Question: Geometric Optics: Reflection at Plane and Spherical Mirrors (Topic) WRAP-UP 1. Give all the characteristics of an image formed by Plane Mirror 2. Fill out
Geometric Optics: Reflection at Plane and Spherical Mirrors (Topic)
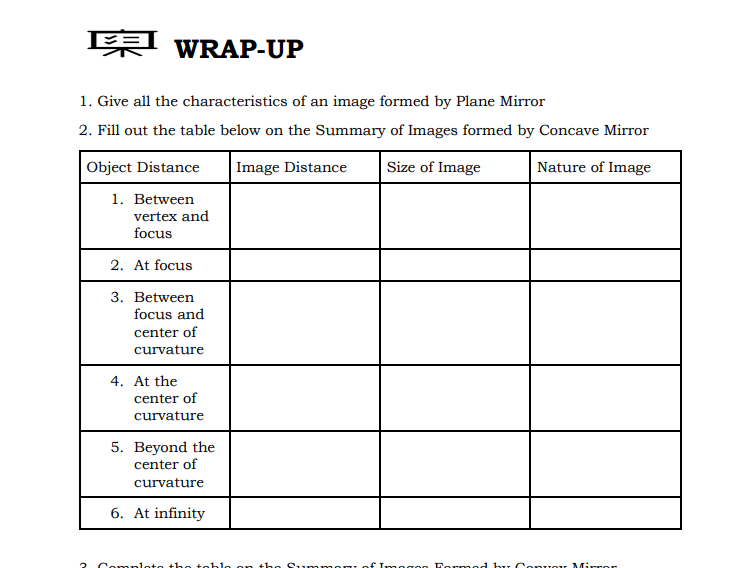
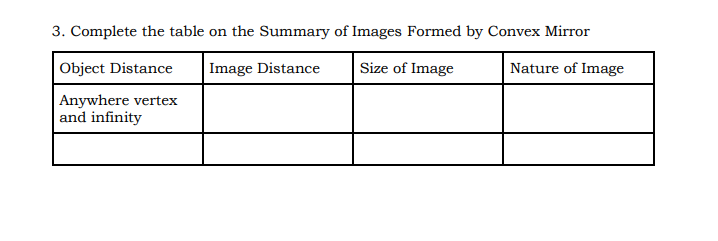


