Question: for 9a and 9b please find WACC using rs and re budgeting exercise, at year-end 1994, the treasurer used a before-tax debt cost of 9.5%,
for 9a and 9b please find WACC using rs and re
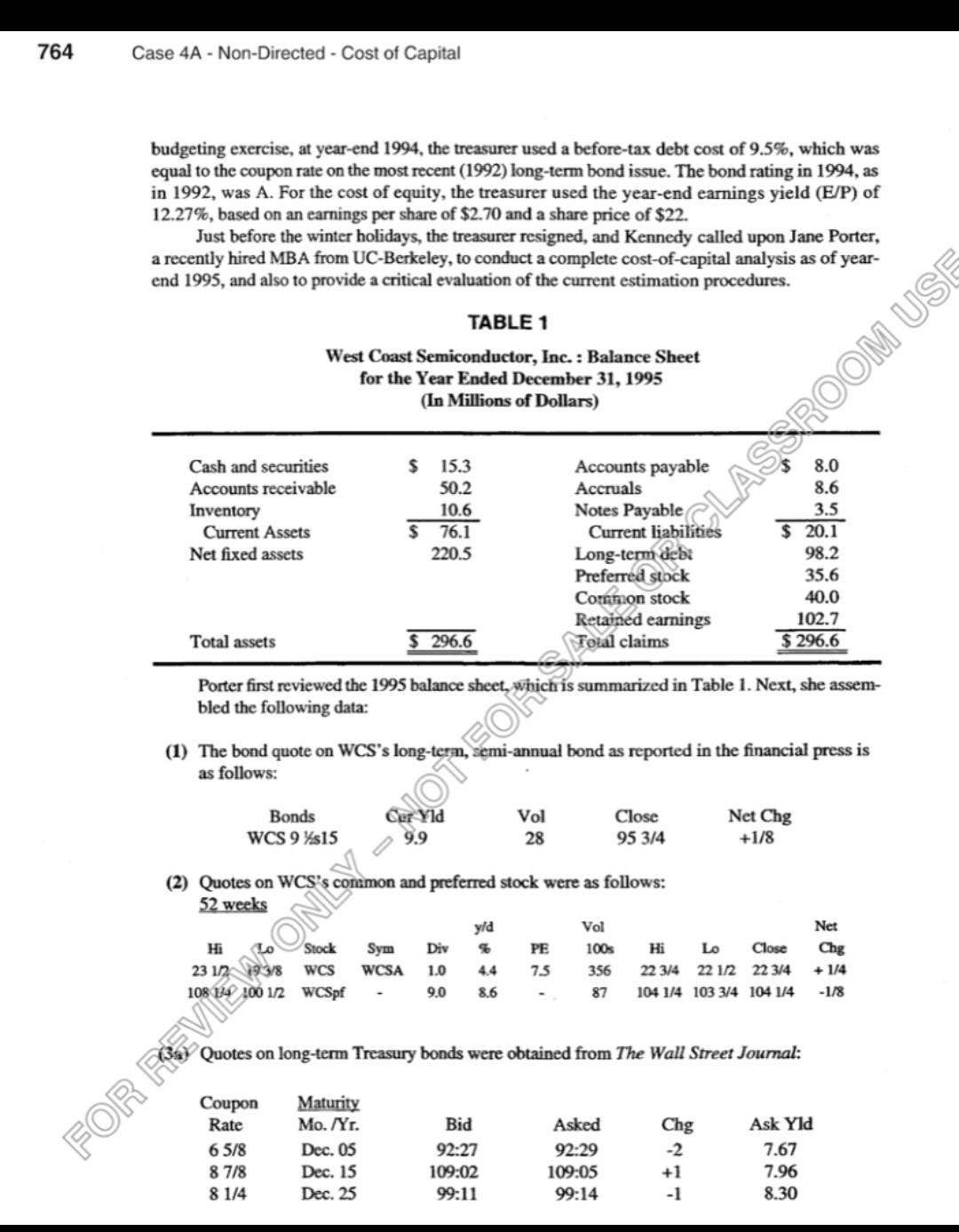
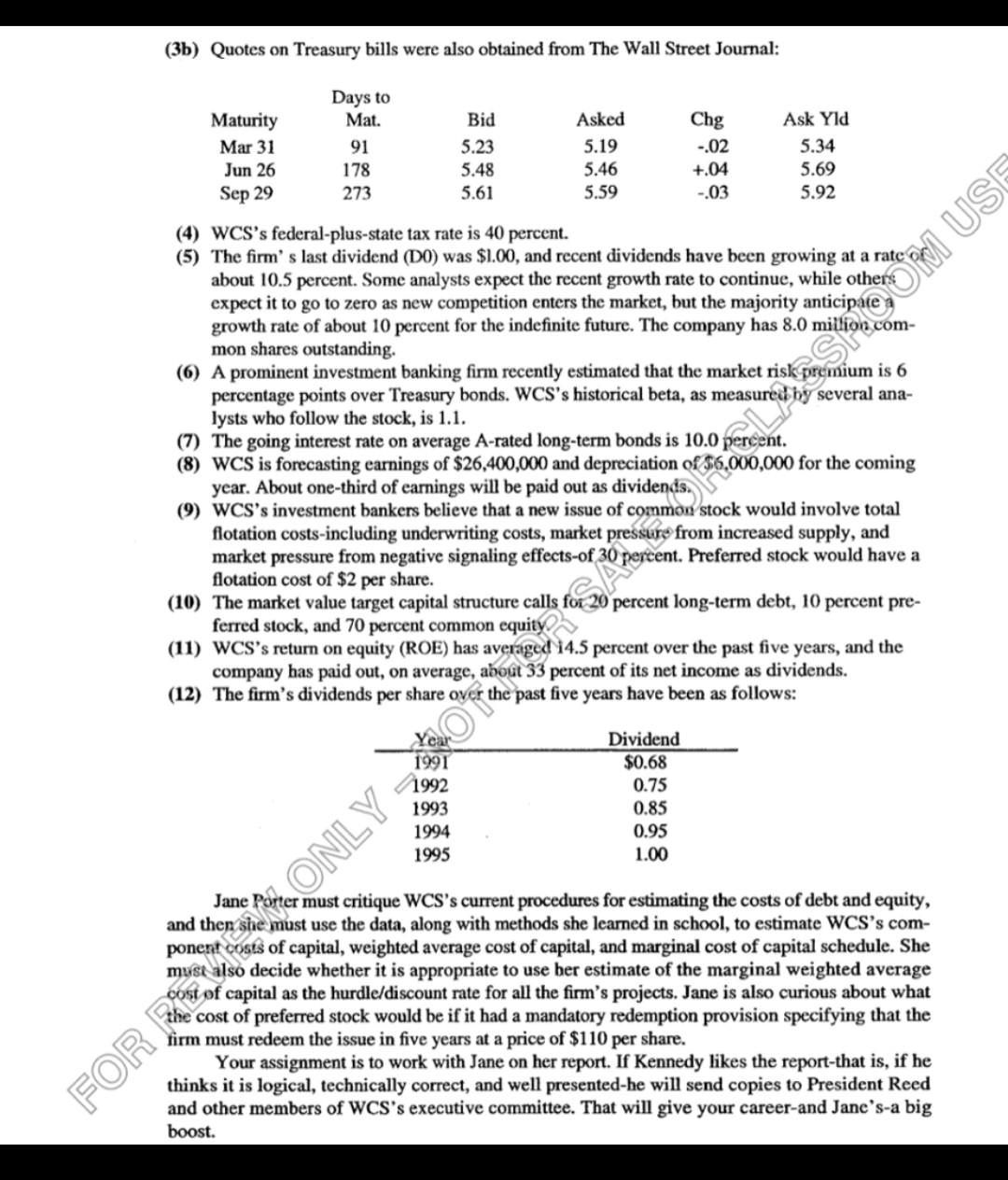
budgeting exercise, at year-end 1994, the treasurer used a before-tax debt cost of 9.5\%, which was equal to the coupon rate on the most recent (1992) long-term bond issue. The bond rating in 1994 , as in 1992, was A. For the cost of equity, the treasurer used the year-end earnings yield (E/P) of 12.27%, based on an earnings per share of $2.70 and a share price of $22. Just before the winter holidays, the treasurer resigned, and Kennedy called upon Jane Porter, a recently hired MBA from UC-Berkeley, to conduct a complete cost-of-capital analysis as of yearend 1995, and also to provide a critical evaluation of the current estimation procedures. Porter first reviewed the 1995 balance sheet, which is summarized in Table 1 . Next, she assembled the following data: (1) The bond quote on WCS's long-tern, semi-annual bond as reported in the financial press is as follows: (2) Quotes on WCS's conmmon and preferred stock were as follows: 52 weeks (3a) Quotes on long-term Treasury bonds were obtained from The Wall Street Journal: (3b) Quotes on Treasury bills were also obtained from The Wall Street Journal: (4) WCS's federal-plus-state tax rate is 40 percent. (5) The firm's last dividend (D0) was $1.00, and recent dividends have been growing at a rate or about 10.5 percent. Some analysts expect the recent growth rate to continue, while others expect it to go to zero as new competition enters the market, but the majority anticipare growth rate of about 10 percent for the indefinite future. The company has 8.0 milionscommon shares outstanding. (6) A prominent investment banking firm recently estimated that the market riskipromium is 6 percentage points over Treasury bonds. WCS's historical beta, as measure bhy several analysts who follow the stock, is 1.1. (7) The going interest rate on average A-rated long-term bonds is 10.0 percent. (8) WCS is forecasting earnings of $26,400,000 and depreciation of$6,000,000 for the coming year. About one-third of earnings will be paid out as dividends. (9) WCS's investment bankers believe that a new issue of common stock would involve total flotation costs-including underwriting costs, market pressure from increased supply, and market pressure from negative signaling effects-of 30 percent. Preferred stock would have a