Question: Give me another example with the same method of solution Goal and objectives 1 1. Database design process flowchart 2 2. Data model 3 3.
Give me another example with the same method of solution

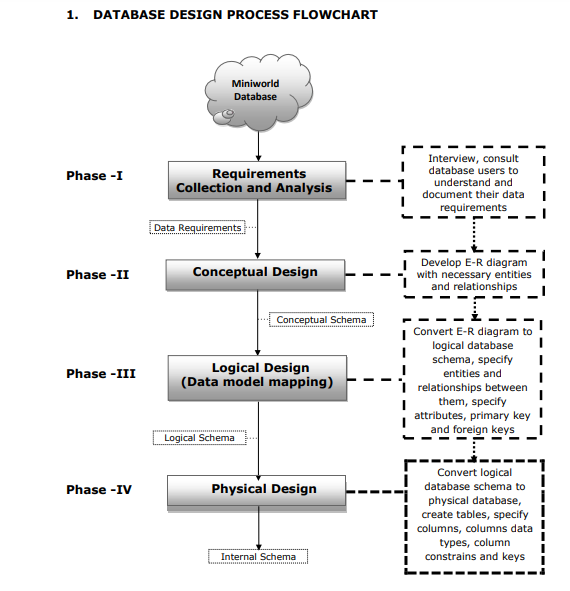
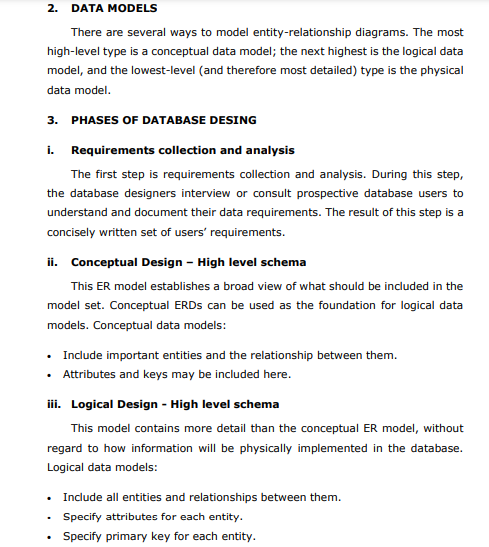
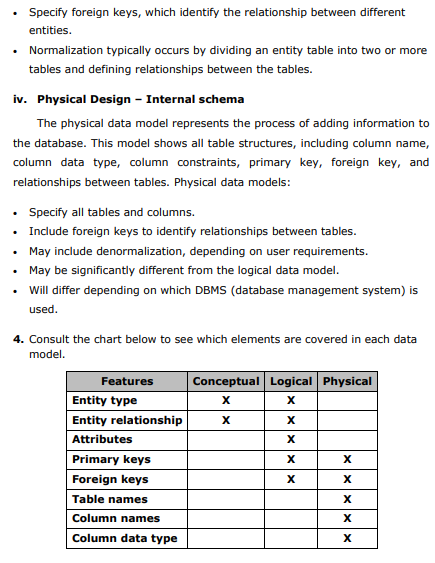
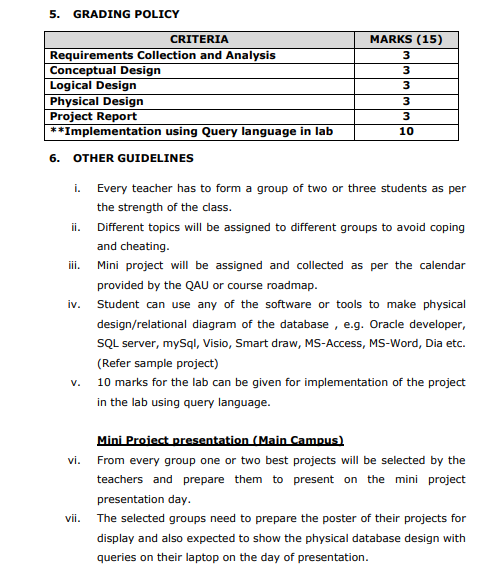

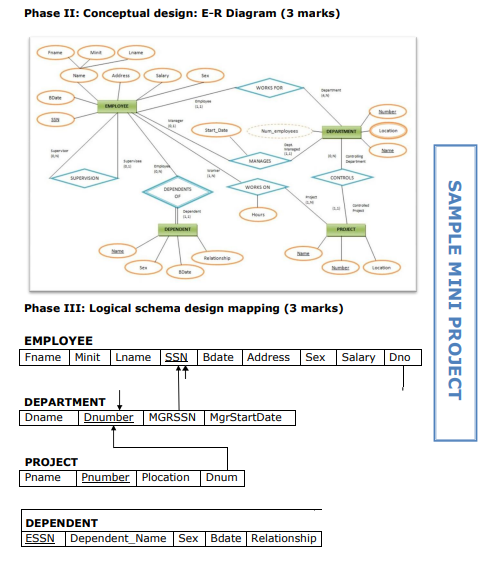
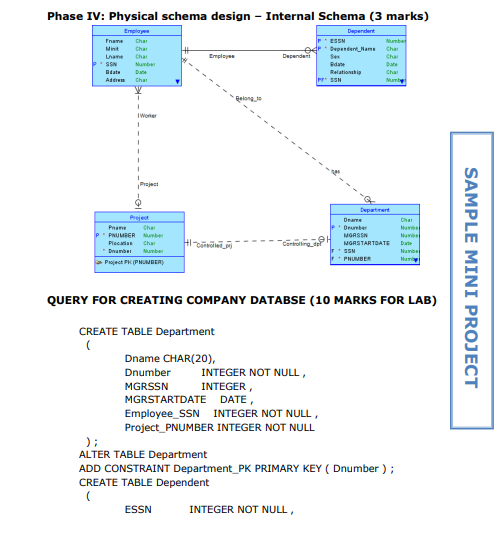

Goal and objectives 1 1. Database design process flowchart 2 2. Data model 3 3. Phases of database design 3 i. Requirements collection and analysis 3 ii. Conceptual data model design 3 iii. Logical data model design 34 iv. Physical data model design 3-4 4. Data model chart 4 5. Grading policy and criteria 5 6. Other guidelines 5 7. Sample mini project 610 GOAL: To understand the complete design process of a mini word database system. OBJECTIVES: i. To analysis and gather basic requirements of a database system. ii. To create conceptual, logical and physical design of the system. 1. DATABASE DESIGN PROCESS FLOWCHART 2. DATA MODELS There are several ways to model entity-relationship diagrams. The most high-level type is a conceptual data model; the next highest is the logical data model, and the lowest-level (and therefore most detailed) type is the physical data model. 3. PHASES OF DATABASE DESING i. Requirements collection and analysis The first step is requirements collection and analysis. During this step, the database designers interview or consult prospective database users to understand and document their data requirements. The result of this step is a concisely written set of users' requirements. ii. Conceptual Design - High level schema This ER model establishes a broad view of what should be included in the model set. Conceptual ERDs can be used as the foundation for logical data models. Conceptual data models: - Include important entities and the relationship between them. - Attributes and keys may be included here. iii. Logical Design - High level schema This model contains more detail than the conceptual ER model, without regard to how information will be physically implemented in the database. Logical data models: - Include all entities and relationships between them. - Specify attributes for each entity. - Specify primary key for each entity. - Specify foreign keys, which identify the relationship between different entities. - Normalization typically occurs by dividing an entity table into two