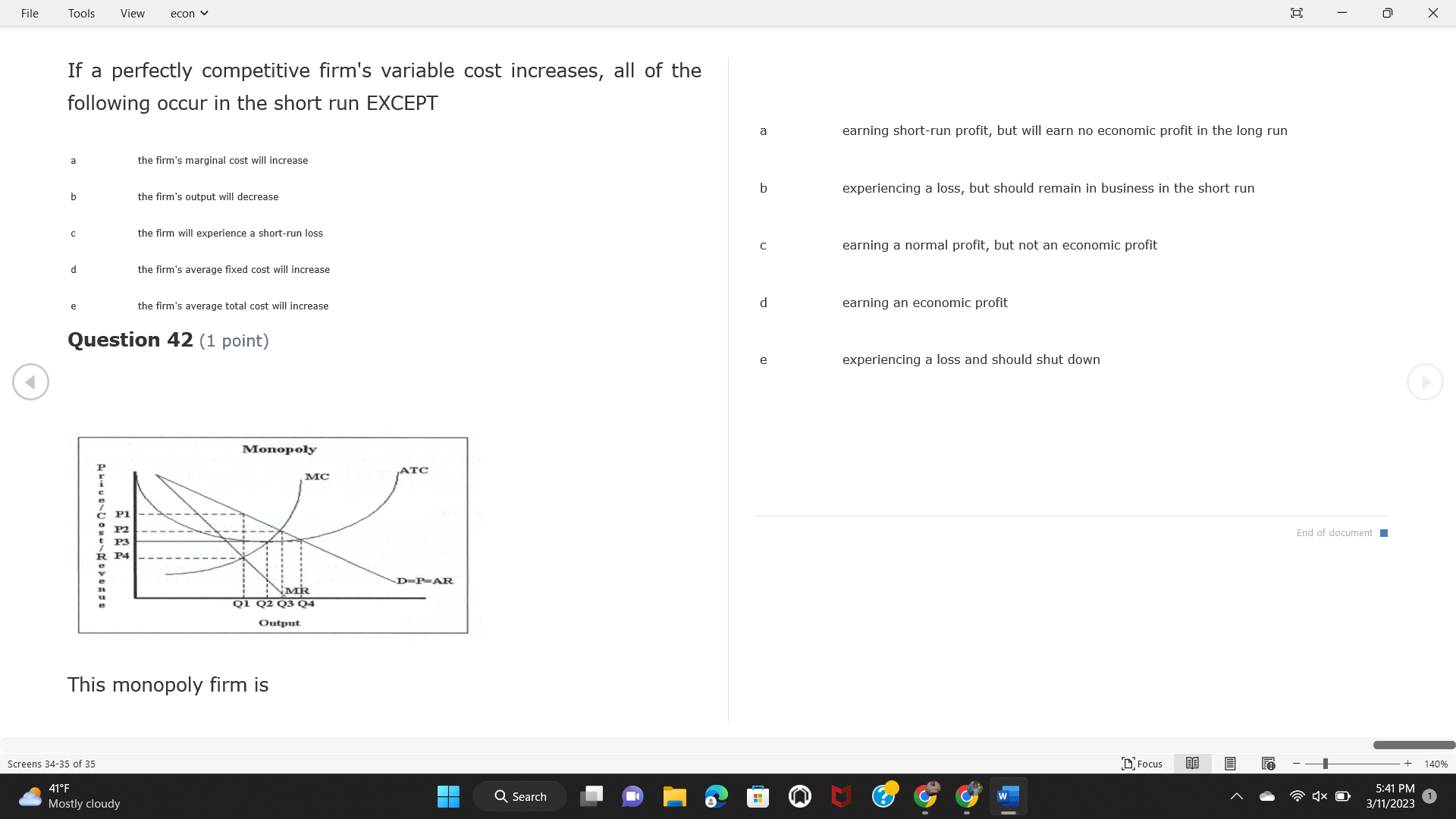
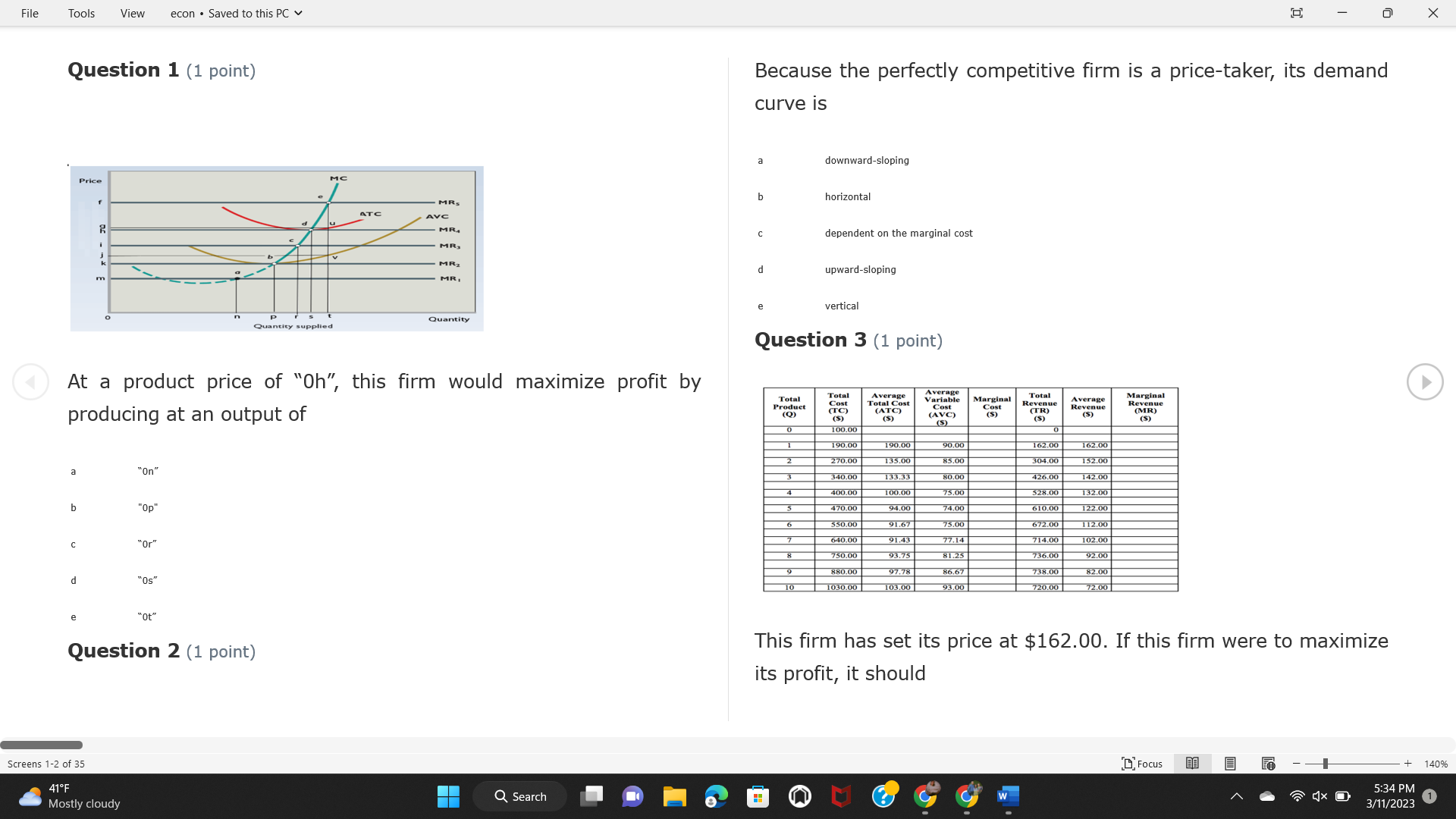
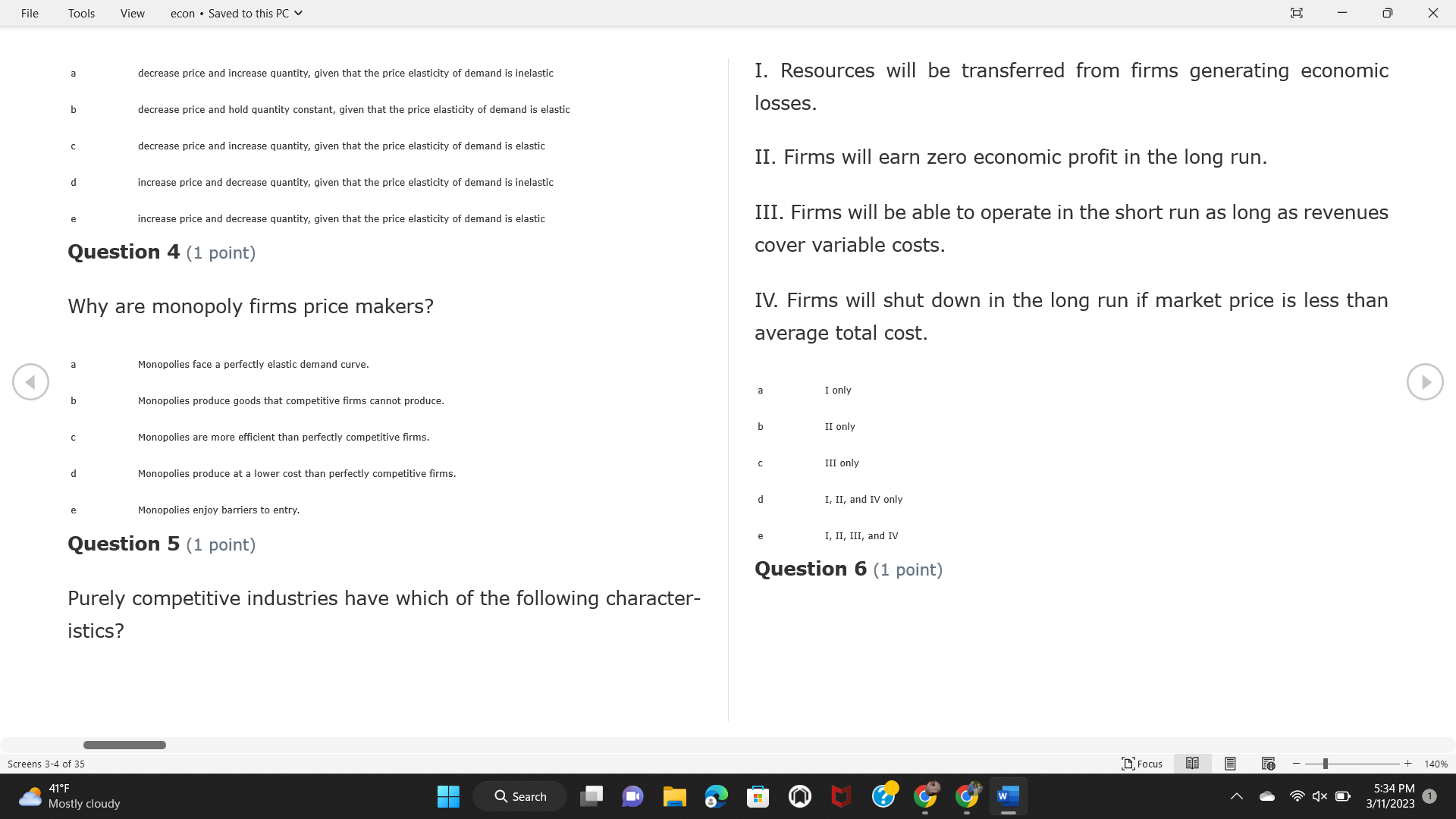
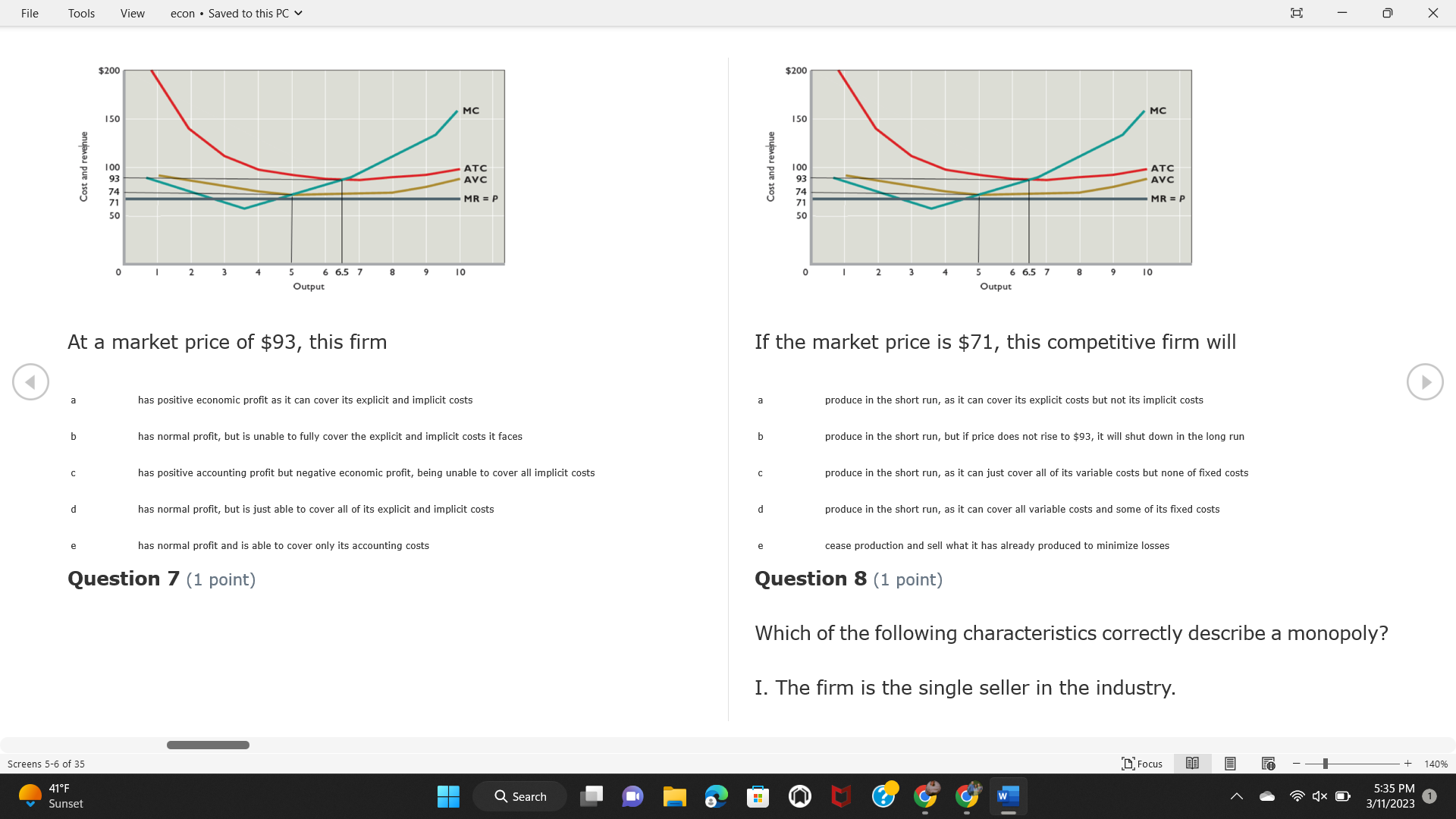
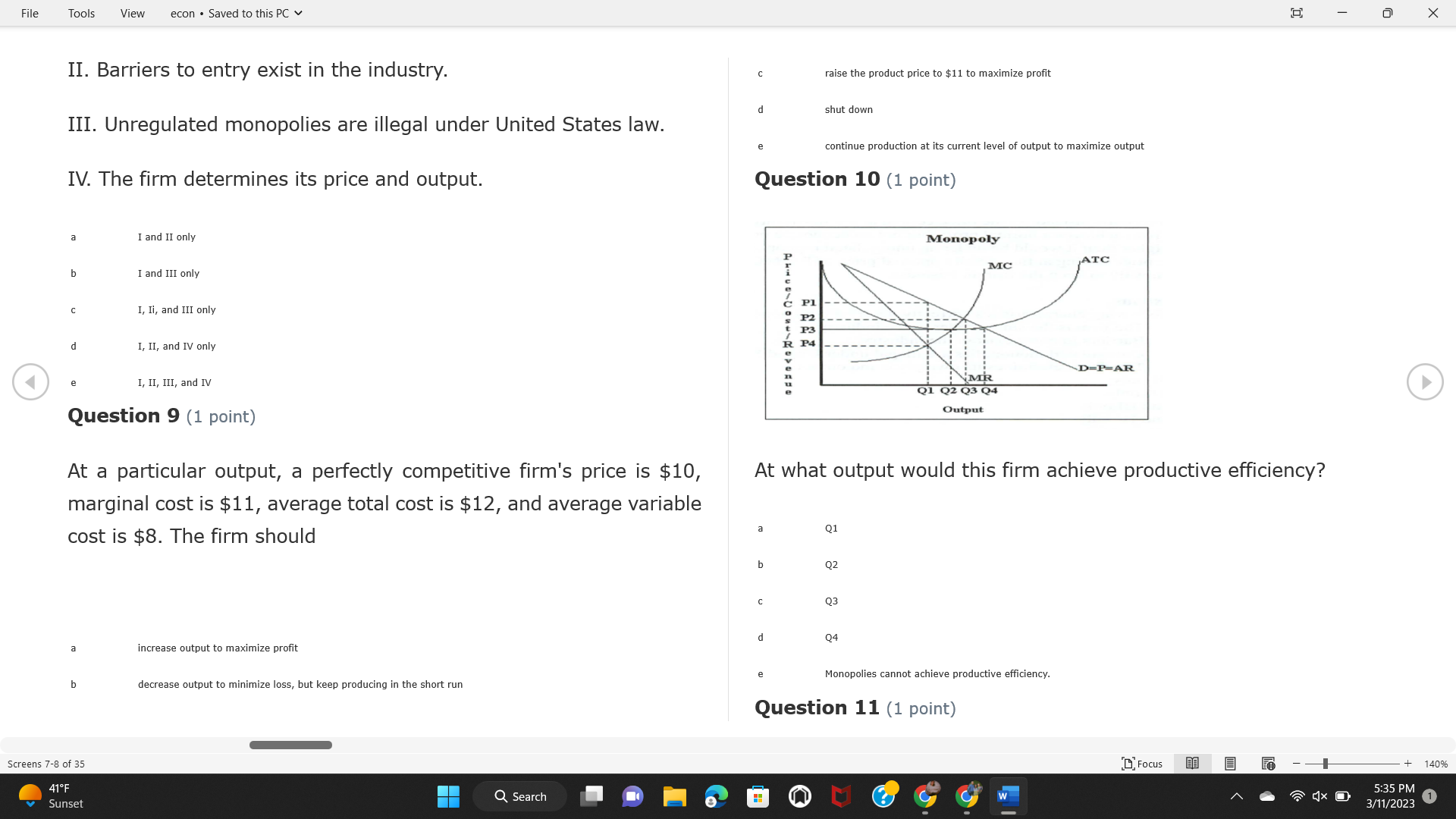
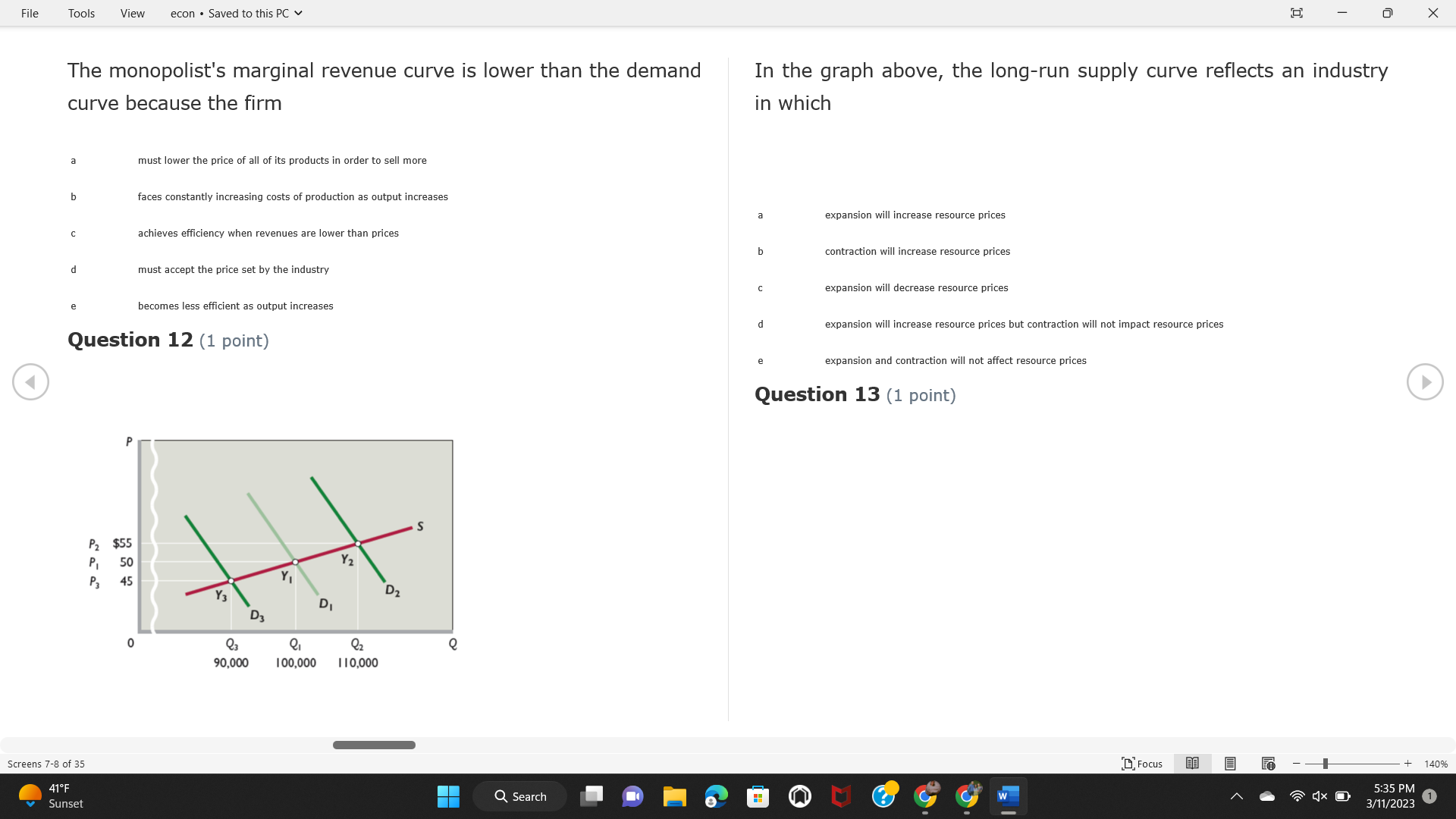
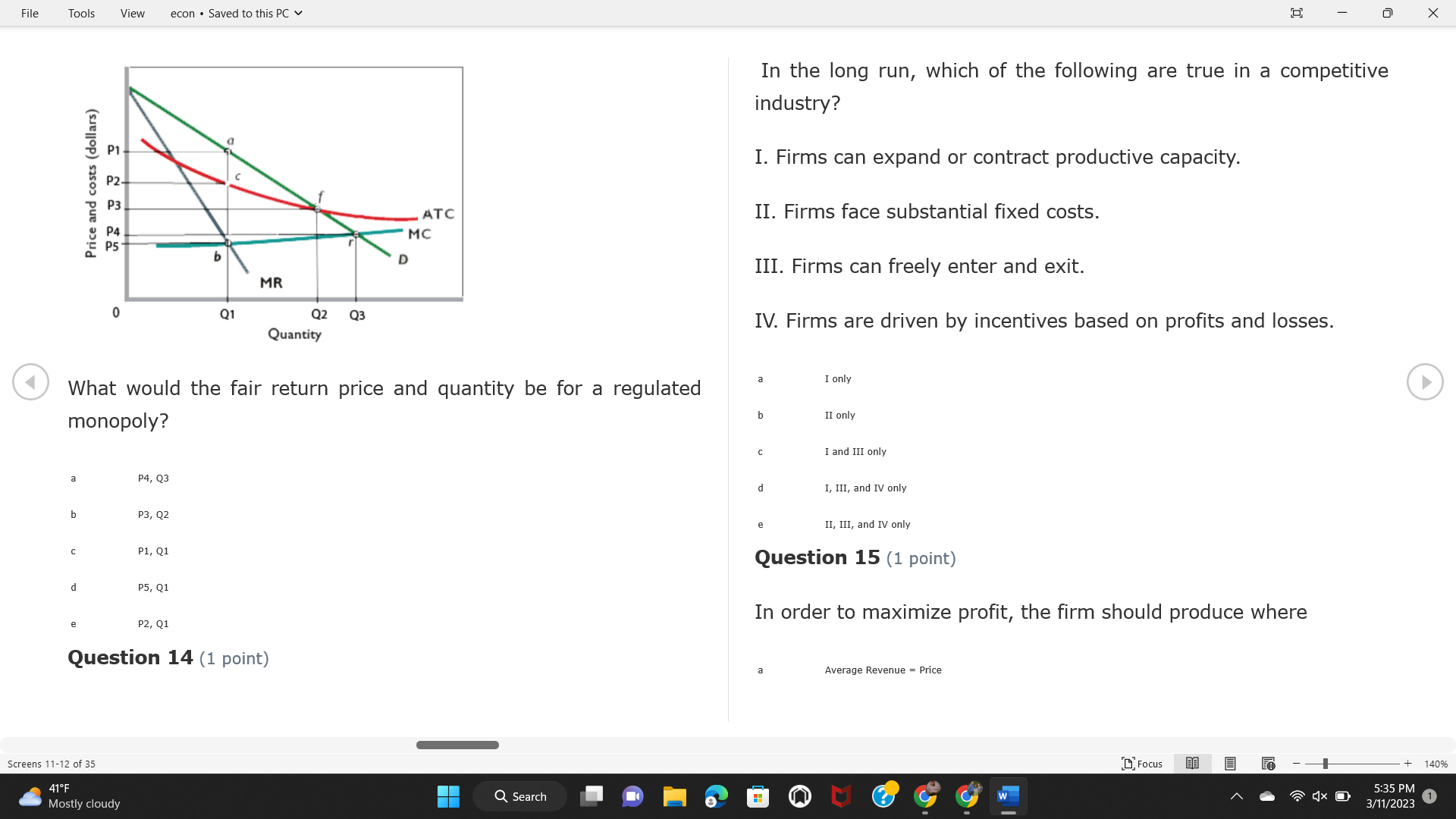
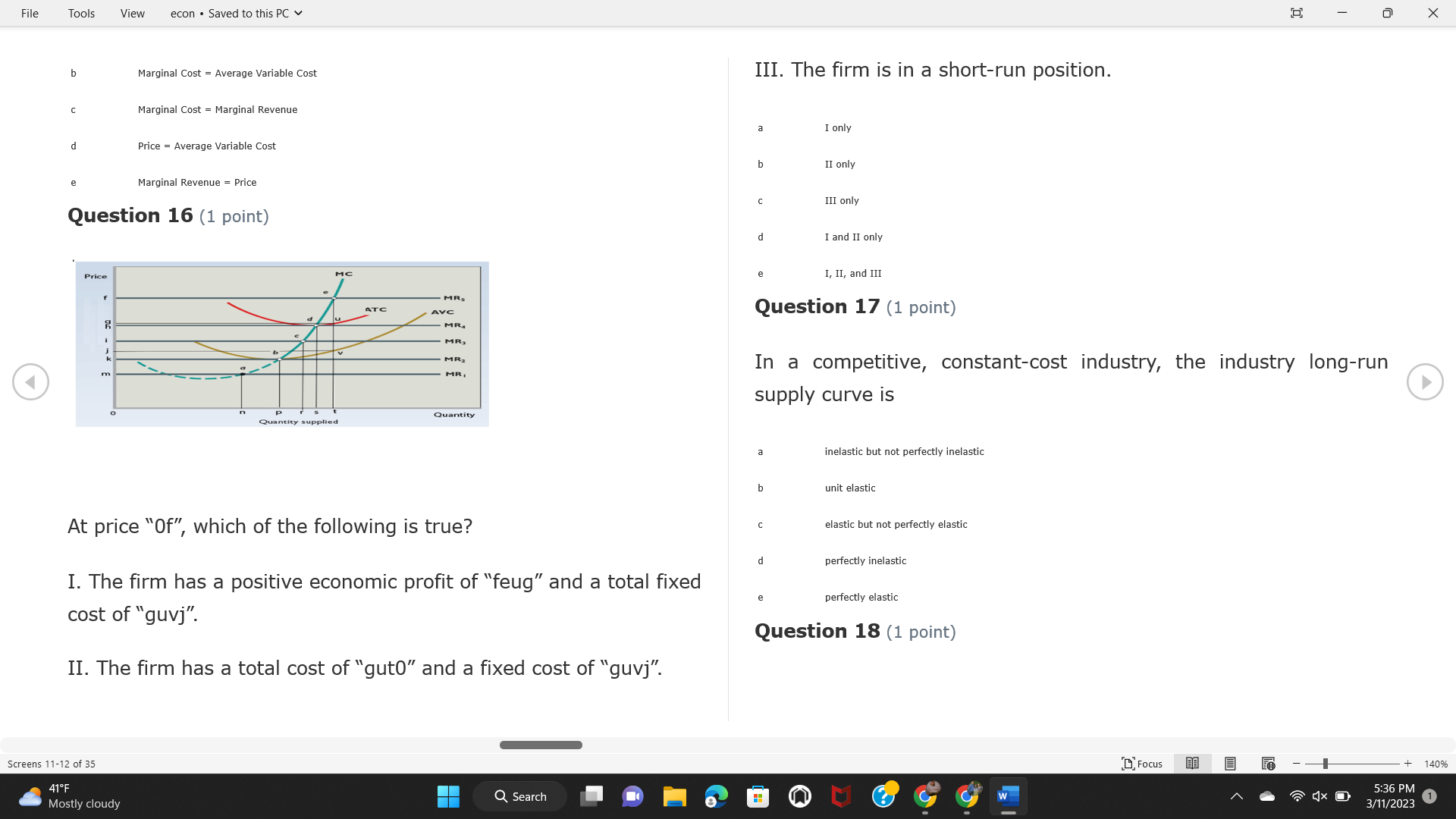
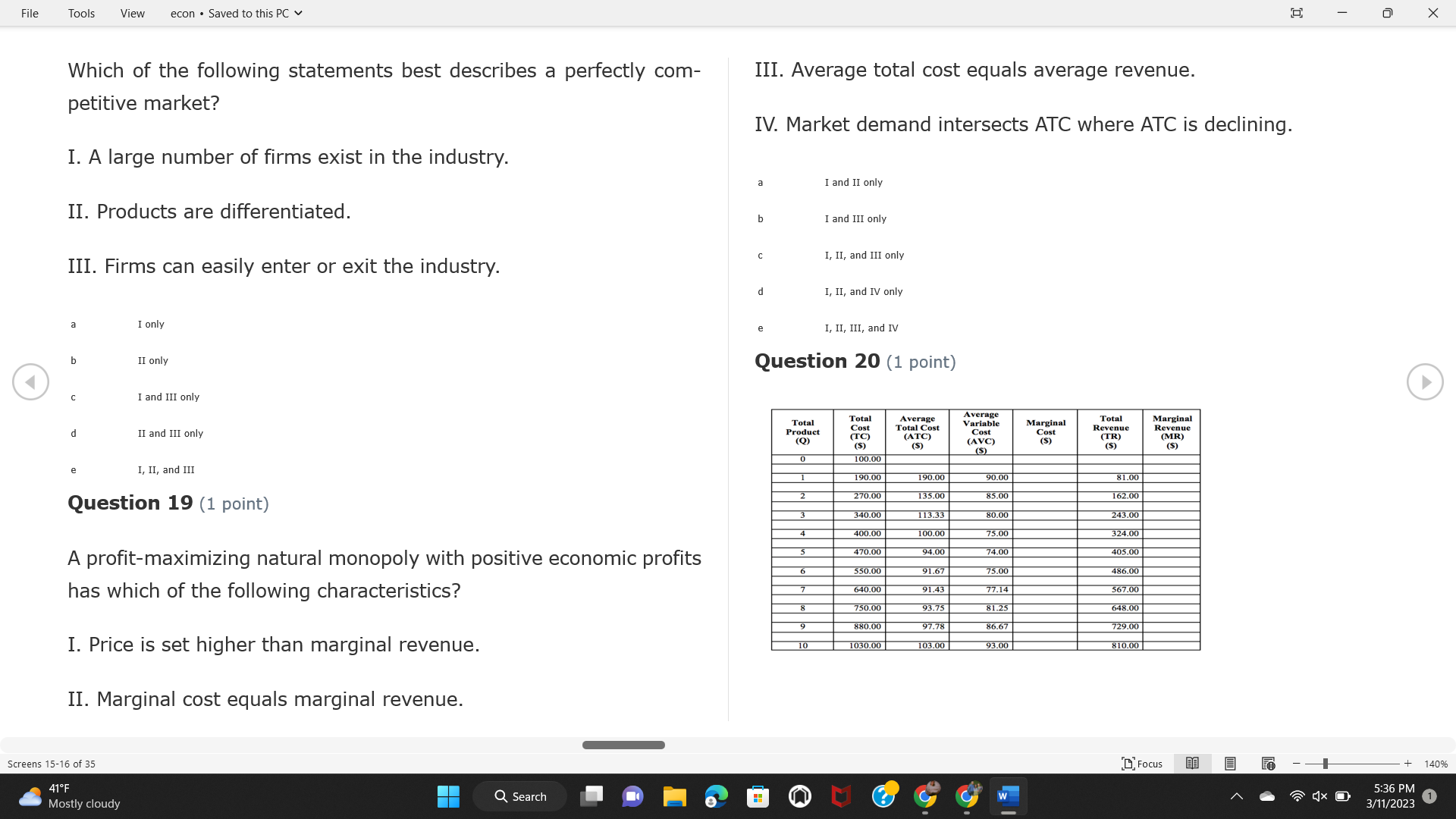
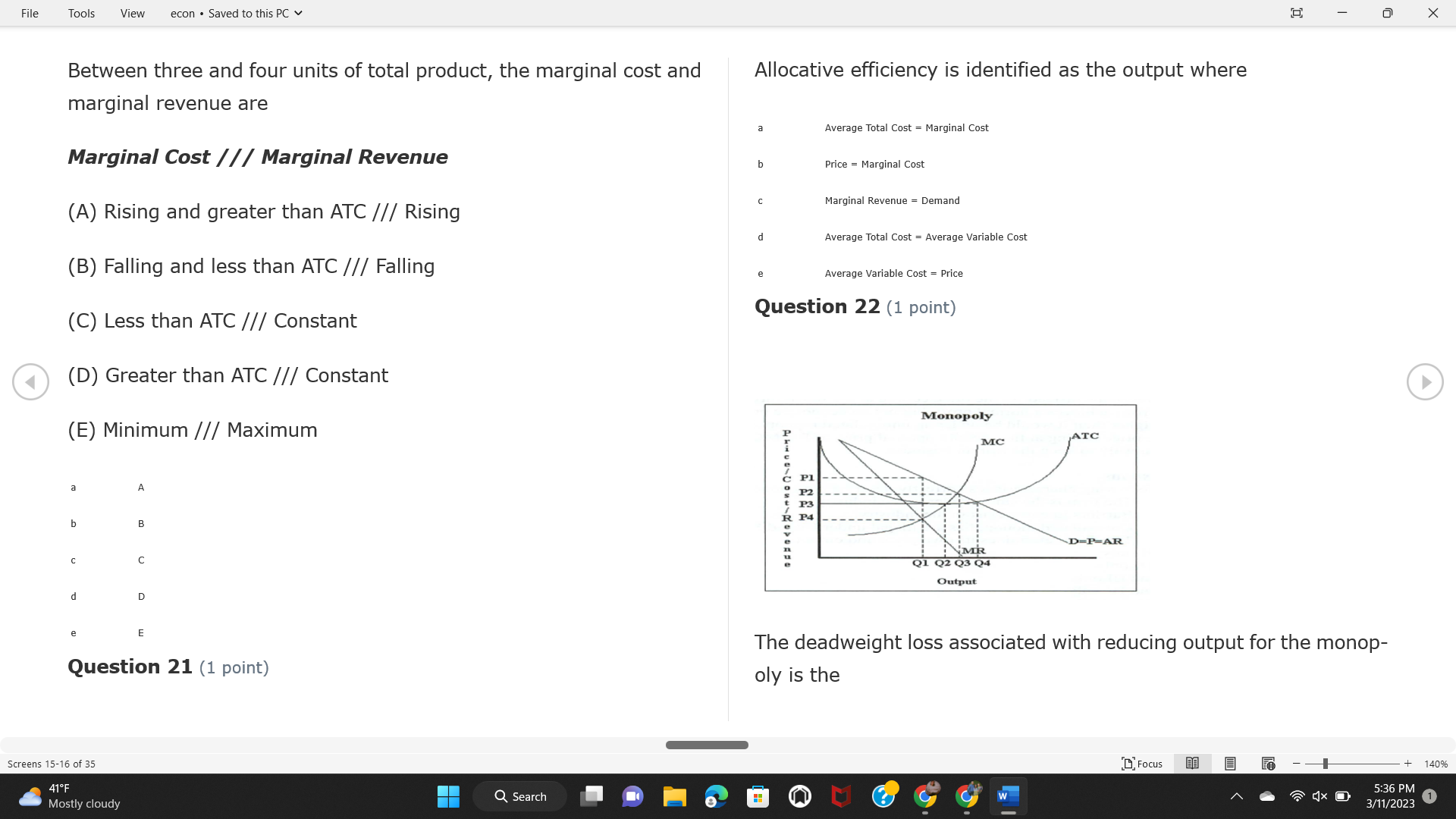
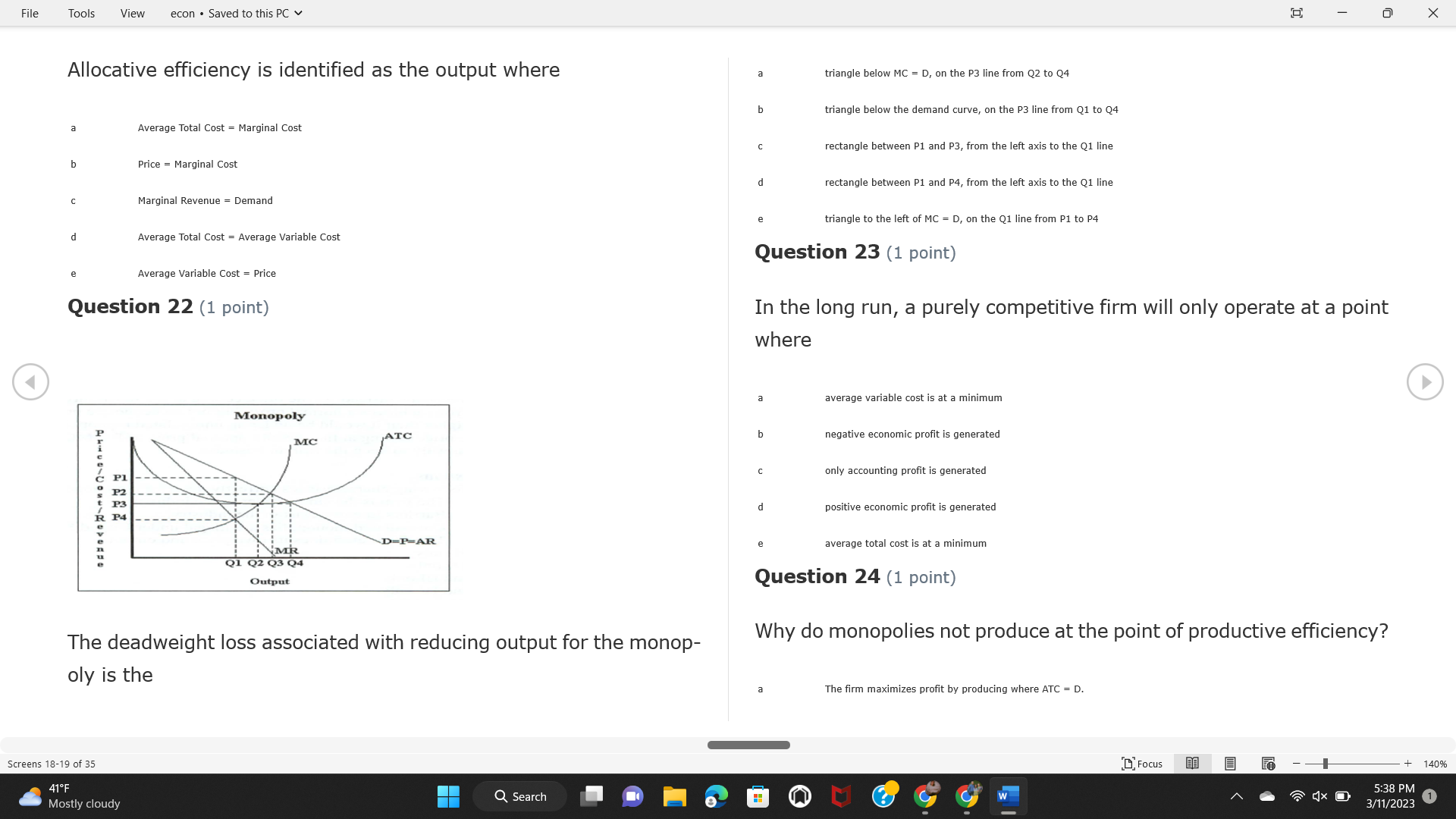
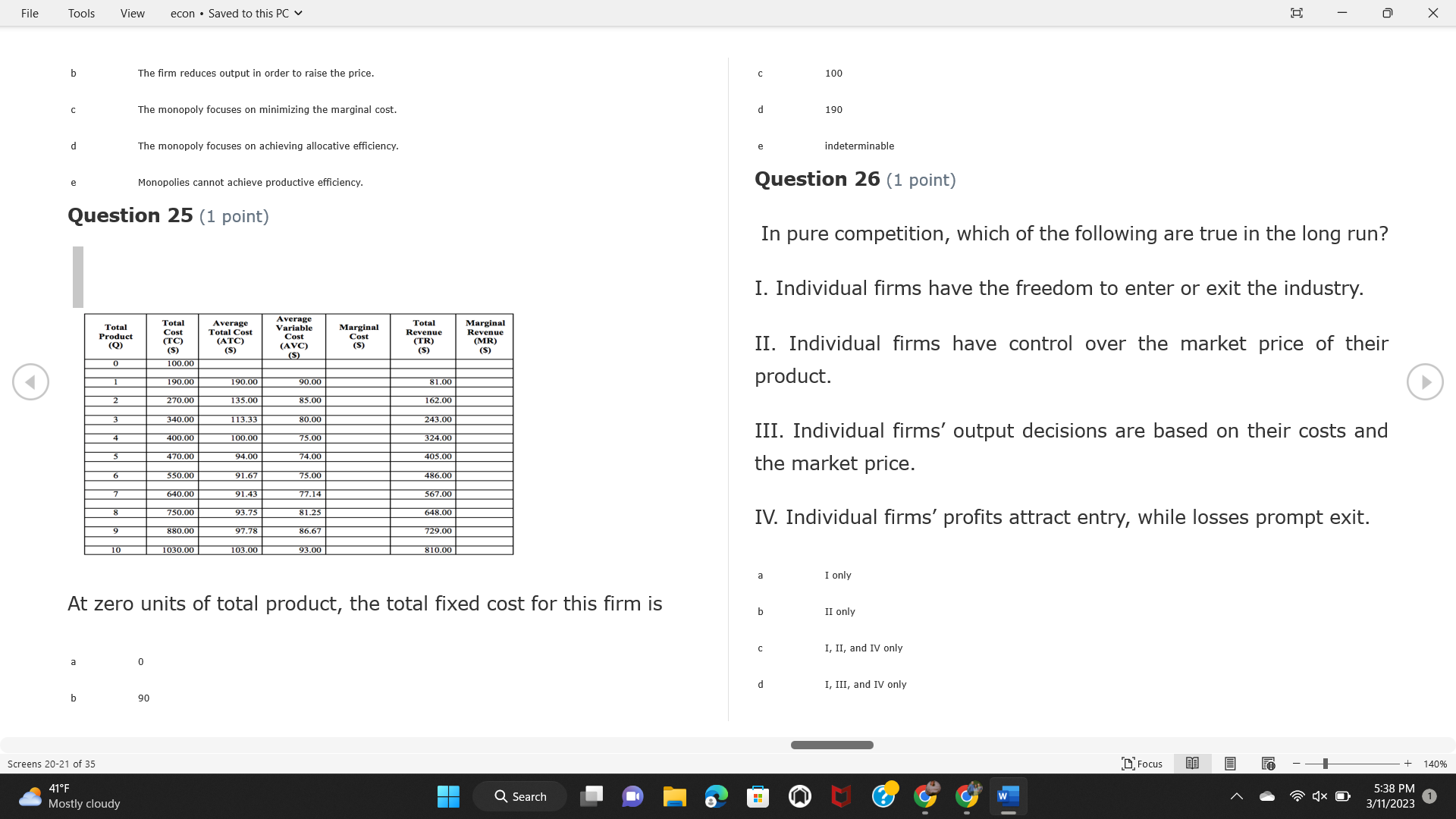
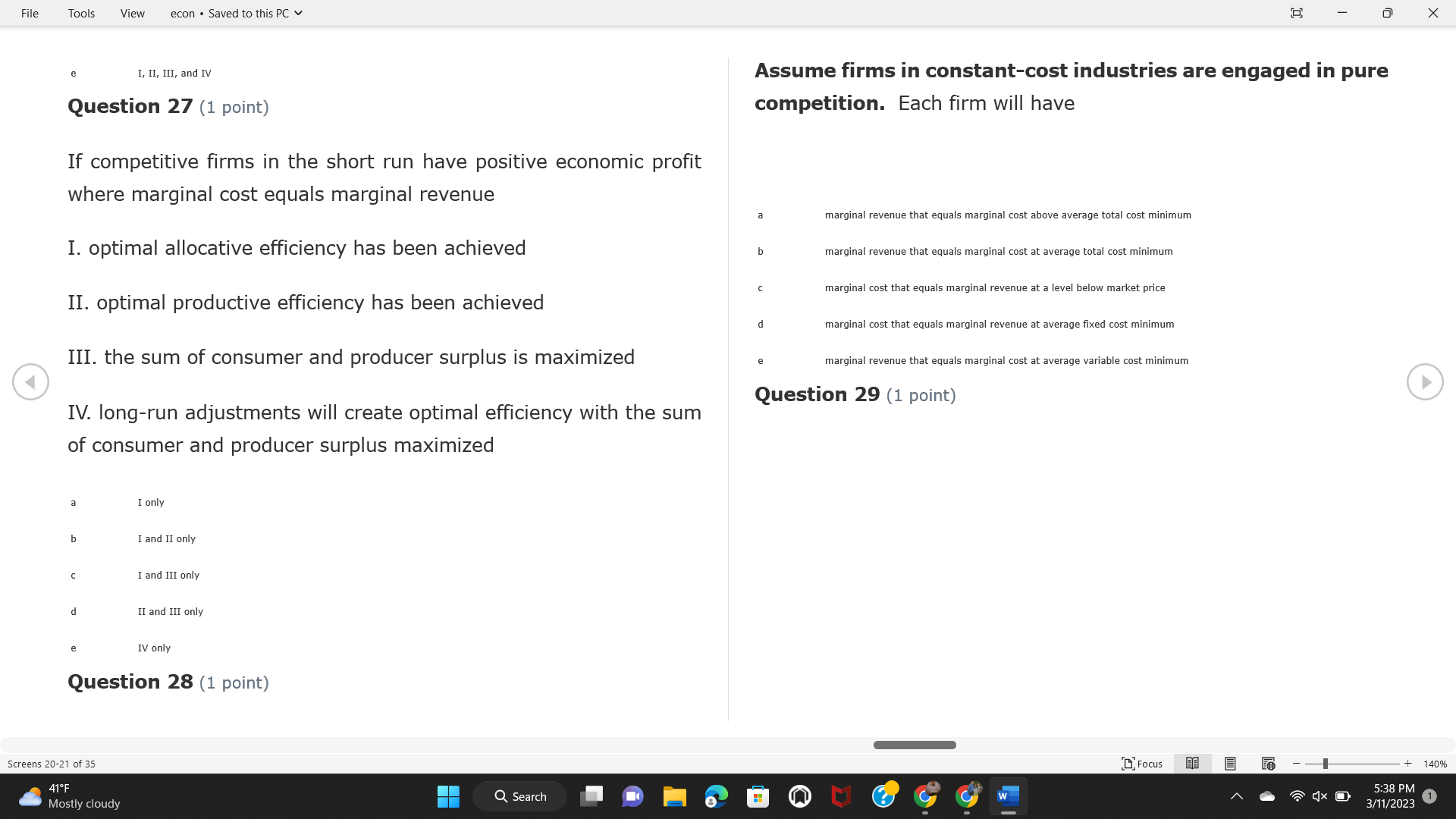
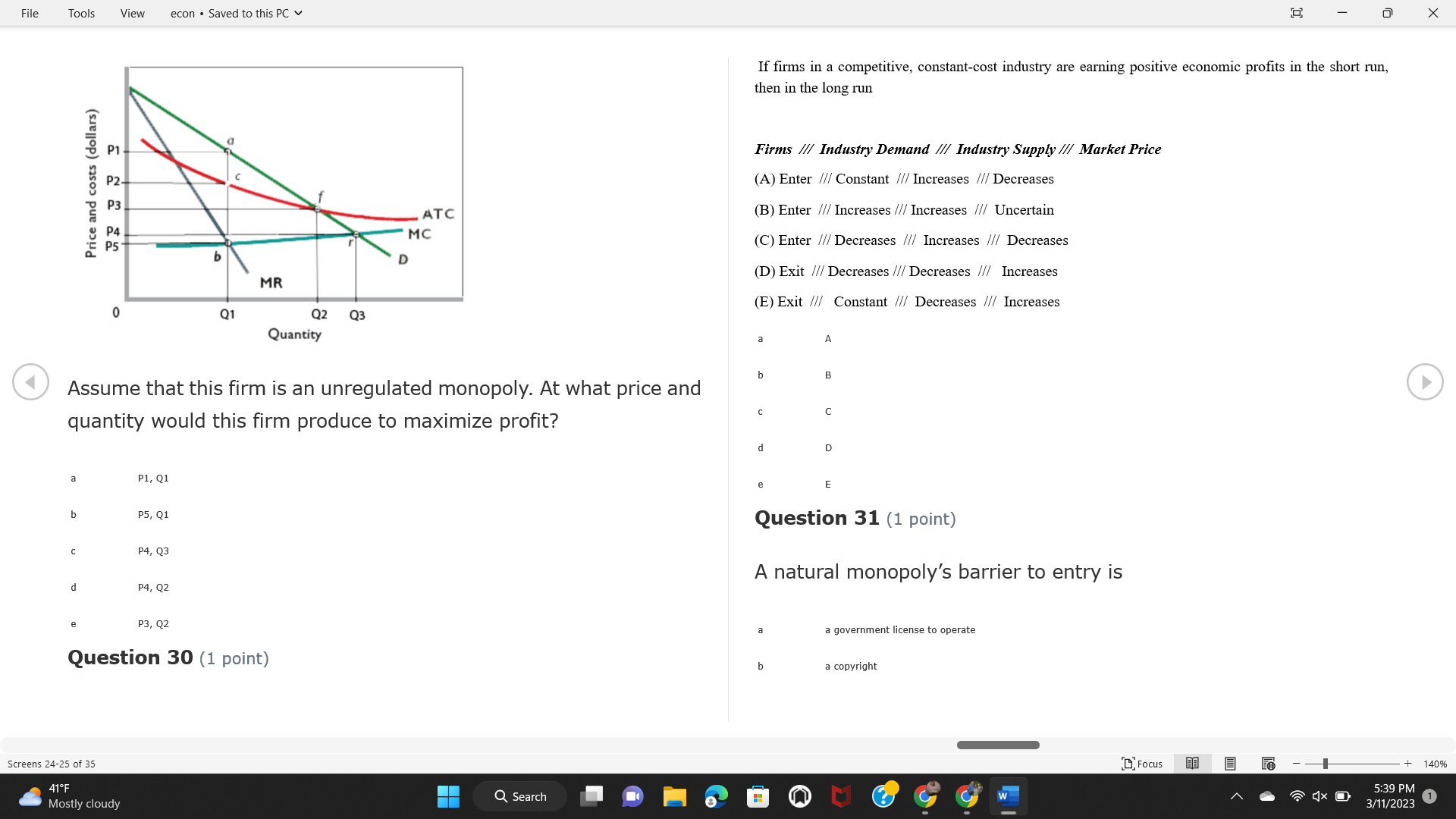
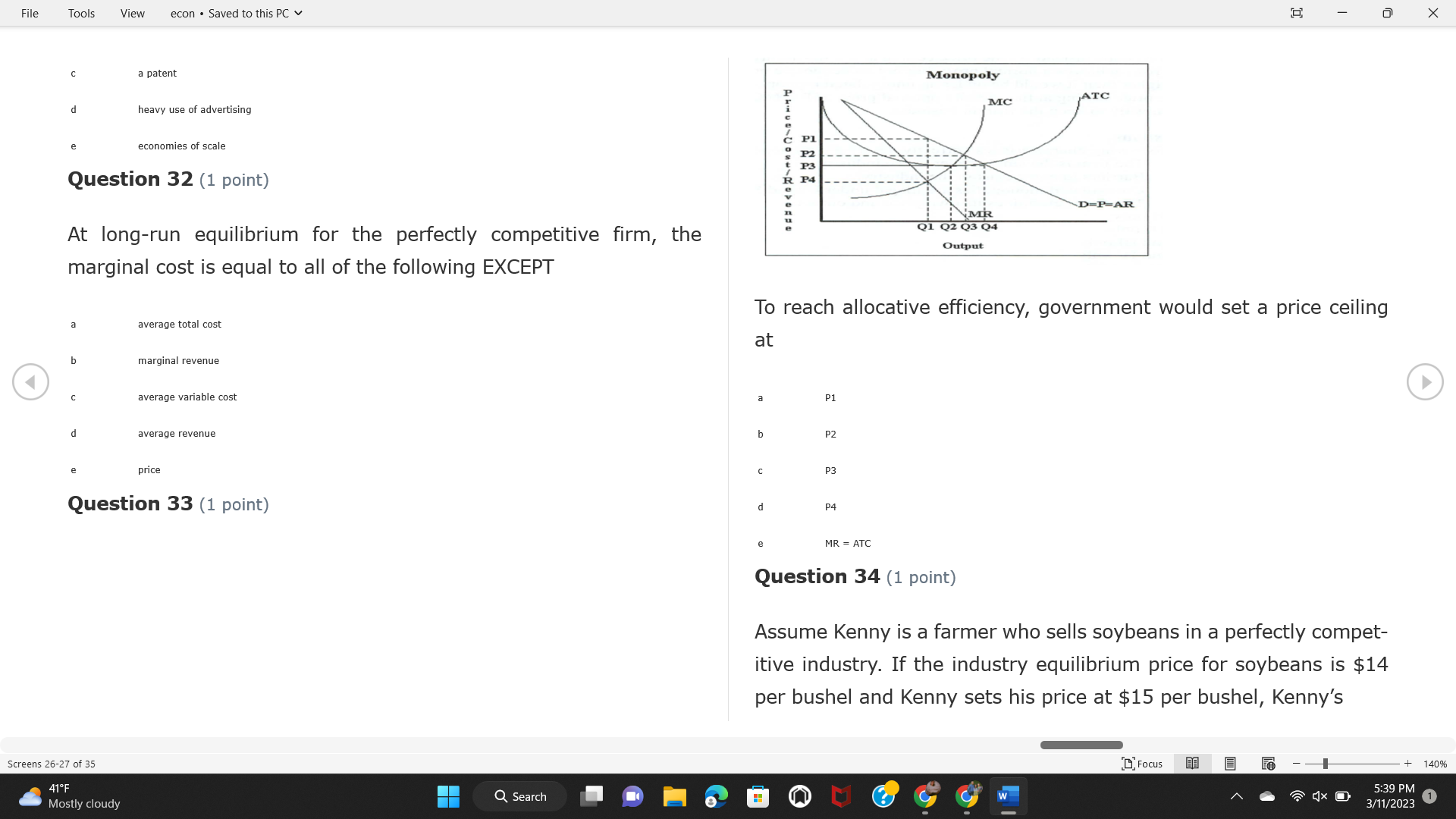
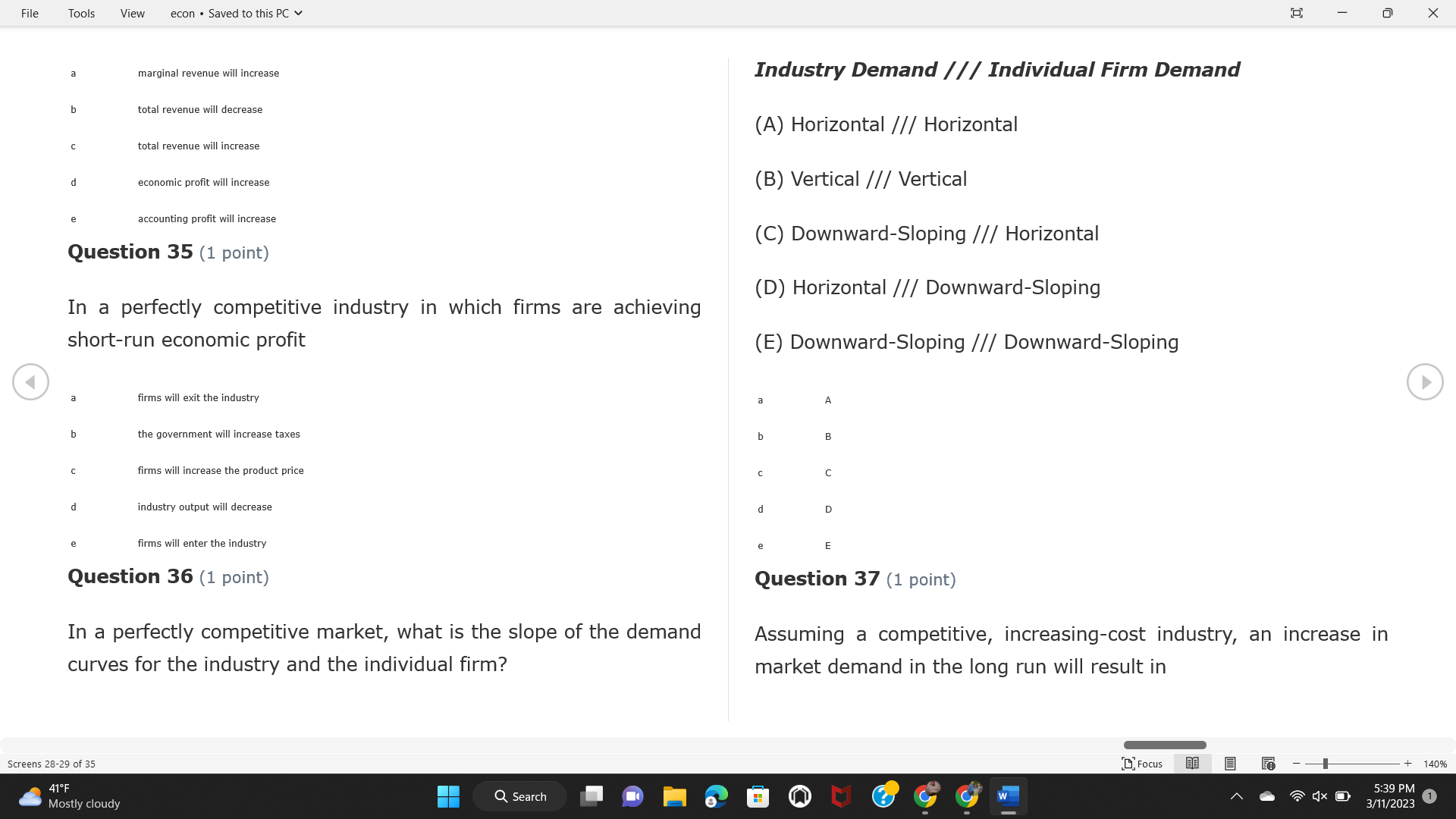
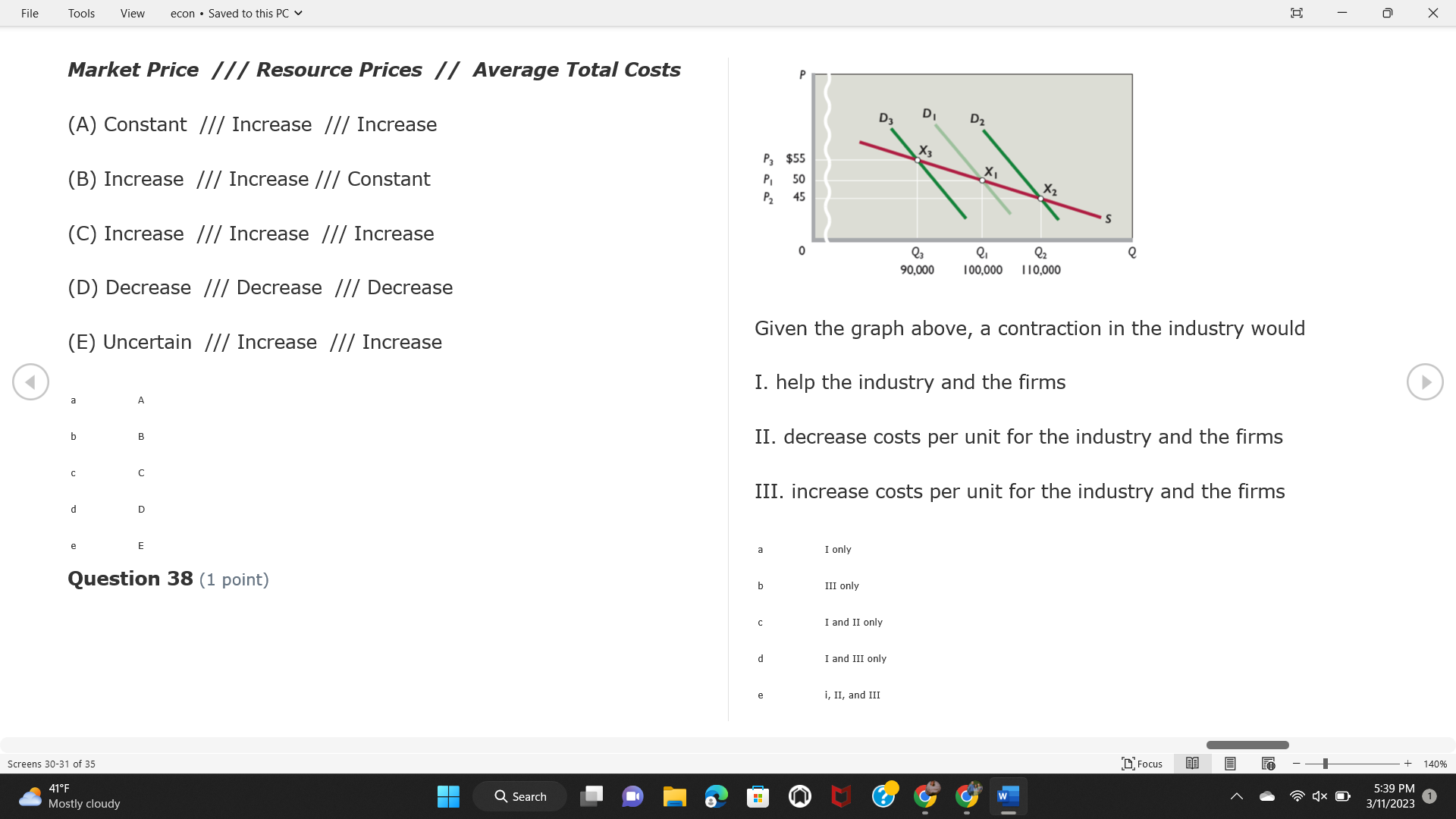
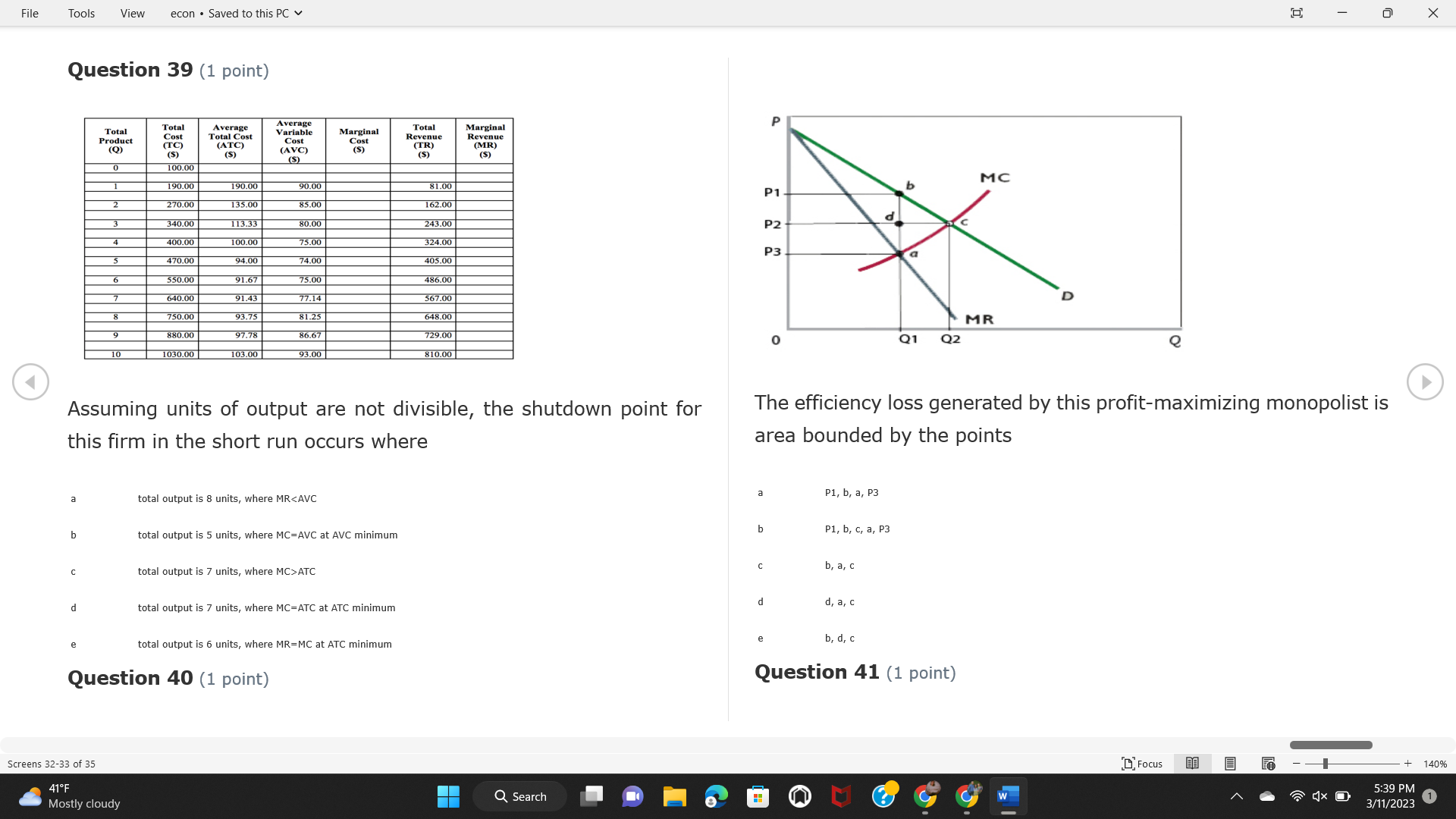
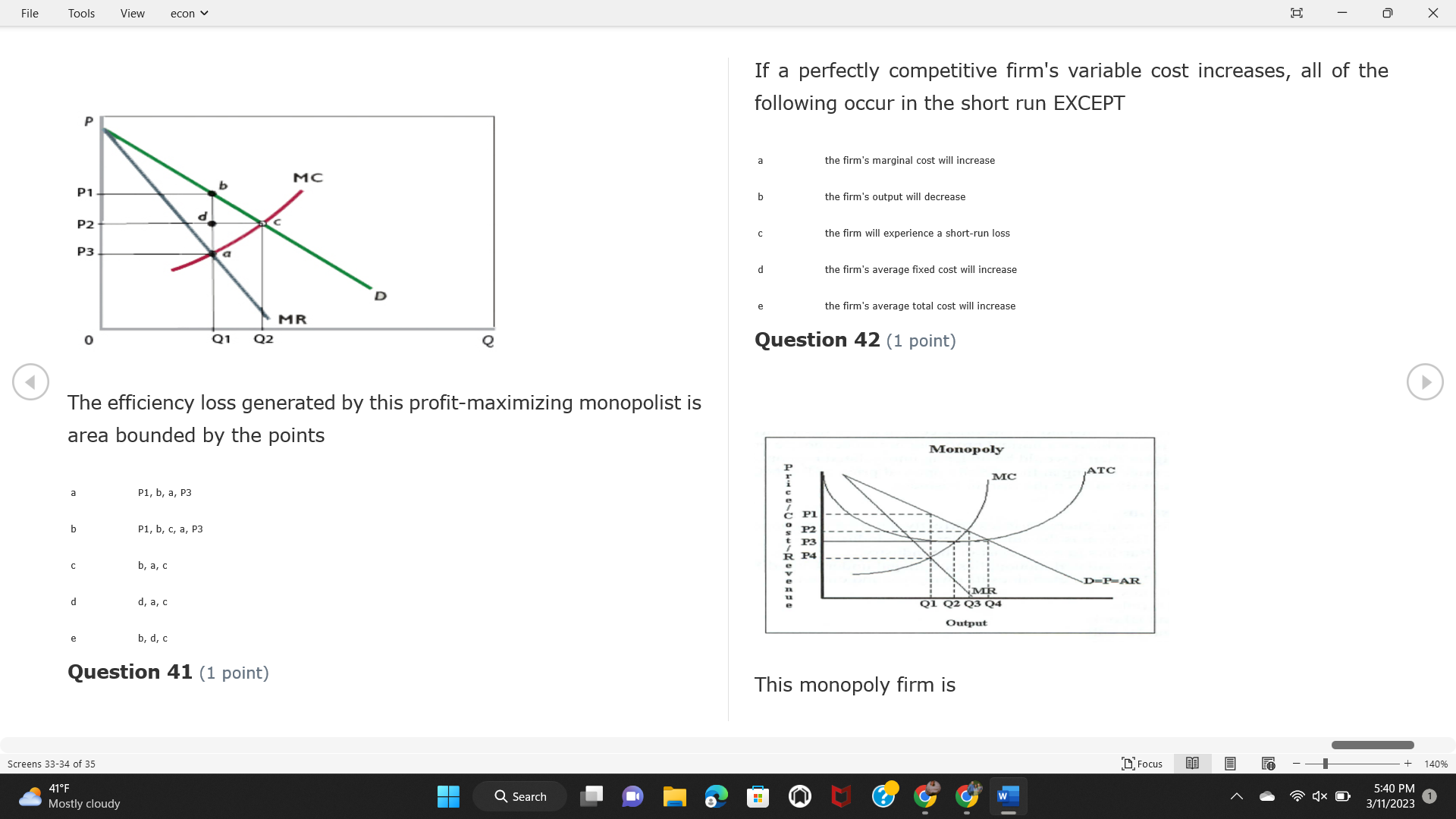
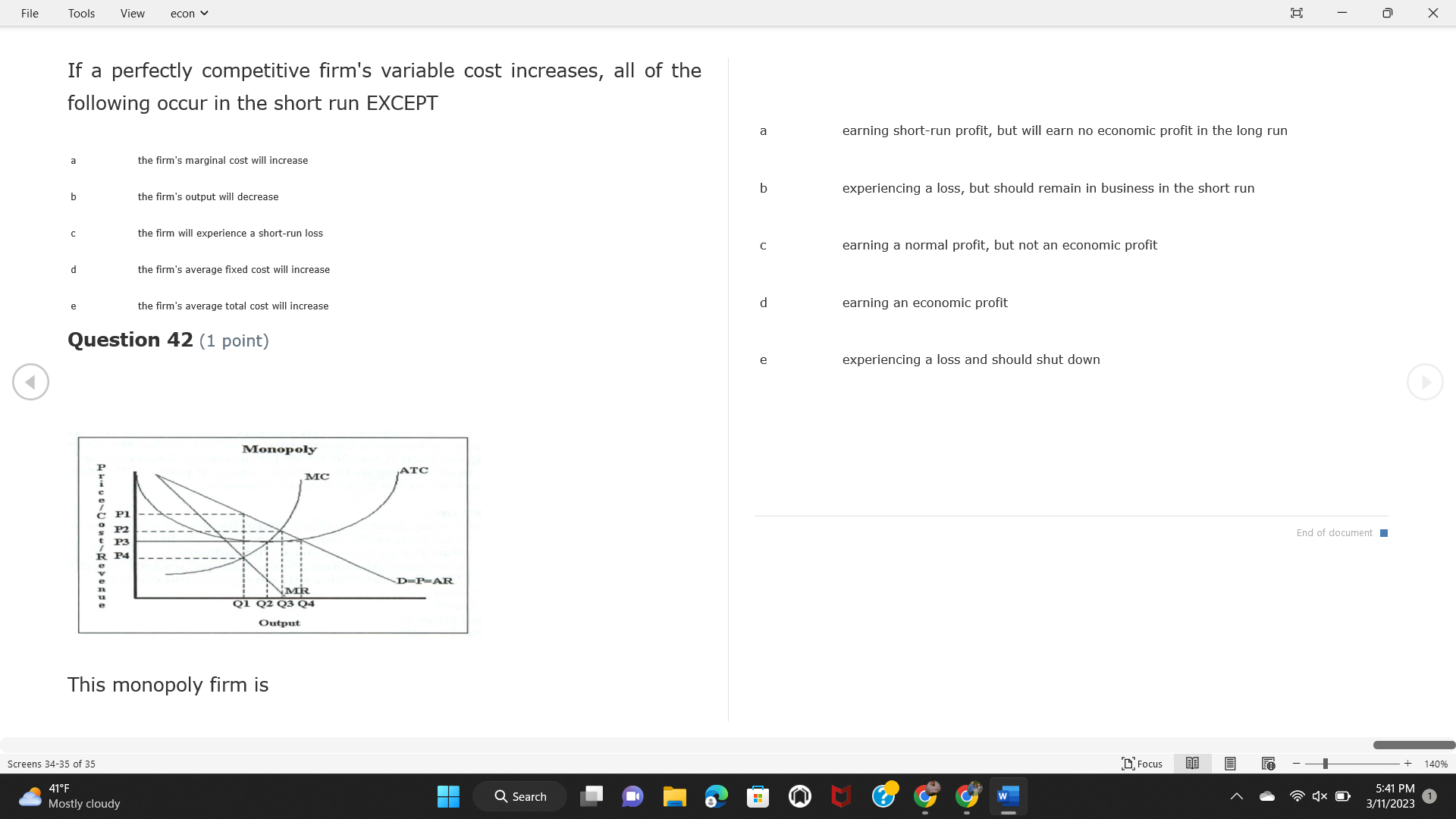
File Tools View econ . Saved to this PC v X Question 1 (1 point) Because the perfectly competitive firm is a price-taker, its demand curve is downward-sloping Price MC b MRS horizontal ATC AVC - MR. C dependent on the marginal cost MR, MR2 d upward-sloping MR, e vertical Quantity supplied Quantity Question 3 (1 point) At a product price of "Oh", this firm would maximize profit by Total Total Average Average Variable Marginal Total Average Marginal Revenue producing at an output of Product Cost (ATC) Revenue (S ) (MR) (5) (AVC IS (S) ($) 100.00 190.00 190.00 90.00 162.00 162.00 270.00 135.0 85.00 304.00 132.00 a "On" 340.00 133.33 80.00 426.00 142.00 400.00 100.00 75.00 528.00 132.00 b "Op" 470.00 94.00 74.00 610.00 122.00 $50.00 91.67 75.00 672.00 1 12.00 C "or " 640.00 91.43 77.14 714.00 102.00 750.00 93.75 81.25 736.00 92.00 380.00 97.78 86.67 738.00 82.00 d "0s" 1030.00 103.00 93.00 720.00 72.00 e "of " Question 2 (1 point) This firm has set its price at $162.00. If this firm were to maximize its profit, it should Screens 1-2 of 35 " Focus + 140% 41 F Q Search 5:34 PM Mostly cloudy W 3/11/2023 1File Tools View econ . Saved to this PC v X a decrease price and increase quantity, given that the price elasticity of demand is inelastic I. Resources will be transferred from firms generating economic b decrease price and hold quantity constant, given that the price elasticity of demand is elastic losses. C decrease price and increase quantity, given that the price elasticity of demand is elastic II. Firms will