Question: Fluid Mechanics Problem # 0 2 Navier - Stokes Equations A steady, axisymmetric, incompressible fluid of density p Flows radially ( in the r
Fluid Mechanics
Problem # NavierStokes Equations
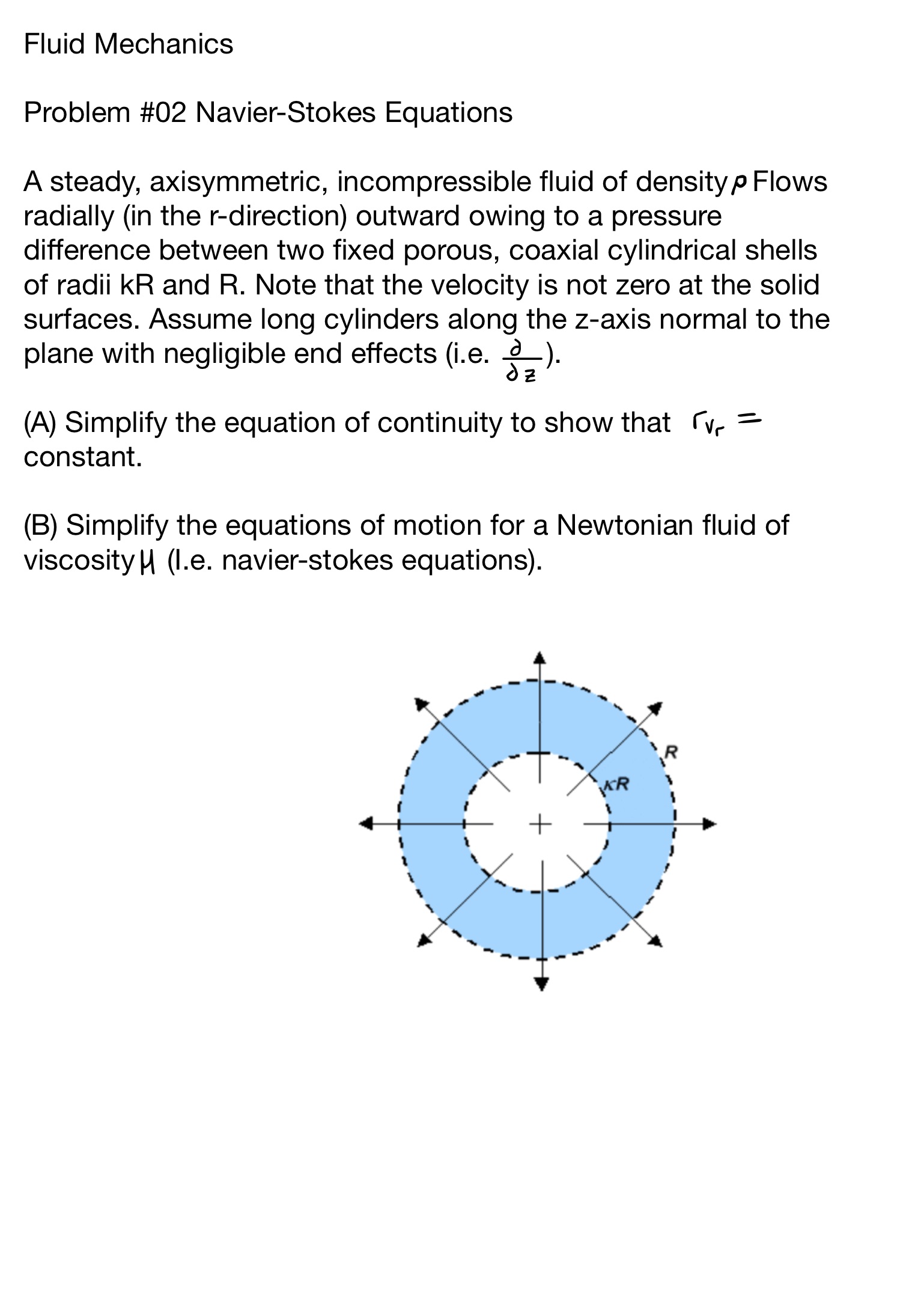
A steady, axisymmetric, incompressible fluid of density p Flows radially in the rdirection outward owing to a pressure difference between two fixed porous, coaxial cylindrical shells of radii k R and R Note that the velocity is not zero at the solid surfaces. Assume long cylinders along the zaxis normal to the plane with negligible end effects iefracpartialpartial z
A Simplify the equation of continuity to show that Gammavr constant.
B Simplify the equations of motion for a Newtonian fluid of viscosity H Ie navierstokes equations
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