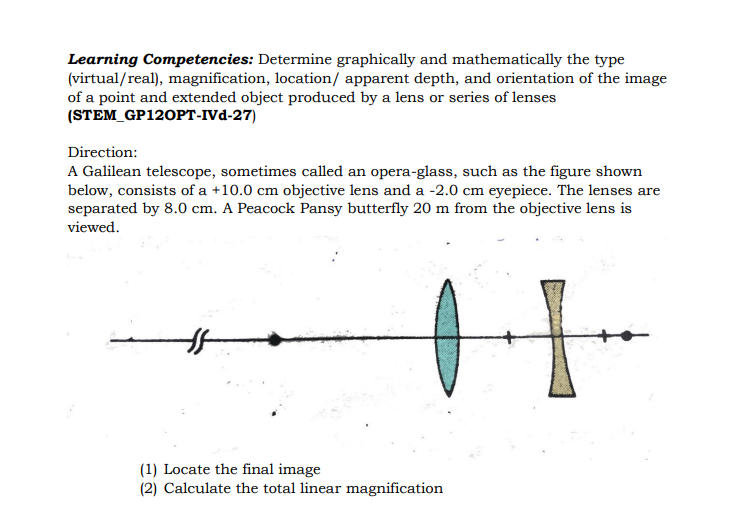

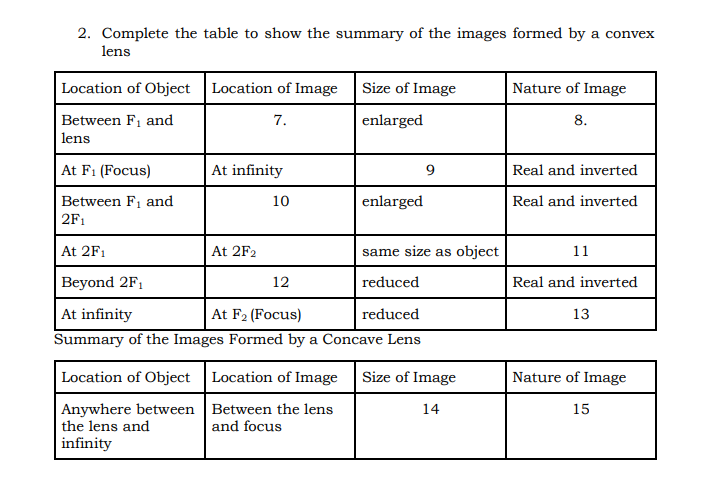

WRAP-UP 1. Give all the characteristics of an image formed by Plane Mirror 2. Fill out the table below on the Summary of Images formed by Concave Mirror Object Distance Image Distance Size of Image Nature of Image 1. Between vertex and focus 2. At focus 3. Between focus and center of curvature 4. At the center of curvature 5. Beyond the center of curvature 6. At infinity3. Complete the table on the Summary of Images Formed by Convex Mirror Object Distance Image Distance Size of Image Nature of Image Anywhere vertex and infinityPOSTTEST Multiple Choice: Encircle the letter that corresponds to the correct answer. 1. A man stands 10 m in front of a large plane mirror. How far must he walk before he is 5m away from his image? A. 10 cm B. 7.5 m C. 5 m D. 2.5 m 2. What is the focal length of the mirror if an object 3 cm high is placed at a distance of 8 cm from a concave mirror which produces a virtual image 4.5 cm high? A. 21 cm B. 22 cm D. 23 cm D. 24 cm 3. Which of the following distances should a person hold his face from a concave mirror with a focal length of 25 cm so that it may act as a shaving mirror? A. 45 cm B. 20 cm C. 25 cm D. 30 cm 4. What is the distance of the image if an object is placed at a large distance in front of a concave mirror of a radius of curvature of 40 cm? A. 20 cm B. 30 cm C. 40 cm D. 50 cm 5. What is the distance and the radius of curvature of a convex mirror used as a rear-view mirror in a moving car is 2.0 m? A truck is coming from behind it at a distance of 3.5 m. A. 0.77 m behind the mirror C. 7.7 m behind the mirror B. 0.77 m in front of the mirror D. 7.7 m in front of the mirrorACTIVITIES Quarter 4: Week: 3 Day: 2 Title of the Activity: Image Formation by Lenses Activity no. 1 Learning Competencies: Determine graphically and mathematically the type (virtual/real), magnification, location/ apparent depth, and orientation of the image of a point and extended object produced by a lens or series of lenses (STEM_GP120PT-IVd-27) Direction: Use ray diagrams to locate the images of the following objects (1) an object that is 10 cm from a converging lens of 15.0 cm focal length, (2) an object that is 10 cm from a diverging lens of -15 cm focal length (3-4) Calculate the image location of parts (1) and (2) using the thin-lens equation (5-6) How large is the image formed in parts (1) and (2). you may use the following equations below: 1/f = 1/do + 1/dj (Eq. 1) m = hi/ho = -di/do (Eq 2) Quarter 4: Week: 3 Day: 2 Title of the Activity: An Image of an Image Activity no. 2Learning Competencies: Determine graphically and mathematically the type (virtual/real), magnification, location/ apparent depth, and orientation of the image of a point and extended object produced by a lens or series of lenses (STEM_GP120PT-IVd-27) Direction: A Galilean telescope, sometimes called an opera-glass, such as the figure shown below, consists of a +10.0 cm objective lens and a -2.0 cm eyepiece. The lenses are separated by 8.0 cm. A Peacock Pansy butterfly 20 m from the objective lens is viewed. (1) Locate the final image (2) Calculate the total linear magnificationWRAP-UP Fill in the blanks with suitable words to complete the statements. 1. A lens is an (1) device that changes the apparent location of an object by changing the path of (2) coming from an object.A (3) causes parallel rays to to converge at the focal point, while a (4). causes parallel rays to appear to diverge from a single point called the focal point. The image formed by lenses can be located by using (5) or by using the (6) equation.2. Complete the table to show the summary of the images formed by a convex lens Location of Object Location of Image Size of Image Nature of Image Between F, and 7. enlarged 8. lens At F1 (Focus) At infinity g Real and inverted Between F, and 10 enlarged Real and inverted 2F1 At 2F1 At 2F2 same size as object 11 Beyond 2F1 12 reduced Real and inverted At infinity At F2 (Focus) reduced 13 Summary of the Images Formed by a Concave Lens Location of Object Location of Image Size of Image Nature of Image Anywhere between Between the lens 14 15 the lens and and focus infinityVALUING Mica is playing with a lens given as a gift by her older brother Mikel. Mica is fascinated with the lens and she holds it towards the sun and starts looking at the sun through it. On seeing this, Mica's older brother Mikel ran towards her and snatched the lens from him. Mikel firmly told Mica never to do it again. (a) What could be the nature of the lens? (b) Why did Mikel snatch the lens from Mica? (c) What could have happened to Mica if Mikel had not snatched away the lens from him? Explain. (d) What values are shown by Mikel
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