earn zero economic profit in the long run. d increase price and decrease quantity, given that the price elasticity of demand is inelastic e increase price and decrease quantity, given that the price elasticity of demand is elastic III. Firms will be able to operate in the short run as long as revenues Question 4 (1 point) cover variable costs. Why are monopoly firms price makers? IV. Firms will shut down in the long run if market price is less than average total cost. Monopolies face a perfectly elastic demand curve. a I only Monopolies produce goods that competitive firms cannot produce. b II only Monopolies are more efficient than perfectly competitive firms. C III only d Monopolies produce at a lower cost than perfectly competitive firms. d I, II, and IV only e Monopolies enjoy barriers to entry. e Question 5 (1 point) I, II, III, and IV Question 6 (1 point) Purely competitive industries have which of the following character- istics? Screens 3-4 of 35 Focus + 140% 41OF Mostly cloudy Q Search 5:34 PM 3/11/2023 1File Tools View econ . Saved to this PC v - X $200 $200 MC 150 MC 150 Cost and revenue - ATC Cost and revenue ATC AVC AV - MR = P MR = P 6 6.5 7 10 6 6.5 7 Output Output At a market price of $93, this firm If the market price is $71, this competitive firm will has positive economic profit as it can cover its explicit and implicit costs produce in the short run, as it can cover its explicit costs but not its implicit costs b has normal profit, but is unable to fully cover the explicit and implicit costs it faces b produce in the short run, but if price does not rise to $93, it will shut down in the long run C has positive accounting profit but negative economic profit, being unable to cover all implicit costs C produce in the short run, as it can just cover all of its variable costs but none of fixed costs d has normal profit, but is just able to cover all of its explicit and implicit costs d produce in the short run, as it can cover all variable costs and some of its fixed costs has normal profit and is able to cover only its accounting costs cease production and sell what it has already produced to minimize losses Question 7 (1 point) Question 8 (1 point) Which of the following characteristics correctly describe a monopoly? I. The firm is the single seller in the industry. Screens 5-6 of 35 "Focus + 