Question: FUZZY LOGIC INFERENCE APPROACH 4. In vehicle analysis loop and piezo detectors are used to determine a vehicle's length, speed and weight. Due to the
FUZZY LOGIC INFERENCE APPROACH
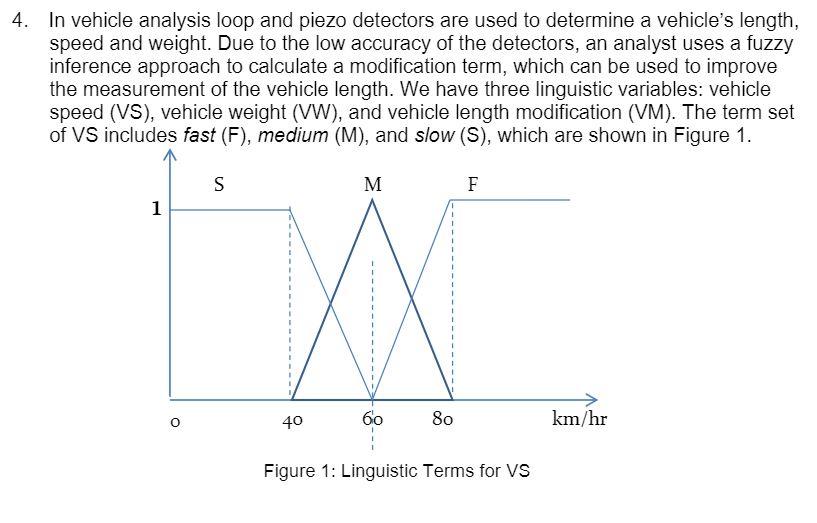
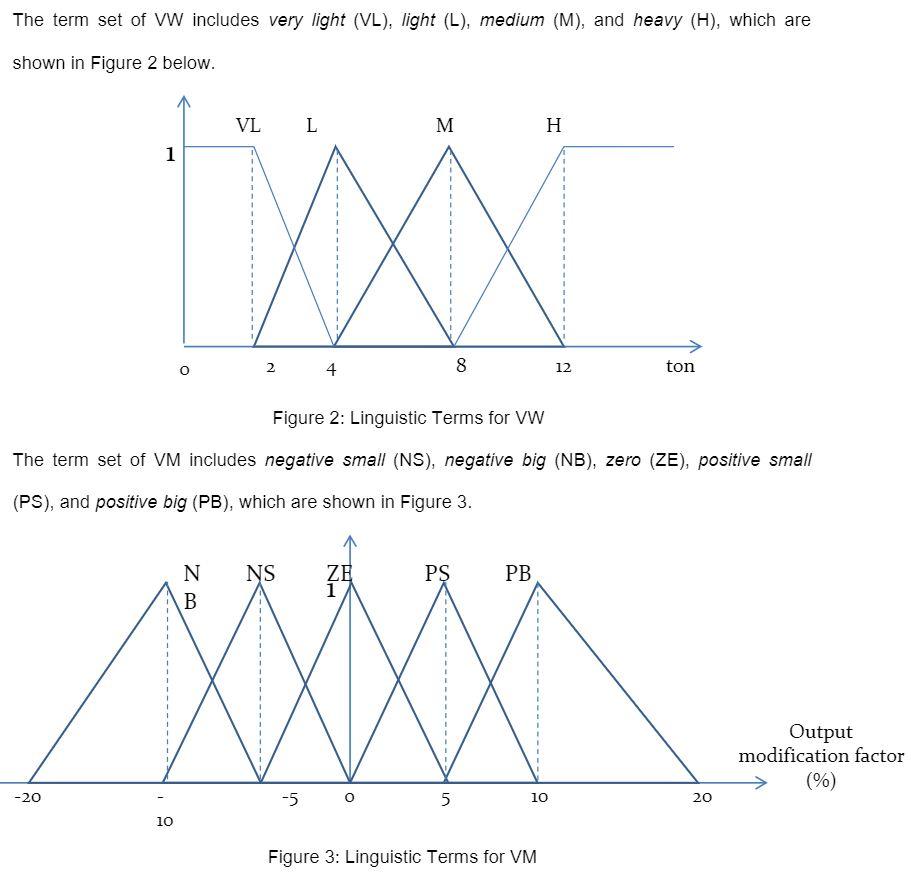
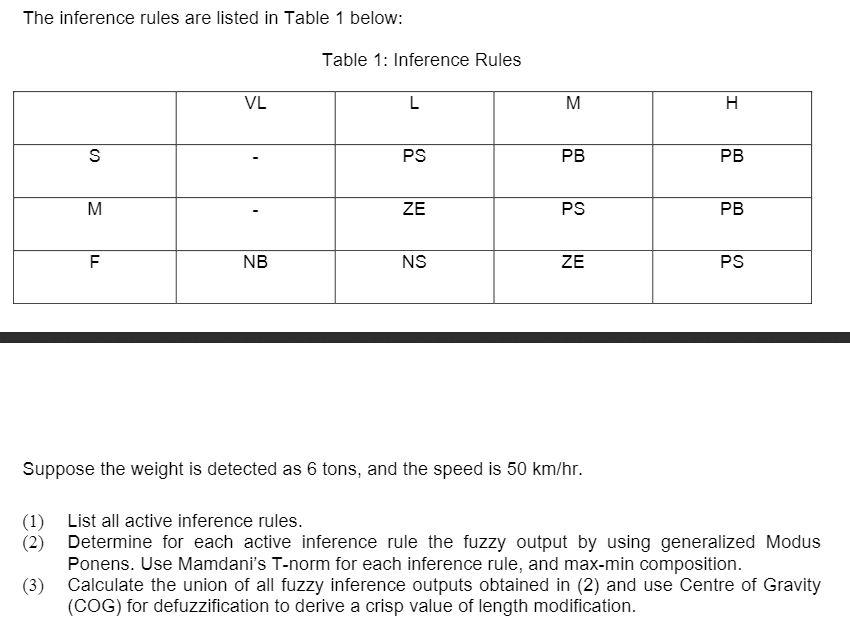
4. In vehicle analysis loop and piezo detectors are used to determine a vehicle's length, speed and weight. Due to the low accuracy of the detectors, an analyst uses a fuzzy inference approach to calculate a modification term, which can be used to improve the measurement of the vehicle length. We have three linguistic variables: vehicle speed (VS), vehicle weight (WW), and vehicle length modification (VM). The term set of VS includes fast (F), medium (M), and slow (S), which are shown in Figure 1. S M F 1 w 40 60 80 km/hr Figure 1: Linguistic Terms for VS The term set of WW includes very light (VL), light (L), medium (M), and heavy (H), which are shown in Figure 2 below. VLL M H 1 1 w 2 O 4 8 12 ton Figure 2: Linguistic Terms for VW The term set of VM includes negative small (NS), negative big (NB), zero (ZE), positive small (PS), and positive big (PB), which are shown in Figure 3. NS ZE 1 PS N B PB Output modification factor (%) -20 -5 5 10 20 10 Figure 3: Linguistic Terms for VM The inference rules are listed in Table 1 below: Table 1: Inference Rules VL L M H S PS PB PB M ZE PS PB NB NS ZE PS Suppose the weight is detected as 6 tons, and the speed is 50 km/hr. (1) List all active inference rules. (2) Determine for each active inference rule the fuzzy output by using generalized Modus Ponens. Use Mamdani's T-norm for each inference rule, and max-min composition. (3) Calculate the union of all fuzzy inference outputs obtained in (2) and use Centre of Gravity (COG) for defuzzification to derive a crisp value of length modification. 