Question: For this problem you will create the algorithm that you will implement. Your algorithm will take as input an unsigned number: A. It must then
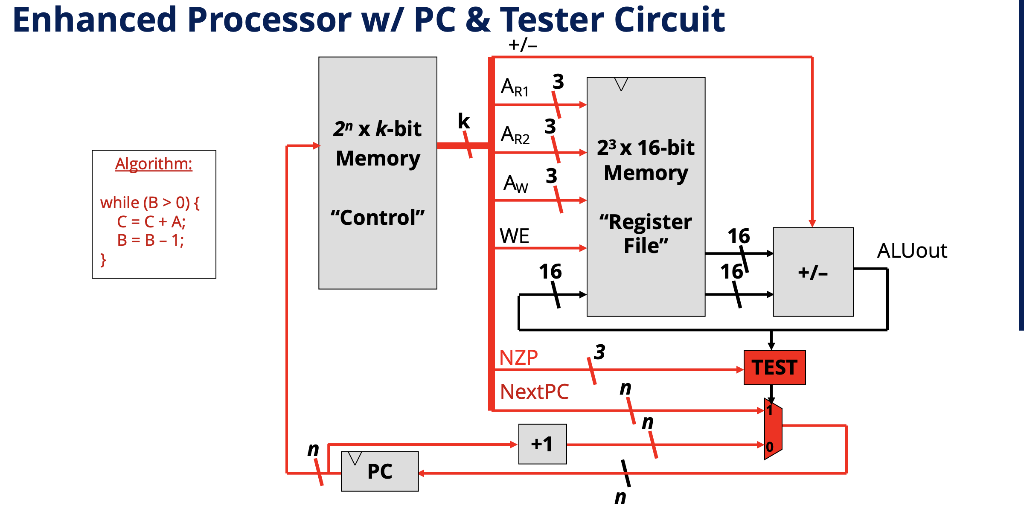
For this problem you will create the algorithm that you will implement. Your algorithm will take as input an unsigned number: A. It must then compute the sum of all the numbers from 1 up to and including A. As an example, if A=5, your algorithm will compute 15 by adding: 1+2+3+4+5. You may assume that the input A is already loaded in your register file, as well as any other numbers you require. You must use a loop to implement your algorithm. The algorithm will use the enhanced processor w/PC & tester circuit shown below.
a) Write out your algorithm in pseudocode.
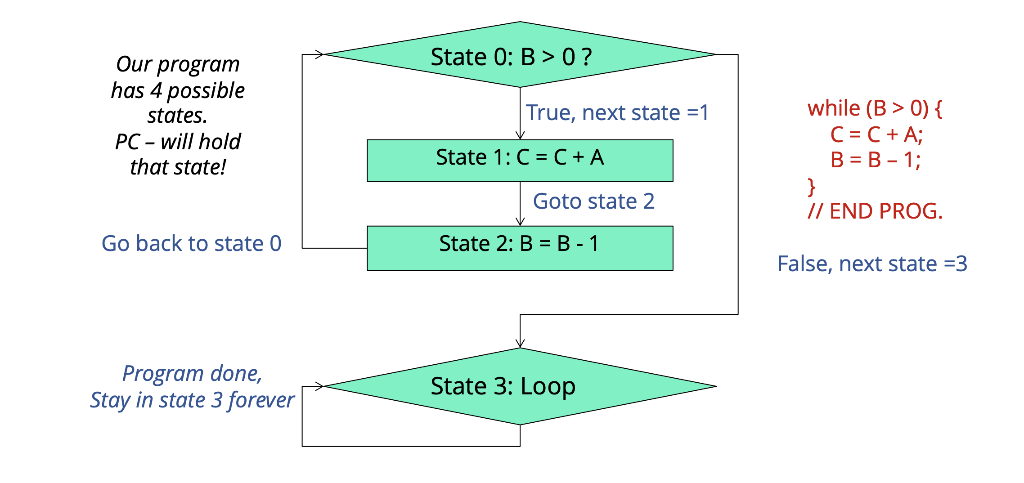
b) Show a flowchart of your program. Example format below.
