Question: For a simple explicit approach, take the first-order approximate forward difference for the temporal derivative of dT/dt, not the centered finite difference. Q2) (50 points)
For a simple explicit approach, take the first-order approximate forward difference for the temporal derivative of dT/dt, not the centered finite difference.
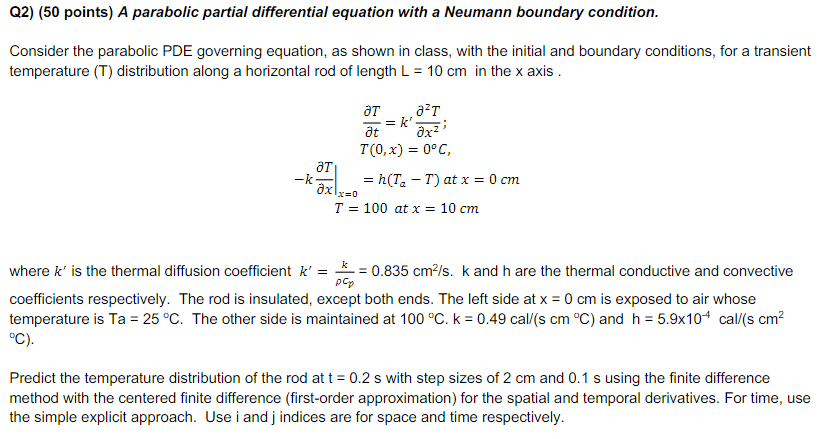
Q2) (50 points) A parabolic partial differential equation with a Neumann boundary condition. Consider the parabolic PDE governing equation, as shown in class, with the initial and boundary conditions, for a transient temperature (T) distribution along a horizontal rod of length L=10cm in the x axis . tT=kx22T;T(0,x)=0CkxTx=0=h(TaT)atx=0cmT=100atx=10cm where k is the thermal diffusion coefficient k=cpk=0.835cm2/s.k and h are the thermal conductive and convective coefficients respectively. The rod is insulated, except both ends. The left side at x=0cm is exposed to air whose temperature is Ta=25C. The other side is maintained at 100Ck=0.49cal/(scmC) and h=5.9104cal/(scm2 C) Predict the temperature distribution of the rod at t=0.2s with step sizes of 2cm and 0.1s using the finite difference method with the centered finite difference (first-order approximation) for the spatial and temporal derivatives. For time, use the simple explicit approach. Use i and j indices are for space and time respectively
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