flotation cost of $2 per share. (10) The market value target capital structure calls for 20 percent long-term debt, 10 percent preferred stock, and 70 percent common equity. (11) WCS's return on equity (ROE) has averiged 14.5 percent over the past five years, and the company bas paid out, on average, about 33 percent of its net income as dividends. (12) The firm's dividends per share over the past five years have been as follows: Jane Porter must critique WCS's current procedures for estimating the costs of debt and equity, and then she must use the data, along with methods she learned in school, to estimate WCS's component costs of capital, weighted average cost of capital, and marginal cost of capital schedule. She muse also decide whether it is appropriate to use ber estimate of the marginal weighted average cost of capital as the hurdle/discount rate for all the firm's projects. Jane is also curious about what the cost of preferred stock would be if it had a mandatory redemption provision specifying that the firm must redeem the issue in five years at a price of $110 per share. Your assignment is to work with Jane on her report. If Kennedy likes the report-that is, if he thinks it is logical, technically correct, and well presented-he will send copies to President Reed and other members of WCS's executive committee. That will give your career-and Jane's-a big boost. budgeting exercise, at year-end 1994, the treasurer used a before-tax debt cost of 9.5\%, which was equal to the coupon rate on the most recent (1992) long-term bond issue. The bond rating in 1994 , as in 1992, was A. For the cost of equity, the treasurer used the year-end earnings yield (E/P) of 12.27%, based on an earnings per share of $2.70 and a share price of $22. Just before the winter holidays, the treasurer resigned, and Kennedy called upon Jane Porter, a recently hired MBA from UC-Berkeley, to conduct a complete cost-of-capital analysis as of yearend 1995, and also to provide a critical evaluation of the current estimation procedures. Porter first reviewed the 1995 balance sheet, which is summarized in Table 1 . Next, she assembled the following data: (1) The bond quote on WCS's long-tern, semi-annual bond as reported in the financial press is as follows: (2) Quotes on WCS's conmmon and preferred stock were as follows: 52 weeks (3a) Quotes on long-term Treasury bonds were obtained from The Wall Street Journal: (3b) Quotes on Treasury bills were also obtained from The Wall Street Journal: (4) WCS's federal-plus-state tax rate is 40 percent. (5) The