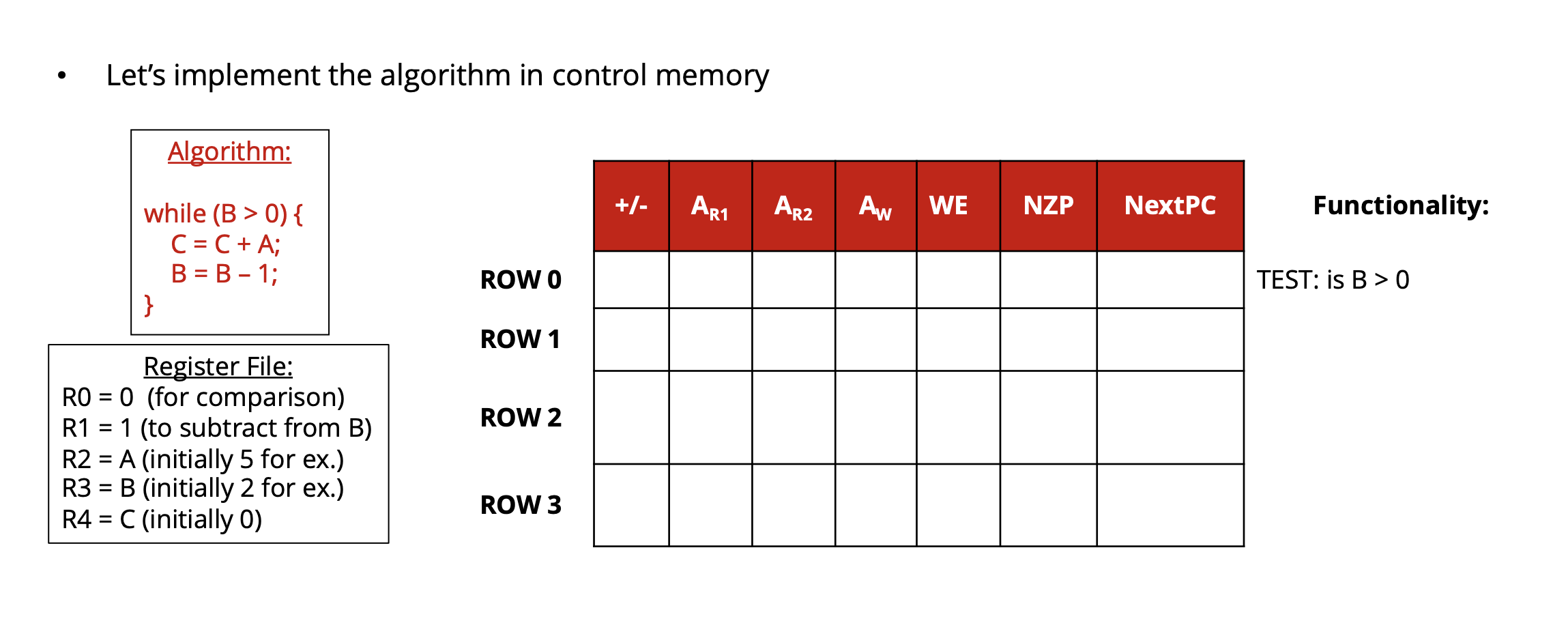
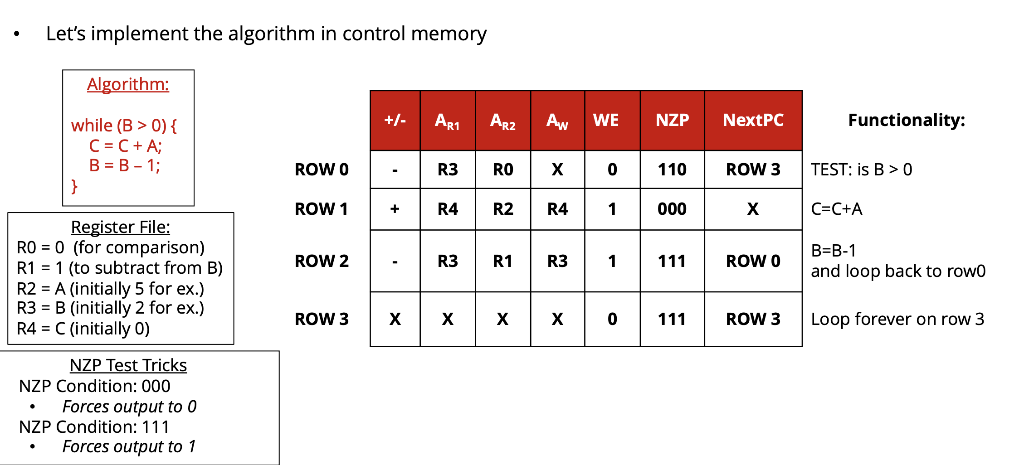
c) Show a table (example format shown below) listing the values of the control signals necessary to implement the algorithm above. You may assign registers any way you like to hold your variables and necessary data, but state it up front!