140% 41OF Sunset Q Search G 5:35 PM 3/11/2023 1File Tools View econ . Saved to this PC v - X II. Barriers to entry exist in the industry. C raise the product price to $11 to maximize profit shut down III. Unregulated monopolies are illegal under United States law. continue production at its current level of output to maximize output IV. The firm determines its price and output. Question 10 (1 point) I and II only Monopoly b I and III only MC C I, li, and III only d I, II, and IV only D-P-AR e I, II, III, and IV MR Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4 Question 9 (1 point) Output At a particular output, a perfectly competitive firm's price is $10, At what output would this firm achieve productive efficiency? marginal cost is $11, average total cost is $12, and average variable cost is $8. The firm should Q1 b 02 C 03 d 04 increase output to maximize profit e b Monopolies cannot achieve productive efficiency. decrease output to minimize loss, but keep producing in the short run Question 11 (1 point) Screens 7-8 of 35 " Focus + 140% 41 F Q Search W 5:35 PM Sunset 3/11/2023 1File Tools View econ . Saved to this PC v X The monopolist's marginal revenue curve is lower than the demand In the graph above, the long-run supply curve reflects an industry curve because the firm in which must lower the price of all of its products in order to sell more b faces constantly increasing costs of production as output increases a expansion will increase resource prices achieves efficiency when revenues are lower than prices b contraction will increase resource prices d must accept the price set by the industry C expansion will decrease resource prices e becomes less efficient as output increases expansion will increase resource prices but contraction will not impact resource prices Question 12 (1 point) expansion and contraction will not affect resource prices Question 13 (1 point) S $55 45 D2 DI D3 Q3 QI Q2 Q 90,000 100,000 1 10,000 Screens 7-8 of 35 Focus + 140% 41 F Sunset Q Search 5:35 PM 3/11/2023 1File Tools View econ . Saved to this PC v X In the long run, which of the following are true in a competitive industry? I. Firms can expand or contract productive capacity. C Price and costs (dollars) ATC II. Firms face substantial fixed costs. MC III. Firms can freely enter and exit. MR Q1 Q3 IV. Firms are driven