firm's last dividend (D0) was $1.00, and recent dividends have been growing at a rate or about 10.5 percent. Some analysts expect the recent growth rate to continue, while others expect it to go to zero as new competition enters the market, but the majority anticipare growth rate of about 10 percent for the indefinite future. The company has 8.0 milionscommon shares outstanding. (6) A prominent investment banking firm recently estimated that the market riskipromium is 6 percentage points over Treasury bonds. WCS's historical beta, as measure bhy several analysts who follow the stock, is 1.1. (7) The going interest rate on average A-rated long-term bonds is 10.0 percent. (8) WCS is forecasting earnings of $26,400,000 and depreciation of$6,000,000 for the coming year. About one-third of earnings will be paid out as dividends. (9) WCS's investment bankers believe that a new issue of common stock would involve total flotation costs-including underwriting costs, market pressure from increased supply, and market pressure from negative signaling effects-of 30 percent. Preferred stock would have a flotation cost of $2 per share. (10) The market value target capital structure calls for 20 percent long-term debt, 10 percent preferred stock, and 70 percent common equity. (11) WCS's return on equity (ROE) has averiged 14.5 percent over the past five years, and the company bas paid out, on average, about 33 percent of its net income as dividends. (12) The firm's dividends per share over the past five years have been as follows: Jane Porter must critique WCS's current procedures for estimating the costs of debt and equity, and then she must use the data, along with methods she learned in school, to estimate WCS's component costs of capital, weighted average cost of capital, and marginal cost of capital schedule. She muse also decide whether it is appropriate to use ber estimate of the marginal weighted average cost of capital as the hurdle/discount rate for all the firm's projects. Jane is also curious about what the cost of preferred stock would be if it had a mandatory redemption provision specifying that the firm must redeem the issue in five years at a price of $110 per share. Your assignment is to work with Jane on her report. If Kennedy likes the report-that is, if he thinks it is logical, technically correct, and well presented-he will send copies to President Reed and other members of WCS's executive committee. That will give your career-and Jane's-a big boost
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