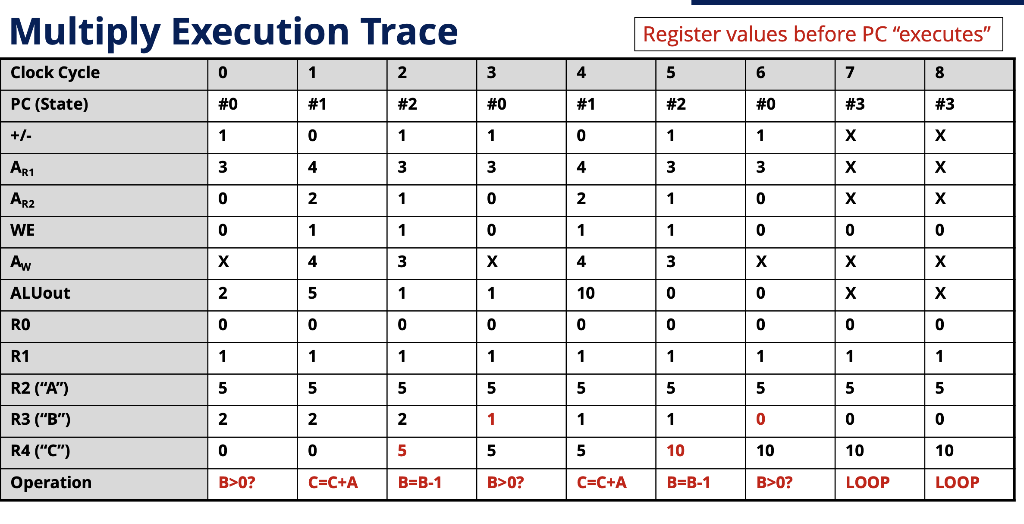
d) Show an Execution Trace (example below) your program in step (c). For your trace, assume A=3.
e) Take into account the limits of our processor; determine the largest value for the unsigned integer A that your algorithm will still compute the correct answer.
Enhanced Processor w/ PC & Tester Circuit +/- ARI 3 21 x k-bit Memory AR2 3 23 x 16-bit Algorithm: Memory Aw while (B > 0) { C = C+A; B=B-1; "Control" WE "Register File" ALUout +/- TEST NZP NextPC LAPC State 0: B > 0? Our program has 4 possible states. PC - will hold that state! True, next state =1 while (B>0){ C = C +A; B = B - 1; State 1: C = C+ A // END PROG. Goto state 2 State 2: B = B-1 Go back to state 0 False, next state = 3 Program done, Stay in state 3 forever State 3: Loop Let's implement the algorithm in control memory Algorithm: +- ARI ARz Aw we | nzp | Nextpc Functionality: while (B > 0) { C = C + A; In + um 11 ROWO TEST: is B > 0 ROW 1 ROW 2 Register File: RO = 0 (for comparison) R1 = 1 (to subtract from B) R2 = A (initially 5 for ex.) R3 = B (initially 2 for ex.) R4 = C (initially 0) ROW 3 Let's implement the algorithm in control memory Algorithm: AR1 ARZ AN WE NZP NextPC Functionality: while (B > 0) { C = C + A; B = B-1; ROW O R3 RO ROW 3 TEST: is B > 0 ROW 1 R2 000 C=C+A ROW 2 ROW O Register File: RO = 0 (for comparison) R1 = 1 (to subtract from B) R2 = A (initially 5 for ex.) R3 = B (initially 2 for ex.) R4 = C(initially O) B=B-1 and loop back to rowo ROW 3 1 x | x X 111 ROW 3 Loop forever on row 3 NZP Test Tricks NZP Condition: 000 Forces output to O NZP Condition: 111 Forces output to 1 Multiply Execution Trace Register values before PC "executes" 0 0 2 Clock Cycle PC (State) #0 ART ARZ WE | Aw ALUout 3 10 RO R1 R2 ("A") R3 ("B") R4 ("C") 10 10 10 Operation B>O? C=C+A B=B-1 B>O? C=C+A B=B-1 B>O? LOOP LOOP
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