by incentives based on profits and losses. Quantity What would the fair return price and quantity be for a regulated I only monopoly? b II only C nd III only a P4, Q3 d I, III, and IV only b P3, Q2 e II, III, and IV only C P1, Q1 Question 15 (1 point) d P5, Q1 In order to maximize profit, the firm should produce where P2, Q1 Question 14 (1 point) Average Revenue = Price Screens 11-12 of 35 Focus + 140% 41 F 5:35 PM qX O Mostly cloudy Q Search W 3/11/2023 1File Tools View econ . Saved to this PC v - X b Marginal Cost = Average Variable Cost III. The firm is in a short-run position. C Marginal Cost = Marginal Revenue I only d Price = Average Variable Cost b II only Marginal Revenue = Price C III only Question 16 (1 point) d I and II only Price MC I, II, and III - MRS ATC AVC Question 17 (1 point) - MR. - MR, - MRz - MR, In a competitive, constant-cost industry, the industry long-run supply curve is Quantity supplied Quantity inelastic but not perfectly inelastic b unit elastic At price "Of", which of the following is true? C elastic but not perfectly elastic d perfectly inelastic I. The firm has a positive economic profit of "feug" and a total fixed perfectly elastic cost of "guvj". Question 18 (1 point) II. The firm has a total cost of "gut" and a fixed cost of "guvj". Screens 11-12 of 35 Focus + 140% 41 F 5:36 PM Mostly cloudy Q Search 1X O 3/11/2023 1File Tools View econ . Saved to this PC v - X Which of the following statements best describes a perfectly com- III. Average total cost equals average revenue. petitive market? IV. Market demand intersects ATC where ATC is declining. I. A large number of firms exist in the industry. I and II only II. Products are differentiated. b I and III only III. Firms can easily enter or exit the industry. C I, II, and III only d I, II, and IV only I only I, II, III, and IV b II only Question 20 (1 point) C I and III only d II and III only Total Total Average Average Cost Total Cost Variable Total Product Marginal Marginal Cost (Q) (TC) (ATC) Cost Revenue Revenue ($ ) (S ) AVC (S ) (TR) (MR) (S) (S) e I, II, and III 100.00 190.00 190.00 90.00 81.00 Question 19 (1 point) 270.00 35.00 85.00 162.00 340.00 113.33 80.00 243.00 400.0 100.00 75.00 324.00 A profit-maximizing natural monopoly with positive economic profits 470.00 94.00 74.00 405.00 350.00 91.67 75.00 486.00 has which of the following characteristics? 