Question: For cases where A exactly doubles: if the rate does not change, the order for A is 0 . if the rate doubles, then the
For cases where
Aexactly doubles:\ if the rate does not change, the order for
Ais 0 .\ if the rate doubles, then the order for
Ais 1 .\ if the rate quadruples, the order for
Ais 2 .\ For more complex cases, use the general equation:\
(( rate _(()
1))/(( rate _(()
2))=(([ reactant ]_(1))/([ reactant ]_(2)))^(order )\ What is the reaction order with respect to
A?\ \\\\table[[,
[A],mo(l)/(L),
[B],mo(l)/(L),rate,
mo(l)/(L-min) 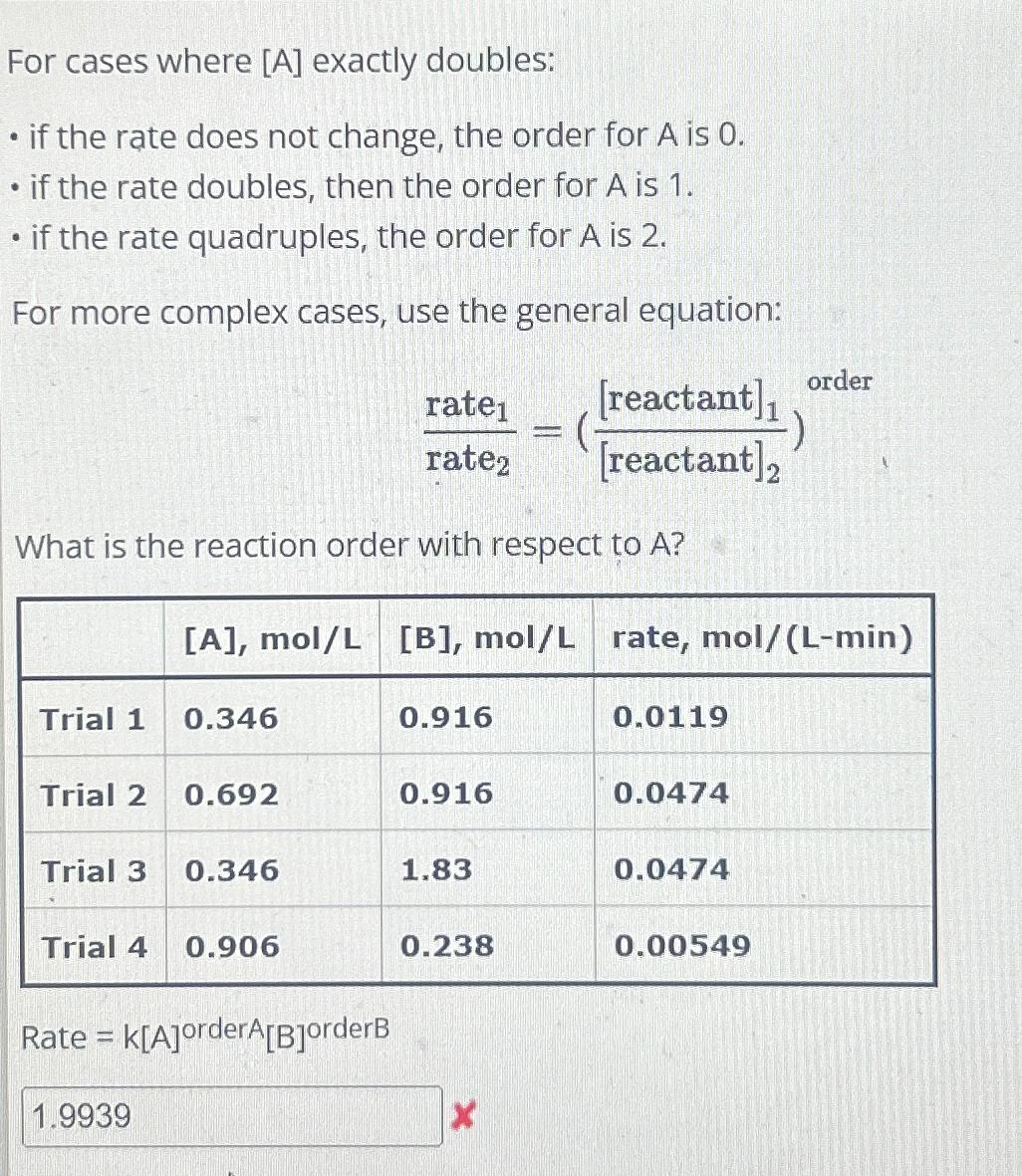
For cases where [A] exactly doubles: - if the rate does not change, the order for A is 0 . - if the rate doubles, then the order for A is 1. - if the rate quadruples, the order for A is 2 . For more complex cases, use the general equation: rate2rate1=([reactant]2[reactant]1)order What is the reaction order with respect to A ? Rate =k[A]orderA[B]orderB
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