4. In vehicle analysis loop and piezo detectors are used to determine a vehicle's length, speed and weight. Due to the low accuracy of the detectors, an analyst uses a fuzzy inference approach to calculate a modification term, which can be used to improve the measurement of the vehicle length. We have three linguistic variables: vehicle speed (VS), vehicle weight (WW), and vehicle length modification (VM). The term set of VS includes fast (F), medium (M), and slow (S), which are shown in Figure 1. S M F 1 w 40 60 80 km/hr Figure 1: Linguistic Terms for VS The term set of WW includes very light (VL), light (L), medium (M), and heavy (H), which are shown in Figure 2 below. VLL M H 1 1 w 2 O 4 8 12 ton Figure 2: Linguistic Terms for VW The term set of VM includes negative small (NS), negative big (NB), zero (ZE), positive small (PS), and positive big (PB), which are shown in Figure 3. NS ZE 1 PS N B PB Output modification factor (%) -20 -5 5 10 20 10 Figure 3: Linguistic Terms for VM The inference rules are listed in Table 1 below: Table 1: Inference Rules VL L M H S PS PB PB M ZE PS PB NB NS ZE PS Suppose the weight is detected as 6 tons, and the speed is 50 km/hr. (1) List all active inference rules. (2) Determine for each active inference rule the fuzzy output by using generalized Modus Ponens. Use Mamdani's T-norm for each inference rule, and max-min composition. (3) Calculate the union of all fuzzy inference outputs obtained in (2) and use Centre of Gravity (COG) for defuzzification to derive a crisp value of length modification
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


