Question: For this question: (a) x Ay = (A, xy ) for all & E RM, y e R, Ac Rixn We know that zy, A
For this question:


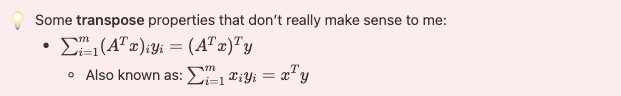
(a) x Ay = (A, xy ) for all & E RM, y e R", Ac Rixn We know that zy, A c Rmxx, meaning they're the same dimension. Let's expand the right hand side: (A, xy") = trace(ATxy]) = _ _ Ajay] = _()Ajay] i=l j=1 i=lil We can rewrite the summation because order of summation doesn't matter. ECAny! )= = [(Ay)TZ = (x(Ay)?)] = ] Ay il j=1 i=13. Recall that the (Frobenius) inner product between two matrices of the same dimensions A, B E RX is defined to be (A, B) = trace (ATB) (sometimes written (A, B) to be clear). The Frobenius norm of a matrix is defined to be |Alls = /E,, E", AP. Prove some of the following matrix identities. the Cauchy-Schwarz inequality and the identities above may be helpful to you. (a) xAy = (A, xy ) for all r ER", y ER", AER"x.Some transpose properties that don't really make sense to me: . EMI(ATx)yi = (ATx)Ty Also known as: my = x y
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