640.00 91.43 77.14 567.00 750.00 93.75 81.25 648.00 880.00 97.78 86.67 I. Price is set higher than marginal revenue. 729.00 10 1030.00 103.00 93.00 810.00 II. Marginal cost equals marginal revenue. Screens 15-16 of 35 "D Focus + 140% 41 F Mostly cloudy Q Search W 1X O 5:36 PM 3/11/2023 1File Tools View econ . Saved to this PC v - X Between three and four units of total product, the marginal cost and Allocation efficiency is identified as the output where marginal revenue are Average Total Cost = Marginal Cost Marginal Cost / / / Marginal Revenue b Price = Marginal Cost C Marginal Revenue = Demand (A) Rising and greater than ATC /// Rising d Average Total Cost = Average Variable Cost (B) Falling and less than ATC /// Falling e Average Variable Cost = Price (C) Less than ATC /// Constant Question 22 (1 point) (D) Greater than ATC /// Constant Monopoly (E) Minimum /// Maximum MC ATC a D b B D-P-AR C C Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4 Output d D e m The deadweight loss associated with reducing output for the monop- Question 21 (1 point) oly is the Screens 15-16 of 35 " Focus + 140% 41 F Mostly cloudy Q Search W 5:36 PM 3/11/2023 1File Tools View econ . Saved to this PC v - X Allocation efficiency is identified as the output where triangle below MC = D, on the P3 line from Q2 to Q4 triangle below the demand curve, on the P3 line from Q1 to Q4 Average Total Cost = Marginal Cost C rectangle between P1 and P3, from the left axis to the Q1 line b Price = Marginal Cost d rectangle between P1 and P4, from the left axis to the Q1 line C Marginal Revenue = Demand e triangle to the left of MC = D, on the Q1 line from P1 to P4 d Average Total Cost = Average Variable Cost Question 23 (1 point) e Average Variable Cost = Price Question 22 (1 point) In the long run, a purely competitive firm will only operate at a point where average variable cost is at a minimum Monopoly ATC b negative economic profit is generated MC C only accounting profit is generated d positive economic profit is generated D-P-AR MR e average total cost is at a minimum Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4 Output Question 24 (1 point) The deadweight loss associated with reducing output for the monop- Why do monopolies not produce at the point of productive efficiency? oly is the The firm