or more tables and defining relationships between the tables. iv. Physical Design - Internal schema The physical data model represents the process of adding information to the database. This model shows all table structures, including column name, column data type, column constraints, primary key, foreign key, and relationships between tables. Physical data models: - Specify all tables and columns. - Include foreign keys to identify relationships between tables. - May include denormalization, depending on user requirements. - May be significantly different from the logical data model. - Will differ depending on which DBMS (database management system) is used. 4. Consult the chart below to see which elements are covered in each data model. 5. GRADING POLICY 6. OTHER GUIDELINES i. Every teacher has to form a group of two or three students as per the strength of the class. ii. Different topics will be assigned to different groups to avoid coping and cheating. iii. Mini project will be assigned and collected as per the calendar provided by the QAU or course roadmap. iv. Student can use any of the software or tools to make physical design/relational diagram of the database, e.g. Oracle developer, SQL server, mySql, Visio, Smart draw, MS-Access, MS-Word, Dia etc. (Refer sample project) v. 10 marks for the lab can be given for implementation of the project in the lab using query language. Mini Proiect presentation (Main Campus) vi. From every group one or two best projects will be selected by the teachers and prepare them to present on the mini project presentation day. vii. The selected groups need to prepare the poster of their projects for display and also expected to show the physical database design with queries on their laptop on the day of presentation. COMPANY DATABSE (SAMPLE) In this section we describe a sample database application, called COMPANY, which serves to illustrate the basic ER model concepts and their use in schema design. We list the data requirements for the database here, and then create its conceptual schema step-by-step as we introduce the modeling concepts of the ER model. The COMPANY database keeps track of a company's employees, departments, and projects. Phase I: Requirements collection and Analysis (3 marks) Guidelines: After consultation, the following requirements for a company database have been determined: 1. The company is organized into departments. Each department has a unique name, a unique number, and a particular employee who manages the department. Keep track of the start data when that employee began managing the department. A department may have several locations. 