Question: For this computing project, first you need to derive the equations for the tension in cable AB, the tension in cable CD and the reaction
For this computing project, first you need to derive the equations for the tension in cable AB, the tension in cable CD and the reaction at O in terms of x, which represents the placement of the point load, P, measured from the axis origin, point O. These equations can be implemented into your MATLAB program Beam.m in a while loop. Use the while loop to vary the value of x between 0 and 6 m. You should be able to get this working by adding only a few lines to the template code we have provided for you. 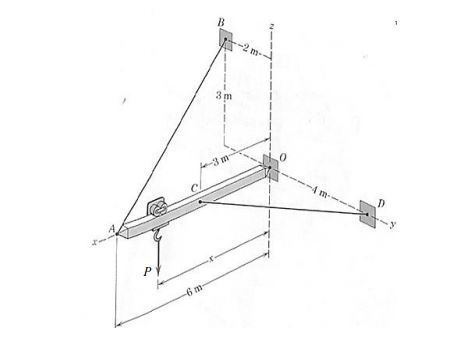 Once you get your code working, use it to study how the reaction force, R changes with the value of x. Determine the value of x, where the ratio R/P is minimum, where R represents the magnitude of the total reaction at O. Create a plot to show how this ratio changes as x changes. Then do some research and find a standard value for weight of a W8x24 beam. Incorporate the self-weight value into your equations and then into your program (use correct units). Discuss the differences between neglecting self-weight and including self-weight. You then need to explore this program by changing around parameters. Your report will be evaluated based on your insight and the interest of your study. This offers you the ability to discover and explore how loads on a beam work. For example, you could change your code to account for placement of multiple loads or move the location of the cables. Report Write a report documenting your work and the results (in accord with the specifications given in the document CEE210 Guidelines for Computing Projects). Include figures, plots, and results. Discuss your discoveries and explorations. Upload your report to Blackboard prior to the deadline. Upload your .m program file to Blackboard as well and follow all of the typical submittal instructions for Statics Computing Projects.
Once you get your code working, use it to study how the reaction force, R changes with the value of x. Determine the value of x, where the ratio R/P is minimum, where R represents the magnitude of the total reaction at O. Create a plot to show how this ratio changes as x changes. Then do some research and find a standard value for weight of a W8x24 beam. Incorporate the self-weight value into your equations and then into your program (use correct units). Discuss the differences between neglecting self-weight and including self-weight. You then need to explore this program by changing around parameters. Your report will be evaluated based on your insight and the interest of your study. This offers you the ability to discover and explore how loads on a beam work. For example, you could change your code to account for placement of multiple loads or move the location of the cables. Report Write a report documenting your work and the results (in accord with the specifications given in the document CEE210 Guidelines for Computing Projects). Include figures, plots, and results. Discuss your discoveries and explorations. Upload your report to Blackboard prior to the deadline. Upload your .m program file to Blackboard as well and follow all of the typical submittal instructions for Statics Computing Projects.
code
%% ----------------------------------------------------------------- %.... Name: %.... Date: %.... Project: %.... Recitation Section: %-----------------------------------------------------------------
% Computing project 2 studies the placement of a load at various % points along a beam and how this affects the support reactions
clear; clc;
%% Print Banner to command window fprintf('%s ','*-----------------------------------------*') fprintf('%s ','| CEE210 Computing Project 2 |') fprintf('%s ','| Amie Baisley |') fprintf('%s ','| Original Version: 09.10.2013 |') fprintf('%s ','| Modified by: Chris Lawrence 2.10.2016 |') fprintf('%s ','*-----------------------------------------*')
% Units used: N, m
% Input physical problem data P = 1000; % magnitude of point load applied to the bar L = 6; % length of the bar T1 = 0; % variable name for tension in cable AB T2 = 0; % variable name for tension in cable CD Ro = [0,0,0]; % variable name for reaction at O rAB = [-6;-2;3]; % direction vector from A to B rCD = [-3;4;0]; % direction vector from C to D n = [-6/7;-2/7;3/7]; % unit vector describing the direction of T1 m = [-3/5;4/5;0]; % unit vector describing the direction of T2 e1 =[1;0;0]; % base vector e1 e2 = [0;1;0]; % base vector e2 e3 = [0;0;1]; % base vector e3 % Set up a history array to save results computed nitems = 4; % total number of items stored in history nreport = 12; % number of items to report history = zeros(nreport,nitems); % initialize storage for history
% Set up any cross products needed for analysis a = cross(e1,n) b = cross(e1,m) c = cross(e1,e3)
% Variables needed for running the loops x=0; %variable describing where P is placed i=1; %variable used for storage location in history %% While loop to go through increments along the length of the bar while (x
history(i,:) = [x,T1,T2,Ratio]
x=x+3; i=i+1; end
%% Create the plot fig=figure(1); clf; grid on; hold on; xlabel('Distance x'); ylabel('Tension'); title('Tension vs. X-distance'); p = plot(history(:,1),history(:,2)); set(p,'Color','blue','LineWidth',4); p = plot(history(:,1),history(:,3)); set(p,'Color','green','LineWidth',4);
D w4 m----- c
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