maximizes profit by producing where ATC = D. Screens 18-19 of 35 " Focus + 140% 41 F Mostly cloudy Q Search G W 5:38 PM 3/11/2023 1File Tools View econ . Saved to this PC v - X b The firm reduces output in order to raise the price. C 100 C The monopoly focuses on minimizing the marginal cost. 190 d The monopoly focuses on achieving allocation efficiency. indeterminable Monopolies cannot achieve productive efficiency. Question 26 (1 point) Question 25 (1 point) In pure competition, which of the following are true in the long run? I. Individual firms have the freedom to enter or exit the industry. Total Total Average Average Cost Total Total Cost Variable Marginal Marginal Product (Q) (TC) (ATC) Cost Revenue (S) (AVC) Cost Revenue (S) (S) (TR) (MR) (S) ($) (S) 00.00 II. Individual firms have control over the market price of their 190.00 190.00 0.00 81.00 product. 270.00 135.00 85.00 162.0 340.00 113.33 80.00 243.00 400.00 100.00 75.00 324.00 III. Individual firms' output decisions are based on their costs and 470.00 94.00 74.00 405.00 $50.00 91.6 75.00 486.00 the market price. 640.00 91.43 77.14 567.00 750.00 93.75 81.25 648.00 880.00 97.78 86.67 729.00 IV. Individual firms' profits attract entry, while losses prompt exit. 1030.00 103.00 93.00 810.00 I only At zero units of total product, the total fixed cost for this firm is b II only a C I, II, and IV only d I, III, and IV only Screens 20-21 of 35 Focus 41OF + 140% Mostly cloudy Q Search W 5:38 PM 3/11/2023 1File Tools View econ . Saved to this PC v - X e I, II, III, and IV Assume firms in constant-cost industries are engaged in pure Question 27 (1 point) competition. Each firm will have If competitive firms in the short run have positive economic profit where marginal cost equals marginal revenue a marginal revenue that equals marginal cost above average total cost minimum I. optimal allocation efficiency has been achieved b marginal revenue that equals marginal cost at average total cost minimum C marginal cost that equals marginal revenue at a level below market price II. optimal productive efficiency has been achieved d marginal cost that equals marginal revenue at average fixed cost minimum III. the sum of consumer and producer surplus is maximized marginal revenue that equals marginal cost at average variable cost minimum Question 29 (1 point) IV. long-run