2. A department controls a number of projects, each of which has a unique name, a unique number, and a single location. 3. Store each employee's name, social security number, address, salary, sex, and birth date. An employee is assigned to one department, but may work on several projects, which are not necessarily controlled by the same department. Keep track of the number of hours per week that an employee works on each project. Also, keep track of the direct supervisor of each employee 4. Keep track of the dependents of each employee for insurance purposes. Keep each dependent's first name, sex, birth date, and relationship to the employee. Phase II: Conceptual design: E-R Diagram (3 marks) Phase III: Logical schema design mapping (3 marks) Phace TV: Dhveiral erhema decinn - Tnternal Srhema (2 marke) QUERY FOR CREATING COMPANY DATABSE (10 MARKS FOR LAB) CREATE TABLE Department ( Dname CHAR(20), Dnumber INTEGER NOT NULL, MGRSSN INTEGER, MGRSTARTDATE DATE, Employee_SSN INTEGER NOT NULL, Project_PNUMBER INTEGER NOT NULL ) ; ALTER TABLE Department ADD CONSTRAINT Department_PK PRIMARY KEY (Dnumber); CREATE TABLE Dependent ( ESSN INTEGER NOT NULL, Dependent_Name CHAR(20), NOT NULL, Sex CHAR(6), Bdate DATE, Relationship CHAR(10), Employee_SSN INTEGER NOT NULL )i ALTER TABLE Dependent ADD CONSTRAINT Dependent_PK PRIMARY KEY (ESSN, Dependent_Name, Employee_SSN ); CREATE TABLE Employee ( Fname CHAR(10), Minit CHAR(10), Lname CHAR(10), SSN INTEGER NOT NULL, Bdate DATE, Address CHAR(100), Sex CHAR(6), Salary INTEGER, Project_PNUMBER INTEGER ); ALTER TABLE Employee ADD CONSTRAINT Employee_PK PRIMARY KEY (SSN ); CREATE TABLE Project ( Pname CHAR(10), PNUMBER INTEGER NOT NULL, Plocation CHAR(10), Dnumber INTEGER NOT NULL ); ALTER TABLE Project ADD CONSTRAINT Project_PK PRIMARY KEY (PNUMBER); ALTER TABLE Department ADD CONSTRAINT Department_Employee_FK OREIGN KEY ( Employee_SSN ) REFERENCES Employee ( SSN) ; ALTER TABLE Department ADD CONSTRAINT Department_Project_FK OREIGN KEY ( Project_PNUMBER) REFERENCES Project ( PNUMBER) ; ALTER TABLE Dependent ADD CONSTRAINT Dependent_Employee_FK OREIGN KEY ( Employee_SSN ) REFERENCES Employee ( SSN ) ; ALTER TABLE Employee ADD CONSTRAINT Employee_Project_FK FOREIGN KEY (Project_PNUMBER) REFERENCES Project (PNUMBER)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


