Question: Function Point Analogous Estimating Budget Estimate Te (note: the e should be subscript to the T ) Rough Order of Magnitude Each time production doubles,
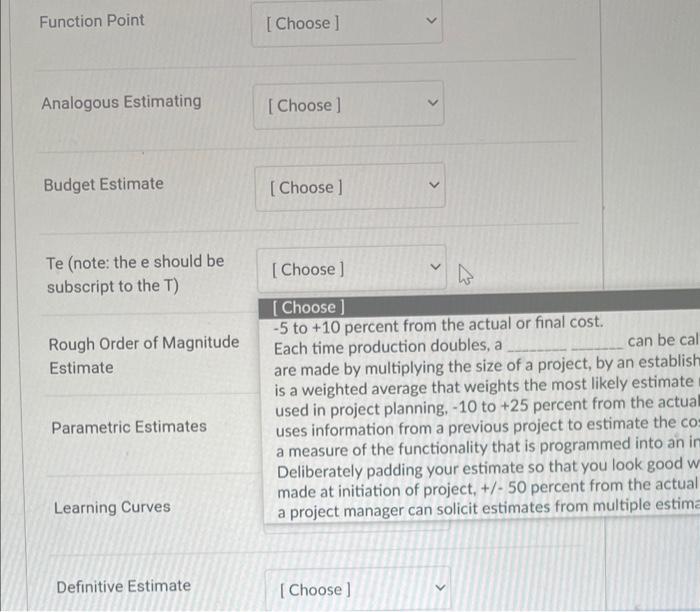
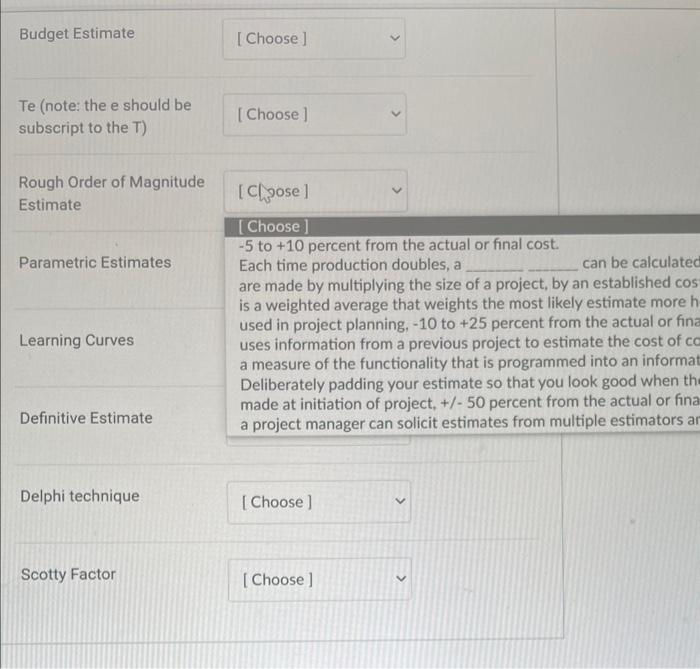
Function Point Analogous Estimating Budget Estimate Te (note: the e should be subscript to the T ) Rough Order of Magnitude Each time production doubles, a Estimate are made by multiplying the size of a project, by an establist is a weighted average that weights the most likely estimate used in project planning, -10 to +25 percent from the actua Parametric Estimates uses information from a previous project to estimate the co a measure of the functionality that is programmed into an ir Deliberately padding your estimate so that you look good w made at initiation of project, +/50 percent from the actual Learning Curves a project manager can solicit estimates from multiple estim Definitive Estimate Budget Estimate Te (note: the e should be subscript to the T ) Rough Order of Magnitude Estimate [Choose ] Parametric Estimates Each time production doubles, a can be calculate are made by multiplying the size of a project, by an established cos is a weighted average that weights the most likely estimate more used in project planning, -10 to +25 percent from the actual or fin uses information from a previous project to estimate the cost of c a measure of the functionality that is programmed into an informa Deliberately padding your estimate so that you look good when th made at initiation of project, +/50 percent from the actual or fina Definitive Estimate a project manager can solicit estimates from multiple estimators a Delphi technique Scotty Factor Function Point Analogous Estimating Budget Estimate Te (note: the e should be subscript to the T ) Rough Order of Magnitude Each time production doubles, a Estimate are made by multiplying the size of a project, by an establist is a weighted average that weights the most likely estimate used in project planning, -10 to +25 percent from the actua Parametric Estimates uses information from a previous project to estimate the co a measure of the functionality that is programmed into an ir Deliberately padding your estimate so that you look good w made at initiation of project, +/50 percent from the actual Learning Curves a project manager can solicit estimates from multiple estim Definitive Estimate Budget Estimate Te (note: the e should be subscript to the T ) Rough Order of Magnitude Estimate [Choose ] Parametric Estimates Each time production doubles, a can be calculate are made by multiplying the size of a project, by an established cos is a weighted average that weights the most likely estimate more used in project planning, -10 to +25 percent from the actual or fin uses information from a previous project to estimate the cost of c a measure of the functionality that is programmed into an informa Deliberately padding your estimate so that you look good when th made at initiation of project, +/50 percent from the actual or fina Definitive Estimate a project manager can solicit estimates from multiple estimators a Delphi technique Scotty Factor
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