adjustments will create optimal efficiency with the sum of consumer and producer surplus maximized I only b I and II only C I and III only d II and III only IV only Question 28 (1 point) Screens 20-21 of 35 Focus + 140% 41 F Mostly cloudy Q Search 5:38 PM 3/11/2023 1File Tools View econ . Saved to this PC v - X If firms in a competitive, constant-cost industry are earning positive economic profits in the short run, then in the long run Firms /// Industry Demand /// Industry Supply /// Market Price C Price and costs (dollars) (A) Enter /// Constant /// Increases /// Decreases ATC (B) Enter /// Increases /// Increases /// Uncertain MC (C) Enter /// Decreases /// Increases /// Decreases (D) Exit /// Decreases /// Decreases /// Increases MR (E) Exit /// Constant /// Decreases /// Increases Q1 Q2 Q3 Quantity a A b Assume that this firm is an unregulated monopoly. At what price and C C quantity would this firm produce to maximize profit? d O a P1, Q1 e E b P5, Q1 Question 31 (1 point) C P4, Q3 A natural monopoly's barrier to entry is d P4, Q2 P3, Q2 a government license to operate Question 30 (1 point) b a copyright Screens 24-25 of 35 Focus + 140% 41 F Q Search W 5:39 PM 1X O 3/11/2023 1 Mostly cloudyFile Tools View econ . Saved to this PC v - X C a patent Monopoly d MC ATC heavy use of advertising economies of scale Question 32 (1 point) D=P-AR At long-run equilibrium for the perfectly competitive firm, the Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4 Output marginal cost is equal to all of the following EXCEPT To reach allocationefficiency, government would set a price ceiling average total cost at b marginal revenue C average variable cost a P1 d average revenue b P2 e price C P3 Question 33 (1 point) d P4 e MR = ATC Question 34 (1 point) Assume Kenny is a farmer who sells soybeans in a perfectly compet- itive industry. If the industry equilibrium price for soybeans is $14 per bushel and Kenny sets his price at $15 per bushel, Kenny's Screens 26-27 of 35 Focus -+ 140% 41 F Q Search 5:39 PM Mostly cloudy G 3/11/2023 1File Tools View econ . Saved to this PC v - X a marginal revenue will increase Industry Demand / / / Individual Firm Demand b total revenue will decrease (A) Horizontal /// Horizontal C total revenue will increase economic profit will increase (B) Vertical /// Vertical accounting profit will increase (C) Downward-Sloping /// Horizontal Question 35 (1 point) (D) Horizontal /// Downward-Sloping In a perfectly competitive industry in which firms are achieving short-run economic profit (E) Downward-Sloping /// Downward-Sloping firms will exit the industry D b the government will increase taxes b C firms will increase the product price C C industry output will decrease d D e firms will enter the industry e E Question 36 (1 point) Question 37 (1 point) In a perfectly competitive market, what is the slope of the demand Assuming a competitive, increasing-cost industry, an increase in curves for the industry and the individual firm? market demand in the long run will result in Screens 28-29 of 35 Focus + 140% 41OF Mostly cloudy Q Search G W 5:39 PM 3/11/2023 1File Tools View econ . Saved to this PC v - X Market Price / / / Resource Prices / / Average Total Costs (A) Constant /// Increase /// Increase D2 P3 $55 (B) Increase /// Increase /// Constant 50 45 (C) Increase /// Increase /// Increase 0 Q3 Q2 90,000 100,000 1 10,000 (D) Decrease /// Decrease /// Decrease Given the graph above, a contraction in the industry would (E) Uncertain /// Increase /// Increase I. help the industry and the firms D b II. decrease costs per unit for the industry and the firms C III. increase costs per unit for the industry and the firms d D E a I only Question 38 (1 point) b III only C I and II only d I and III only e i, II, and III Screens 30-31 of 35 Focus + 140% 41OF 5:39 PM Mostly cloudy Q Search 3/11/2023 1File Tools View econ . Saved to this PC v - X Question 39 (1 point) Total Total Average Average Cost Marginal Total Total Cost Variable Marginal P Product (Q) (TC) (ATC) Cost Cost Revenue Revenue (S) (S) (AVC) ($) (TR) (MR) (S) (S) (S) 100.00 190.00 190.00 90.00 81.00 MC 270.00 135.00 85.00 162.00 P1 . 340.00 113.33 80.00 243.00 P2 400.00 100.00 75.00 324.00 470.00 94.00 74.00 405.00 P3 $50.00 91.67 75.00 486.00 640.00 91.43 77.14 567.00 D 750.00 93.75 81.25 648.00 880.00 97.78 86.67 729.00 MR 1030.00 103.00 93.00 810.00 Q1 Q2 Assuming units of output are not divisible, the shutdown point for The efficiency loss generated by this profit-maximizing monopolist is this firm in the short run occurs where area bounded by the points total output is 8 units, where MR
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


